What is the implementation method of KMP algorithm in Java?
Illustration
The kmp algorithm has a certain similarity with the idea of the bm algorithm mentioned before. As mentioned before, there is the concept of a good suffix in the bm algorithm, and there is a concept of a good prefix in kmp. What is a good prefix? Let's first look at the following example.
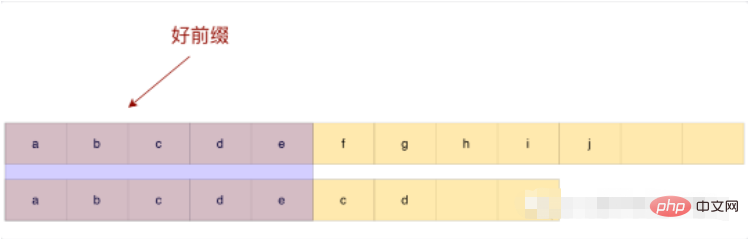
Observe the above example, the already matched abcde is called a good prefix, a does not match the following bcde, so there is no need to compare again, slide directly after e That’s it.
What if there are matching characters in the good prefix?
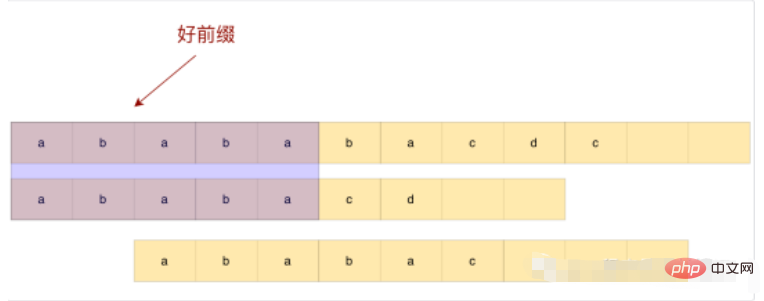
Observe the above example, if we slide directly after the good prefix at this time, we will slide too much and miss the matching substring. So how do we perform reasonable sliding based on good prefixes?
In fact, it is to check whether the prefix and suffix of the current good prefix match, find the longest matching length, and slide directly. In view of finding the longest matching length more than once, we can initialize an array first and save the longest matching length under the current good prefix. At this time, our next array will come out.
We define a next array, which represents the length of the longest matching substring of the prefix and suffix of the good prefix under the current good prefix. This longest matching length means that this substring has been matched before, not It is necessary to match again, starting directly from the next character of the substring.
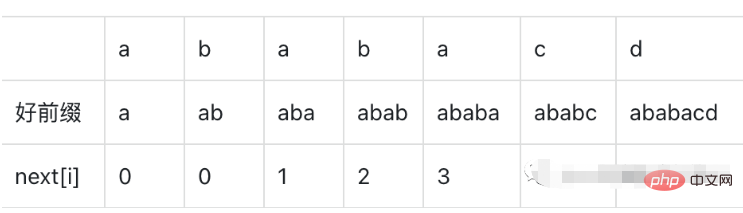
Do we need to match every character every time we calculate next[i]? Can we deduce based on next[i - 1] to reduce unnecessary comparisons? .
With this idea, let’s take a look at the following steps:
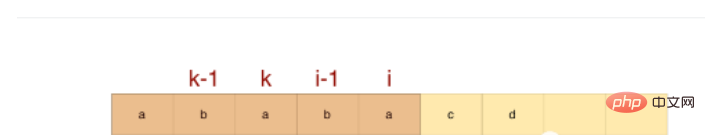
Assume next[i - 1] = k - 1;
If modelStr[k] = modelStr[ i] then next[i]=k


int[] next ;
/**
* 初始化next数组
* @param modelStr
*/
public void init(char[] modelStr) {
//首先计算next数组
//遍历modelStr,遍历到的字符与之前字符组成一个串
next = new int[modelStr.length];
int start = 0;
while (start < modelStr.length) {
next[start] = this.recursion(start, modelStr);
++ start;
}
}
/**
*
* @param i 当前遍历到的字符
* @return
*/
private int recursion(int i, char[] modelStr) {
//next记录的是个数,不是下标
if (0 == i) {
return 0;
}
int last = next[i -1];
//没有匹配的,直接判断第一个是否匹配
if (0 == last) {
if (modelStr[last] == modelStr[i]) {
return 1;
}
return 0;
}
//如果last不为0,有值,可以作为最长匹配的前缀
if (modelStr[last] == modelStr[i]) {
return next[i - 1] + 1;
}
//当next[i-1]对应的子串的下一个值与modelStr不匹配时,需要找到当前要找的最长匹配子串的次长子串
//依据就是次长子串对应的子串的下一个字符==modelStr[i];
int tempIndex = i;
while (tempIndex > 0) {
last = next[tempIndex - 1];
//找到第一个下一个字符是当前字符的匹配子串
if (modelStr[last] == modelStr[i]) {
return last + 1;
}
-- tempIndex;
}
return 0;
}public int kmp(char[] mainStr, char[] modelStr) {
//开始进行匹配
int i = 0, j = 0;
while (i + modelStr.length <= mainStr.length) {
while (j < modelStr.length) {
//找到第一个不匹配的位置
if (modelStr[j] != mainStr[i]) {
break;
}
++ i;
++ j;
}
if (j == modelStr.length) {
//证明完全匹配
return i - j;
}
//走到这里找到的是第一个不匹配的位置
if (j == 0) {
++ i;
continue;
}
//从好前缀后一个匹配
j = next[j - 1];
}
return -1;
}The above is the detailed content of What is the implementation method of KMP algorithm in Java?. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 Square Root in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:26 PM
Square Root in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:26 PM
Guide to Square Root in Java. Here we discuss how Square Root works in Java with example and its code implementation respectively.
 Perfect Number in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:28 PM
Perfect Number in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:28 PM
Guide to Perfect Number in Java. Here we discuss the Definition, How to check Perfect number in Java?, examples with code implementation.
 Random Number Generator in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:27 PM
Random Number Generator in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:27 PM
Guide to Random Number Generator in Java. Here we discuss Functions in Java with examples and two different Generators with ther examples.
 Armstrong Number in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:26 PM
Armstrong Number in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:26 PM
Guide to the Armstrong Number in Java. Here we discuss an introduction to Armstrong's number in java along with some of the code.
 Weka in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:28 PM
Weka in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:28 PM
Guide to Weka in Java. Here we discuss the Introduction, how to use weka java, the type of platform, and advantages with examples.
 Smith Number in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:28 PM
Smith Number in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:28 PM
Guide to Smith Number in Java. Here we discuss the Definition, How to check smith number in Java? example with code implementation.
 Java Spring Interview Questions
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:29 PM
Java Spring Interview Questions
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:29 PM
In this article, we have kept the most asked Java Spring Interview Questions with their detailed answers. So that you can crack the interview.
 Break or return from Java 8 stream forEach?
Feb 07, 2025 pm 12:09 PM
Break or return from Java 8 stream forEach?
Feb 07, 2025 pm 12:09 PM
Java 8 introduces the Stream API, providing a powerful and expressive way to process data collections. However, a common question when using Stream is: How to break or return from a forEach operation? Traditional loops allow for early interruption or return, but Stream's forEach method does not directly support this method. This article will explain the reasons and explore alternative methods for implementing premature termination in Stream processing systems. Further reading: Java Stream API improvements Understand Stream forEach The forEach method is a terminal operation that performs one operation on each element in the Stream. Its design intention is






