Microsoft explains why some driver updates are backdated on Windows 11/10.

If you frequently check for updates on Windows 11 or Windows 10, you may have noticed old drivers or even defunct drivers under the Optional Updates section. For the past few years, users have received driver updates listed as “INTEL – System” that date back to 1968 despite being delivered immediately after upgrading to Windows 11.
Most of these drivers (which may be problematic due to their strange specifications) can be found under the Optional Update settings panel in Windows 11 and Windows 10. In a new blog post, Microsoft explains why and how these drivers are backtracking on Windows.
For those who don’t know, there are three main types of driver releases – drivers released by Windows/Microsoft, drivers from companies like Intel and Nvidia, and custom drivers developed by PC manufacturers program.
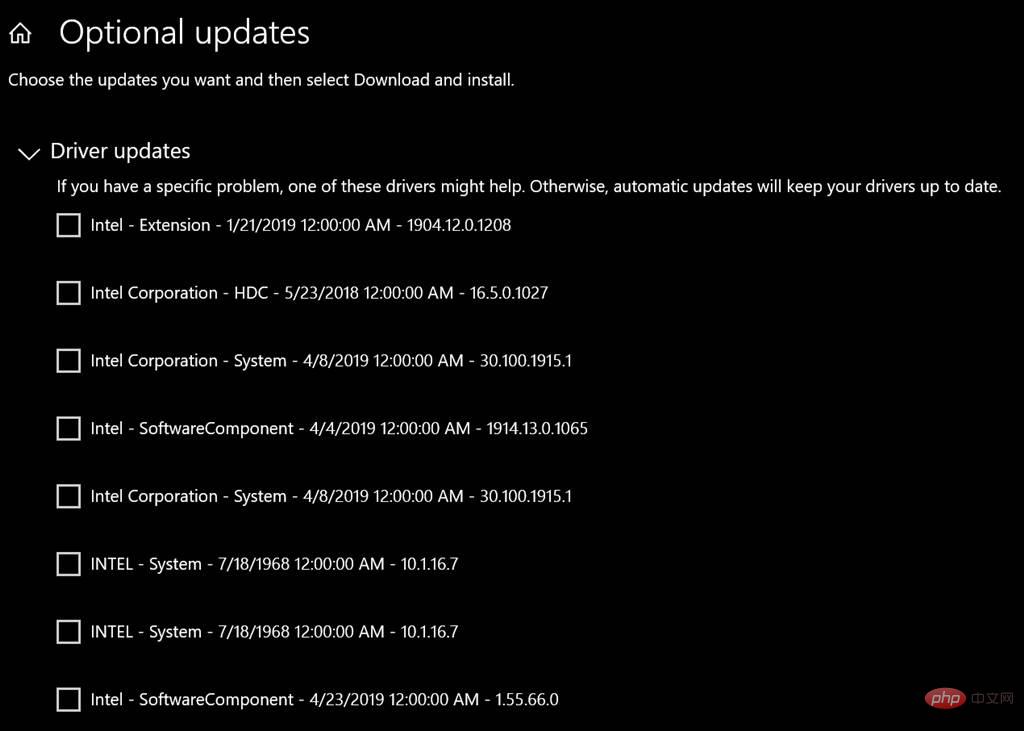
According to the company, all Windows drivers are dated to June 21, 2006 to reduce compatibility issues.
How drivers on Windows are backdated
Windows Update ranks drivers based on a variety of factors, including date. For example, if a driver available in the Microsoft Driver Library perfectly matches the hardware ID of the device, then it will be the best candidate and the user will be able to download it.
However, if multiple drivers match the hardware ID, the driver with the latest timestamp will be automatically selected. If there is a link between multiple drivers in this situation, Microsoft will look at the highest file version number that matches the build release date.
But there's a catch - when you install a new Windows version, the Windows driver will automatically have a newer timestamp than the one provided by the manufacturer. As a result, your manufacturer drivers will be replaced by Windows drivers, which may break certain functionality on your device.
The Windows driver is apparently outdated to avoid the situation highlighted above.
By backdating Windows drivers, Microsoft allows manufacturer drivers to remain in preference to drivers provided by Windows.
In a separate filing, Microsoft said that Intel drivers date back to 1968 (the year Intel was founded) for the same reason - when manufacturer drivers were available, lower Intel Driver level.
"This is necessary as it is a support utility and should not override any other drivers. There is no need to update the Intel(R) Chipset Device Software - don't worry if you don't have the latest version, ” Intel noted in a now-deleted blog post.
The above is the detailed content of Microsoft explains why some driver updates are backdated on Windows 11/10.. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1386
1386
 52
52
 Intel announces Wi-Fi 7 BE201 network card, supports CNVio3 interface
Jun 07, 2024 pm 03:34 PM
Intel announces Wi-Fi 7 BE201 network card, supports CNVio3 interface
Jun 07, 2024 pm 03:34 PM
According to news from this site on June 1, Intel updated the support document on May 27 and announced the product details of the Wi-Fi7 (802.11be) BE201 network card code-named "Fillmore Peak2". Source of the above picture: benchlife website Note: Unlike the existing BE200 and BE202 which use PCIe/USB interface, BE201 supports the latest CNVio3 interface. The main specifications of the BE201 network card are similar to those of the BE200. It supports 2x2TX/RX streams, supports 2.4GHz, 5GHz and 6GHz. The maximum network speed can reach 5Gbps, which is far lower than the maximum standard rate of 40Gbit/s. BE201 also supports Bluetooth 5.4 and Bluetooth LE.
 Intel Core Ultra 9 285K processor exposed: CineBench R23 multi-core running score is 18% higher than i9-14900K
Jul 25, 2024 pm 12:25 PM
Intel Core Ultra 9 285K processor exposed: CineBench R23 multi-core running score is 18% higher than i9-14900K
Jul 25, 2024 pm 12:25 PM
According to news from this website on July 25, the source Jaykihn posted a tweet on the X platform yesterday (July 24), sharing the running score data of the Intel Core Ultra9285K "ArrowLake-S" desktop processor. The results show that it is better than the Core 14900K 18% faster. This site quoted the content of the tweet. The source shared the running scores of the ES2 and QS versions of the Intel Core Ultra9285K processor and compared them with the Core i9-14900K processor. According to reports, the TD of ArrowLake-SQS when running workloads such as CinebenchR23, Geekbench5, SpeedoMeter, WebXPRT4 and CrossMark
 Intel N250 low-power processor exposed: 4 cores, 4 threads, 1.2 GHz frequency
Jun 03, 2024 am 10:26 AM
Intel N250 low-power processor exposed: 4 cores, 4 threads, 1.2 GHz frequency
Jun 03, 2024 am 10:26 AM
According to news from this site on May 16, the source @InstLatX64 recently tweeted that Intel is preparing to launch a new N250 "TwinLake" series of low-power processors to replace the N200 series "AlderLake-N" series. Source: videocardz The N200 series processors are popular in low-cost laptops, thin clients, embedded systems, self-service and point-of-sale terminals, NAS and consumer electronics. "TwinLake" is the code name of the new processor series, which is somewhat similar to the single-chip processor Dies using a ring bus (RingBus) layout, but with an E-core cluster to complete the computing power. The screenshots attached to this site are as follows: AlderLake-N
 Close-up of LGA-1851 socket, Guangji showcases new embedded motherboard: supports Intel Core Ultra 200 series processors
Apr 11, 2024 pm 09:22 PM
Close-up of LGA-1851 socket, Guangji showcases new embedded motherboard: supports Intel Core Ultra 200 series processors
Apr 11, 2024 pm 09:22 PM
According to the news from this site on April 11, according to the German technology media ComputeBase, Guangji Technology attended the EmbeddedWorld2024 conference and publicly demonstrated a motherboard using the LGA-1851 slot for the first time. This motherboard is compatible with Intel Meteor Lake processors and is mainly used in embedded systems. The media took an in-depth look and shared multiple photos, confirming that LGA-1851 is the same size as Intel’s existing LGA-1700 socket. The relevant pictures attached to this site are as follows: Not compatible with CPU, but compatible with CPU coolers but not LGA-1851 socket 151 additional pins were added and the CPU locking system was adjusted, so it is not compatible with existing LGA-1700 socket processors. But because LG
 MSI launches new MS-C918 mini console with Intel Alder Lake-N N100 processor
Jul 03, 2024 am 11:33 AM
MSI launches new MS-C918 mini console with Intel Alder Lake-N N100 processor
Jul 03, 2024 am 11:33 AM
This website reported on July 3 that in order to meet the diversified needs of modern enterprises, MSIIPC, a subsidiary of MSI, has recently launched the MS-C918, an industrial mini host. No public price has been found yet. MS-C918 is positioned for enterprises that focus on cost-effectiveness, ease of use and portability. It is specially designed for non-critical environments and provides a 3-year service life guarantee. MS-C918 is a handheld industrial computer, using Intel AlderLake-NN100 processor, specially tailored for ultra-low power solutions. The main functions and features of MS-C918 attached to this site are as follows: Compact size: 80 mm x 80 mm x 36 mm, palm size, easy to operate and hidden behind the monitor. Display function: via 2 HDMI2.
 ASUS releases BIOS update for Z790 motherboards to alleviate instability issues with Intel's 13th/14th generation Core processors
Aug 09, 2024 am 12:47 AM
ASUS releases BIOS update for Z790 motherboards to alleviate instability issues with Intel's 13th/14th generation Core processors
Aug 09, 2024 am 12:47 AM
According to news from this website on August 8, MSI and ASUS today launched a beta version of BIOS containing the 0x129 microcode update for some Z790 motherboards in response to the instability issues in Intel Core 13th and 14th generation desktop processors. ASUS's first batch of motherboards to provide BIOS updates include: ROGMAXIMUSZ790HEROBetaBios2503ROGMAXIMUSZ790DARKHEROBetaBios1503ROGMAXIMUSZ790HEROBTFBetaBios1503ROGMAXIMUSZ790HEROEVA-02 joint version BetaBios2503ROGMAXIMUSZ790A
 Intel explains in detail the Intel 3 process: applying more EUV lithography, increasing the frequency of the same power consumption by up to 18%
Jun 19, 2024 pm 10:53 PM
Intel explains in detail the Intel 3 process: applying more EUV lithography, increasing the frequency of the same power consumption by up to 18%
Jun 19, 2024 pm 10:53 PM
According to news from this site on June 19, as part of the 2024 IEEEVLSI seminar activities, Intel recently introduced the technical details of the Intel3 process node on its official website. Intel's latest generation of FinFET transistor technology is Intel's latest generation of FinFET transistor technology. Compared with Intel4, it has added steps to use EUV. It will also be a node family that provides foundry services for a long time, including basic Intel3 and three variant nodes. Among them, Intel3-E natively supports 1.2V high voltage, which is suitable for the manufacturing of analog modules; while the future Intel3-PT will further improve the overall performance and support finer 9μm pitch TSV and hybrid bonding. Intel claims that as its
 Intel Panther Lake mobile processor specifications exposed: up to '4+8+4' 16-core CPU, 12 Xe3 core display
Jul 18, 2024 pm 04:43 PM
Intel Panther Lake mobile processor specifications exposed: up to '4+8+4' 16-core CPU, 12 Xe3 core display
Jul 18, 2024 pm 04:43 PM
According to news from this site on July 16, following the revelation of the specifications of the ArrowLake desktop processor and the BartlettLake desktop processor, blogger @jaykihn0 released the specifications of the mobile U and H versions of the Intel PantherLake processor in the early morning. The Panther Lake mobile processor is expected to be named the Core Ultra300 series and will be available in the following versions: PTL-U: 4P+0E+4LPE+4Xe, 15WPL1PTL-H: 4P+8E+4LPE+12Xe, 25WPL1PTL-H: 4P+8E+4LPE+ 4Xe, 25WPL1. The blogger also released the 12Xe nuclear display version of the PantherLake processor.



