
Pronunciation biao zhi fu
Package, class, variable, method&hellip ;Wait, as long as it is the place where the name is given, the name is the identifier
Four can be: numbers, letters, underscores (_), dollar signs ( $), we generally try to use English letters in names.
Two no-nos: it cannot start with a number, and it cannot use keywords in java.
Know the meaning after seeing the name: so that readers can understand what it does through the name, for example: bubble sort (bubble_Sort), we can clearly know that this method is bubble sort .
Camel case naming:
Class name: the first letter is capitalized, and the rest follow camel case naming
Method name/variable name: The first letter is lowercase, and the rest follow camel case naming
Package name: all lowercase
Length limit: There is no limit on the length, but it is not recommended to be too long
is given a special meaning by the Java language and is used as a word for special purposes
Features: All in Java The keywords are all lowercase
Official website: https://docs.oracle.com/javase/tutorial/java/nutsandbolts/_keywords.html
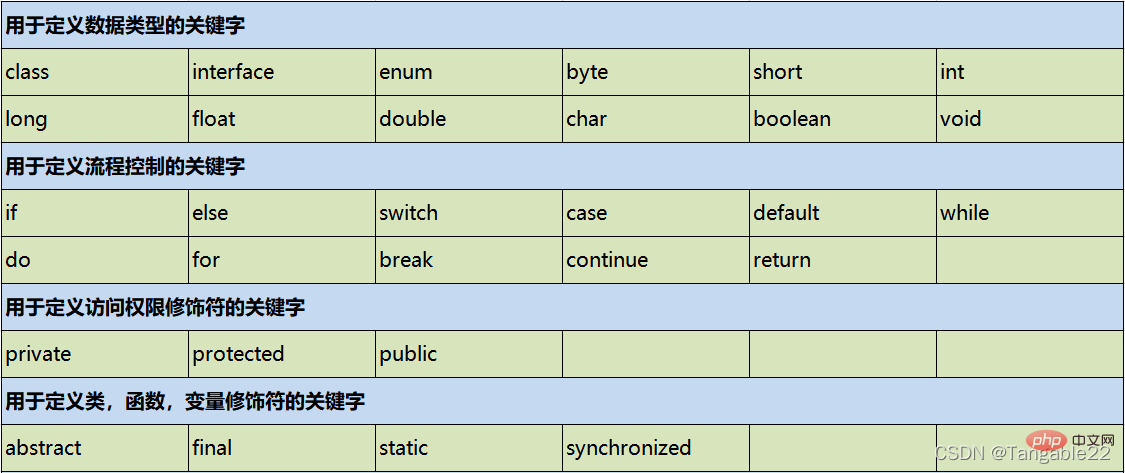
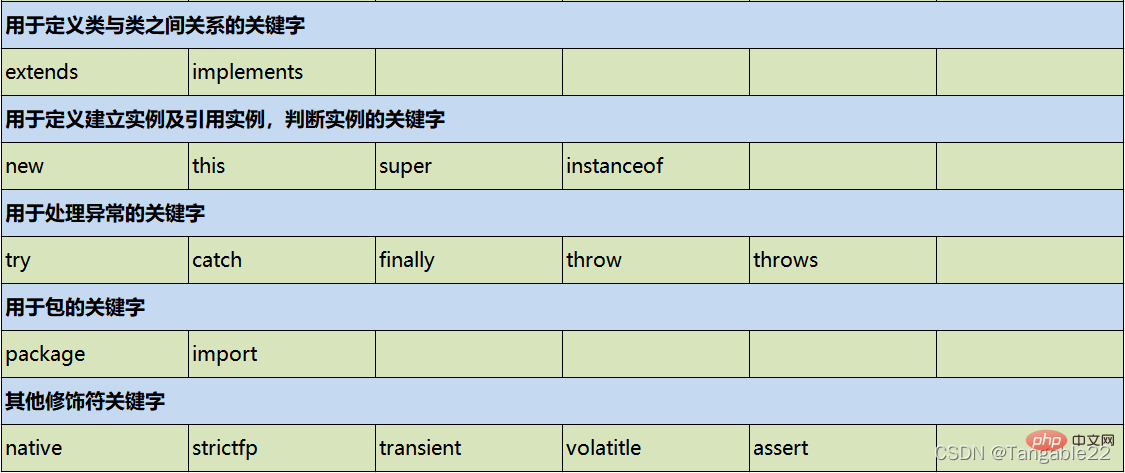
Constant is divided into two types:
Constant usually refers to a fixed Values, such as: 1, 2, 3, ’a’, ’b’, true, false, "helloWorld", etc.
In the Java language, the keyword final is mainly used to define a constant. Once a constant is initialized, its value cannot be changed.
In order to better distinguish and express, 1, 2, 3, ’a’, ’b’, true, false, "helloWorld", etc. are generally called literal constants, and final modified ones are used. PI, etc. are called symbolic constants (character constants).
Type of literal constant:
Integer constant: 123 23
Real constant: 3.1415926
Character constant: ‘a’ ‘b’
Logical constants: true false
String constants: “helloworld”
Note: Logical constants have only two values, one is true, One is false
A variable essentially represents an operable storage space. The location of the space is determined, but the value placed in it is uncertain. We can access the corresponding storage space through the variable name, thereby manipulating the value stored in this storage space.
Java is a strongly typed language, and each variable must declare its data type. The data type of the variable Determines the size of the storage space occupied by the variable. For example, int a=3; means that the space size of variable a is 4 bytes. As the most basic storage unit in the program, variables include variable name, variable type and scope. Variables must be declared before use. Only after the variable is declared can storage space of the corresponding length be allocated to it.
Data type Variable name = initial Value, variable name = initial value...
For example:
public class TestCode01{
public static void main(String[] args){
int a=3,b=4,c=5;
//也可以先定义不赋值
int a,b,c;
}
}If you only define one variable, If the variable is not assigned a value, then the variable is actually not defined;
If the variable is not assigned a value, an error will occur when using it, telling you: the variable has not been initialized;
public class TestCode01{
public static void main(String[] args){
int a;
System.out.println(a);//会报错,未初始化变量a
}
}Assignment of variables
int a=10;//直接定义并赋值 int b;//先定义在赋值 b=20;
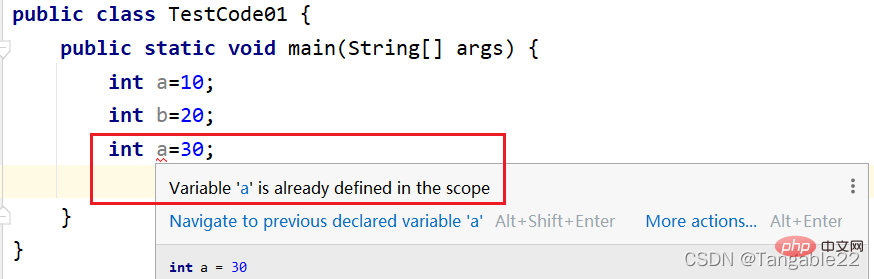
Variables cannot be repeatedly defined
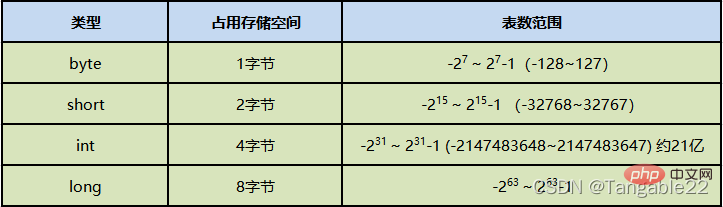
Integer data type:
The following code is used as an example:
public class TestCode01{
public static void main(String[] args){
//定义整数类型的变量:
//给变量赋值的时候,值可以为不同进制的:
int num1 = 12 ;//默认情况下赋值就是十进制的情况
System.out.println(num1);
int num2 = 012;//前面加上0,这个值就是八进制的
System.out.println(num2);
int num3 = 0x12;//前面加上0x或者0X,这个值就是十六进制的
System.out.println(num3);
int num4 = 0b10;//前面加上0x或者0B,这个值就是二进制的
System.out.println(num4);
//定义byte类型的变量:
byte b = 126;//定义了一个byte类型的变量,名字叫b,赋值为12
System.out.println(b);
//注意:超范围的赋值会报错。
short s = 30000;
System.out.println(s);
int i = 1234;
System.out.println(i);
//整数类型默认就是int类型的,所以12345678910是一个int类型的数,对于int类型来说,它超出范围了
//要想把一个数给long类型变量,那么后面加上L(推荐)或者l就可以了
long num5 = 12345678910L;
System.out.println(num5);
//注意:只有这个数超出int类型的范围了后面才需要加上L,否则无需加L也可以赋值给long类型:
long num6 = 12;
System.out.println(num6);
}
}(1) Decimal number form, for example: 3.14 314.0 0.314
(2) Scientific notation form, for example:
//314e2 314E2 (E的大小写没有区分) 314E-2 double f = 314e2; //31410^2-->31400.0 double f2 = 314e-2; //31410^(-2)-->3.14
The float type is also called a single precision type, and the mantissa can be accurate to 7 significant digits. In many cases, the precision of the float type is difficult to meet the demand.
And double represents this The numerical precision of this type is about twice that of the float type. It is also called a double precision type. Most applications use the double type.
The float type has a suffix F or f and no suffix The floating point value of F/f is double type by default.
You can also add the suffix D or d after the floating point value to make it clear that it is double type.
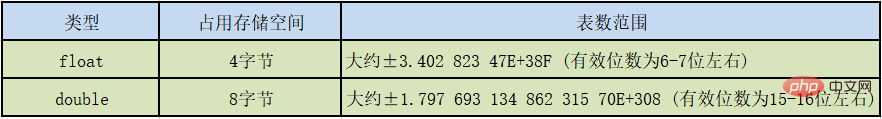
PS: Valid digits refer to the first number that is not 0 from the left to the last number
public class TestCode02{
public static void main(String[] args){
//浮点类型的常量有两种形式:
//十进制形式:
double num1 = 3.14;
System.out.println(num1);
//科学计数法形式:
double num2 = 314E-2;
System.out.println(num2);
//浮点类型的变量:
//注意:浮点型默认是double类型的,要想将一个double类型的数赋给float类型,必须后面加上F或者f
float f1 = 3.14234567898623F;
System.out.println(f1);
//注意:double类型后面可以加D或者d,但是一般我们都省略不写
double d1 = 3.14234567898623D;
System.out.println(d1);
//注意:我们最好不要进行浮点类型的比较:
float f2 = 0.3F;
double d2 = 0.3;
System.out.println(f2==d2);
/*
区别:
= 赋值运算: 将等号右侧的值赋给等号左侧
== 判断==左右两侧的值是否相等 :结果要么相等 要么不相等
==运算符的结果就是要么是true,要么是false
*/
}
}Java的字符使用16位的Unicode编码表示,而计算机语言通常使用ASCII码,用8位表示一个字符。
字符型是用两个单引号括起来的一个字符,如’a’,’1’,’A’等。其中,’a’和’A’分别表示ASCII码中的字符a和A,而’1’表示字符型1,而不是整数的数值1。除了一般字符外,Java还定义了一些特殊字符,如图:
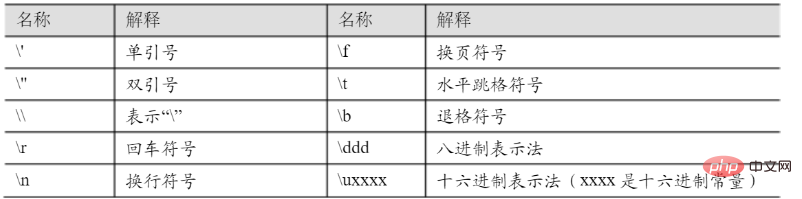
字符型除了常数值的表示方式与整数型不同外,在其他方面几乎可以将它视为一般整数来处理。
字符串是指括在两个双引号之间0个或多个字符组成的序列。若两个双引号之间没有任何字符,则为空串。下面是有关字符串的一些例子:
""
"hello world!"
"hello java"
Java语言把字符串当作String类型的一个对象来处理。
boolean类型有两个常量值,true和false,在内存中占一位(不是一个字节),不可以使用 0 或非 0 的整数替代 true 和 false ,这点和C语言不同。 boolean 类型用来判断逻辑条件,一般用于程序流程控制 。
public class TestCode03{
public static void main(String[] args){
//创建一个布尔类型的变量:
boolean flag1 = true;
System.out.println(flag1);
boolean flag2 = false;
System.out.println(flag2);
boolean flag3 = 5==9;
System.out.println(flag3);
boolean flag4 = 5<9;
System.out.println(flag4);
}
}即精度小的类型自动转换为精度大的数据类型
数据类型按精度大小排序为:
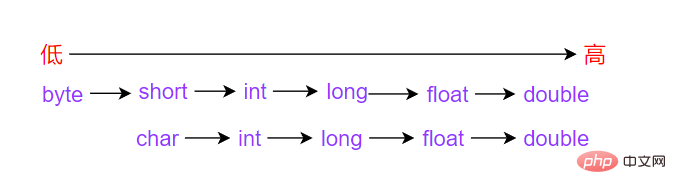
在类型转换的时候需要遵循哪些规则:
第一条:八种基本数据类型中,除boolean 类型不能转换,剩下七种类型之间都可以进行转换;
第二条:小容量向大容量转换称为自动类型转换,大容量转换小容量必须使用强制类型转,但运行时可能出现精度损失,谨慎使用
第三条:byte,short,char 类型混合运算时,先各自转换成 int 类型再做运算;
第四条:整数的默认类型是 int,小数默认是 double 类型浮点型,在定义 float 类型时必须在数字后面跟上 F 或者 f。
第五条:浮点数到整数的转换是通过舍弃小数得到,而不是四舍五入
当一个表达式中有多种数据类型的时候,要找出当前表达式中级别最高的那个类型,然后其余的类型都转换为当前表达式中级别最高的类型进行计算。
double d2 = 12+1294L+8.5F+3.81+'a';//都转换成最高的double类型,相当于= 12.0+1294.0+8.5+3.81+97.0
把精度大的数据类型的数据赋值给精度小的数据类型。
double b=3.1415926; int a=(int)b;//强制转换 高-->低
在进行运算的时候:
左=右 : 直接赋值
左
左>右 :直接自动转换
The above is the detailed content of Java Data Types: Definition and Usage. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!




