How to implement Java redis to store Map object type data
Background Description
The project needs to store the latest latitude and longitude information collected by the device into the redis cache to facilitate timely query and retrieval. Considering that the equipment queried is different depending on the search conditions. The data is stored in the redis cache as a map type and is recorded here.
Entity class
Note: Be sure to implement the serialization interface
Parent class
public class Redis implements Serializable{
private String name;
private Integer age;
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public Integer getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(Integer age) {
this.age = age;
}
}Subclass
import java.io.Serializable;
public class RedisCustom extends Redis {
private String stuCode;
public String getStuCode() {
return stuCode;
}
public void setStuCode(String stuCode) {
this.stuCode = stuCode;
}
}Method 1°
redisTemplate.opsForHash()
Sample code
@Controller
@RequestMapping("/redis")
public class RedisController {
@Autowired
private RedisTemplate redisTemplate;
/**
* @param
* @return
*/
@RequestMapping(value = "/setRedisData", method = RequestMethod.GET)
@ResponseBody
public Map<String, Object> setRedisData() {
RedisCustom redis1 = new RedisCustom();
redis1.setName("小明");
redis1.setAge(12);
redis1.setStuCode("36");
RedisCustom redis2 = new RedisCustom();
redis2.setName("小红");
redis2.setAge(11);
redis2.setStuCode("24");
//构造存入redis中的map
Map<String, RedisCustom> redisDataMap = new HashMap<String, RedisCustom>();
redisDataMap.put(redis1.getName(), redis1);
redisDataMap.put(redis2.getName(), redis2);
//存入redis
redisTemplate.opsForHash().putAll("redisTest",redisDataMap);
//获取缓存内容
Map<String,RedisCustom> resultMap = redisTemplate.opsForHash().entries("redisTest");
//List<RedisCustom> reslutMapList = redisTemplate.opsForHash().values("redisTest");
//Set<RedisCustom> resultMapSet = redisTemplate.opsForHash().keys("redisTest");
//RedisCustom value = (RedisCustom)redisTemplate.opsForHash().get("redisTest","小明");
return ResponseData.success(resultMap);
}
}Result

Reference
https://www.yisu.com/article/246815.htm
Method 2°
Convert the object into byte[]
Serialization and deserialization tool class
import java.io.*;
/**
* 序列化及反序列化工具类
*/
public class SerializeObjectTool {
//序列化
public static byte[] serialize(Object obj) {
ObjectOutputStream obi = null;
ByteArrayOutputStream bai = null;
try {
bai = new ByteArrayOutputStream();
obi = new ObjectOutputStream(bai);
obi.writeObject(obj);
byte[] byt = bai.toByteArray();
return byt;
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return null;
}
// 反序列化
public static Object unserizlize(byte[] byt) {
ObjectInputStream oii = null;
ByteArrayInputStream bis = null;
bis = new ByteArrayInputStream(byt);
try {
oii = new ObjectInputStream(bis);
Object obj = oii.readObject();
return obj;
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return null;
}
}Sample code
@Controller
@RequestMapping("/redis")
public class RedisController {
/**
* @param
* @return
*/
@RequestMapping(value = "/setRedisData", method = RequestMethod.GET)
@ResponseBody
public Map<String, Object> setRedisData() {
RedisCustom redis1 = new RedisCustom();
redis1.setName("小明");
redis1.setAge(12);
redis1.setStuCode("36");
RedisCustom redis2 = new RedisCustom();
redis2.setName("小红");
redis2.setAge(11);
redis2.setStuCode("24");
//构造存入redis中的map
Map<String, RedisCustom> redisDataMap = new HashMap<String, RedisCustom>();
redisDataMap.put(redis1.getName(), redis1);
redisDataMap.put(redis2.getName(), redis2);
//连接redis
Jedis redis = new Jedis("xx.xx.xxx.xx", 6379);
redis.auth("xxxxxxxxxxx");
//存
byte[] personByte = SerializeObjectTool.serialize(redisDataMap);
redis.set("redisData".getBytes(), personByte);
//取
byte[] byt = redis.get("redisData".getBytes());
Object obj = SerializeObjectTool.unserizlize(byt);
Map<String, RedisCustom> redisData = (Map<String, RedisCustom>) obj;
return ResponseData.success(redisData);
}
}The above is the detailed content of How to implement Java redis to store Map object type data. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 Break or return from Java 8 stream forEach?
Feb 07, 2025 pm 12:09 PM
Break or return from Java 8 stream forEach?
Feb 07, 2025 pm 12:09 PM
Java 8 introduces the Stream API, providing a powerful and expressive way to process data collections. However, a common question when using Stream is: How to break or return from a forEach operation? Traditional loops allow for early interruption or return, but Stream's forEach method does not directly support this method. This article will explain the reasons and explore alternative methods for implementing premature termination in Stream processing systems. Further reading: Java Stream API improvements Understand Stream forEach The forEach method is a terminal operation that performs one operation on each element in the Stream. Its design intention is
 Create the Future: Java Programming for Absolute Beginners
Oct 13, 2024 pm 01:32 PM
Create the Future: Java Programming for Absolute Beginners
Oct 13, 2024 pm 01:32 PM
Java is a popular programming language that can be learned by both beginners and experienced developers. This tutorial starts with basic concepts and progresses through advanced topics. After installing the Java Development Kit, you can practice programming by creating a simple "Hello, World!" program. After you understand the code, use the command prompt to compile and run the program, and "Hello, World!" will be output on the console. Learning Java starts your programming journey, and as your mastery deepens, you can create more complex applications.
 Java Made Simple: A Beginner's Guide to Programming Power
Oct 11, 2024 pm 06:30 PM
Java Made Simple: A Beginner's Guide to Programming Power
Oct 11, 2024 pm 06:30 PM
Java Made Simple: A Beginner's Guide to Programming Power Introduction Java is a powerful programming language used in everything from mobile applications to enterprise-level systems. For beginners, Java's syntax is simple and easy to understand, making it an ideal choice for learning programming. Basic Syntax Java uses a class-based object-oriented programming paradigm. Classes are templates that organize related data and behavior together. Here is a simple Java class example: publicclassPerson{privateStringname;privateintage;
 Java Program to Find the Volume of Capsule
Feb 07, 2025 am 11:37 AM
Java Program to Find the Volume of Capsule
Feb 07, 2025 am 11:37 AM
Capsules are three-dimensional geometric figures, composed of a cylinder and a hemisphere at both ends. The volume of the capsule can be calculated by adding the volume of the cylinder and the volume of the hemisphere at both ends. This tutorial will discuss how to calculate the volume of a given capsule in Java using different methods. Capsule volume formula The formula for capsule volume is as follows: Capsule volume = Cylindrical volume Volume Two hemisphere volume in, r: The radius of the hemisphere. h: The height of the cylinder (excluding the hemisphere). Example 1 enter Radius = 5 units Height = 10 units Output Volume = 1570.8 cubic units explain Calculate volume using formula: Volume = π × r2 × h (4
 How to Run Your First Spring Boot Application in Spring Tool Suite?
Feb 07, 2025 pm 12:11 PM
How to Run Your First Spring Boot Application in Spring Tool Suite?
Feb 07, 2025 pm 12:11 PM
Spring Boot simplifies the creation of robust, scalable, and production-ready Java applications, revolutionizing Java development. Its "convention over configuration" approach, inherent to the Spring ecosystem, minimizes manual setup, allo
 Why does an error occur when installing an extension using PECL in a Docker environment? How to solve it?
Apr 01, 2025 pm 03:06 PM
Why does an error occur when installing an extension using PECL in a Docker environment? How to solve it?
Apr 01, 2025 pm 03:06 PM
Causes and solutions for errors when using PECL to install extensions in Docker environment When using Docker environment, we often encounter some headaches...
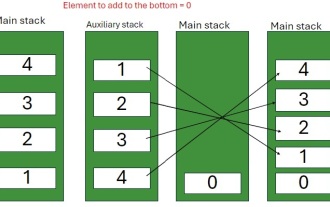 Java Program to insert an element at the Bottom of a Stack
Feb 07, 2025 am 11:59 AM
Java Program to insert an element at the Bottom of a Stack
Feb 07, 2025 am 11:59 AM
A stack is a data structure that follows the LIFO (Last In, First Out) principle. In other words, The last element we add to a stack is the first one to be removed. When we add (or push) elements to a stack, they are placed on top; i.e. above all the
 Compilation and installation of Redis on Apple M1 chip Mac failed. How to troubleshoot PHP7.3 compilation errors?
Mar 31, 2025 pm 11:39 PM
Compilation and installation of Redis on Apple M1 chip Mac failed. How to troubleshoot PHP7.3 compilation errors?
Mar 31, 2025 pm 11:39 PM
Problems and solutions encountered when compiling and installing Redis on Apple M1 chip Mac, many users may...






