 Backend Development
Backend Development
 Python Tutorial
Python Tutorial
 What is the method for crawling weather data and visual analysis in Python?
What is the method for crawling weather data and visual analysis in Python?
What is the method for crawling weather data and visual analysis in Python?
1. Data acquisition
Request website link
First check the China Weather Network. Here, visit the local weather website. If you want to crawl different regions, just Just modify the last 101280701 area number. The weather in front represents the 7-day webpage, weather1d represents the current day, and weather15d represents the next 14 days. Here we mainly visit the 7-day and 14-day China Weather Network. Use the requests.get() method to request the web page. If the access is successful, you will get all the string text of the web page. This is the request process.
def getHTMLtext(url):
"""请求获得网页内容"""
try:
r = requests.get(url, timeout = 30)
r.raise_for_status()
r.encoding = r.apparent_encoding
print("成功访问")
return r.text
except:
print("访问错误")
return" "Extracting useful information
The BeautifulSoup library is used to extract data from the string just obtained. First, check the web page and find the tags that need to obtain data:
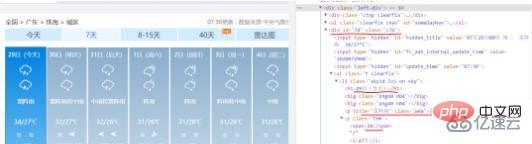
You can find that the 7-day data information is in the div tag with id="7d", and the date, weather, temperature, wind level and other information are in the ul and li tags, so we can use BeautifulSoup Search the obtained web page text for the div tag id="7d", find out all the ul and li tags it contains, and then extract the corresponding data values in the tags and save them in the corresponding list.
One detail to note here is that sometimes the date does not have the highest temperature, and the situation without data needs to be judged and processed. In addition, some data storage formats must be processed in advance, such as the Celsius symbol behind the temperature, the extraction of date numbers, and the extraction of wind-level text. This requires character search and string slicing processing.
def get_content(html):
"""处理得到有用信息保存数据文件"""
final = []# 初始化一个列表保存数据
bs = BeautifulSoup(html, "html.parser")# 创建BeautifulSoup对象
body = bs.body
data = body.find('div', {'id': '7d'})# 找到div标签且id = 7dThe following crawls the data of the current day
data2 = body.find_all('div',{'class':'left-div'})
text = data2[2].find('script').string
text = text[text.index('=')+1 :-2] # 移除改var data=将其变为json数据
jd = json.loads(text)
dayone = jd['od']['od2'] # 找到当天的数据
final_day = [] # 存放当天的数据
count = 0
for i in dayone:
temp = []
if count <=23:
temp.append(i['od21']) # 添加时间
temp.append(i['od22']) # 添加当前时刻温度
temp.append(i['od24']) # 添加当前时刻风力方向
temp.append(i['od25']) # 添加当前时刻风级
temp.append(i['od26']) # 添加当前时刻降水量
temp.append(i['od27']) # 添加当前时刻相对湿度
temp.append(i['od28']) # 添加当前时刻控制质量
#print(temp)
final_day.append(temp)
count = count +1The following crawls the data of 7 days
ul = data.find('ul')# 找到所有的ul标签 li = ul.find_all('li')# 找到左右的li标签 i = 0 # 控制爬取的天数 for day in li:# 遍历找到的每一个li if i < 7 and i > 0: temp = []# 临时存放每天的数据 date = day.find('h2').string # 得到日期 date = date[0:date.index('日')] # 取出日期号 temp.append(date) inf = day.find_all('p')# 找出li下面的p标签,提取第一个p标签的值,即天气 temp.append(inf[0].string) tem_low = inf[1].find('i').string # 找到最低气温 if inf[1].find('span') is None: # 天气预报可能没有最高气温 tem_high = None else: tem_high = inf[1].find('span').string# 找到最高气温 temp.append(tem_low[:-1]) if tem_high[-1] == '℃': temp.append(tem_high[:-1]) else: temp.append(tem_high) wind = inf[2].find_all('span')# 找到风向 for j in wind: temp.append(j['title']) wind_scale = inf[2].find('i').string # 找到风级 index1 = wind_scale.index('级') temp.append(int(wind_scale[index1-1:index1])) final.append(temp) i = i + 1 return final_day,final
Similarly do the same processing for /weather15d: 15 days of information, After checking here, we found that only 8-14 days were included in his 15-day webpage. The previous 1-7 days were in /weather. Here, we visited two webpages respectively and merged the crawled data to obtain the final 14-day data. - The front is the data crawling process for the next 14 days. For the 24-hour weather information data of the day, after searching, it is found that it is a json data. You can obtain the data of the day through the json.loads() method, and then perform the weather information of the day. extract.

Save the csv file
Add the crawled data to the list earlier, introduce the csv library here, and use f_csv.writerow(header) and f_csv. The writerows(data) method writes the data of the table header and each row respectively. Here, the data of 1 day and the next 14 days are stored separately and saved as weather1.csv and weather14.csv respectively. The following is the table they saved:
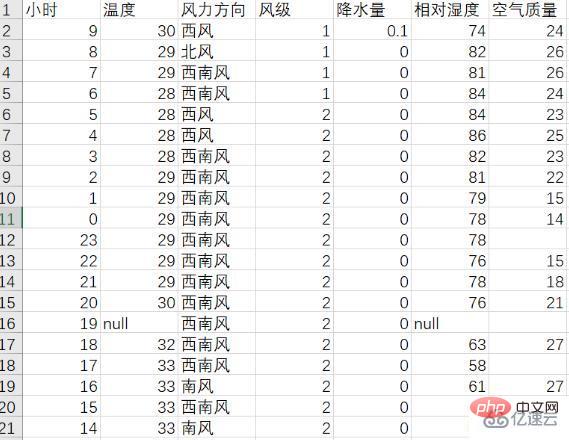
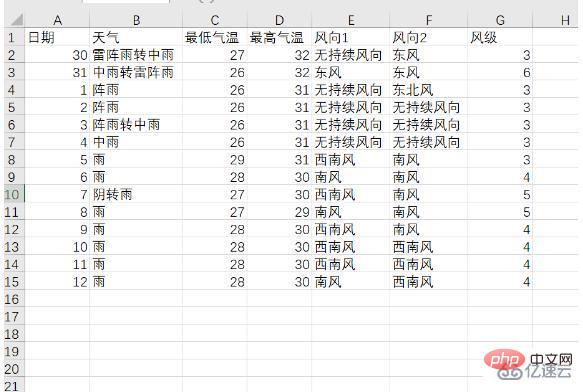
2. Visual analysis
The temperature change curve of the day
Uses plt.plot in matplotlib () method to draw the temperature change curve for 24 hours a day, and use the plt.text() method to point out the highest and lowest temperatures, and draw the average temperature line. The following figure is the temperature change curve: (see the appendix for the code)
Awesome! N open source projects that are essential for taking on private work! Hurry and collect it
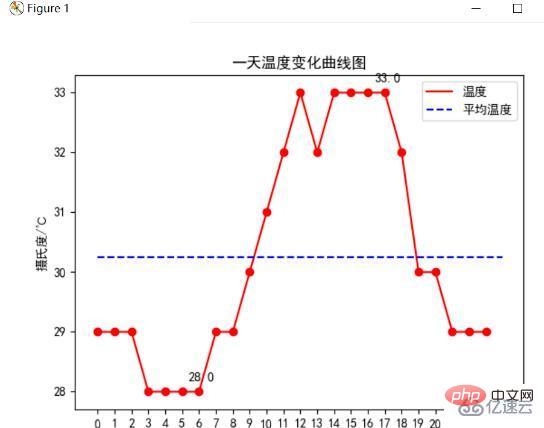
The analysis can find that the highest temperature on this day is 33℃, the lowest temperature is 28℃, and the average temperature is around 20.4℃. Through time analysis, it is found that day and night The temperature difference is 5°C, with low temperatures in the early morning and high temperatures in the period from noon to afternoon.
Relative humidity change curve chart of the day
Use the plt.plot() method in matplotlib to draw the humidity change curve for 24 hours a day, and draw the average relative humidity line. The following figure shows the humidity change Curve graph: (see appendix for code)
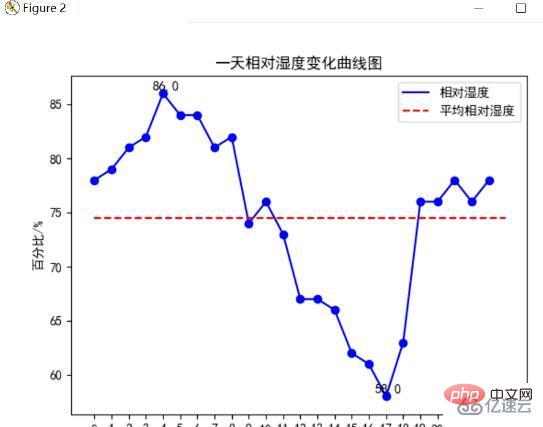
Analysis can find that the highest relative humidity on this day is 86%, the lowest relative humidity is 58℃, and the average relative humidity is around 75% , through time analysis, the humidity is relatively high in the early morning, while the humidity is low from afternoon to dusk.
Temperature and Humidity Correlation Analysis Chart
Through the analysis of the previous two figures, we can feel that there is a relationship between temperature and humidity. In order to feel this relationship more clearly and intuitively, use The plt.scatter() method sets the temperature as the abscissa and the humidity as the ordinate. The points at each moment are pointed out in the graph, and the correlation coefficient is calculated. The following figure is the result:
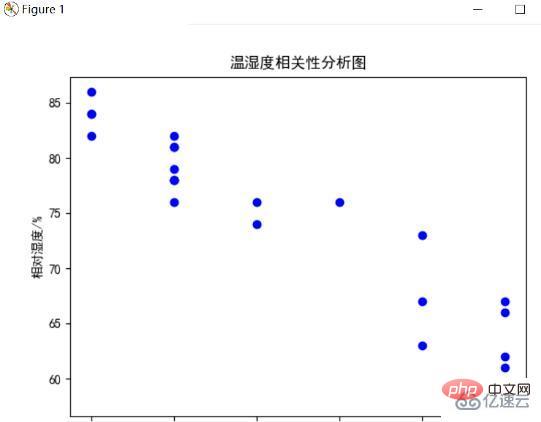
Analysis can find that the temperature and humidity of a day have a strong correlation. They are negatively correlated, which means that they are negatively correlated with time. Further analysis, when the temperature is lower, there is more moisture in the air, and the humidity Naturally, when the temperature is high, water evaporates, and the air becomes drier and the humidity is lower, which is consistent with normal climate phenomena.
Air Quality Index Bar Chart
Air Quality Index AQI is an index that quantitatively describes air quality conditions. The larger the value, the more serious the air pollution is and the greater the harm to human health. . The air quality index is generally divided into 6 levels. The higher the level, the more serious the pollution. The following uses the plt.bar method to draw a histogram of the air quality for 24 hours a day, and according to the six levels, the corresponding histogram The color also goes from light to dark, which also indicates that the pollution is gradually increasing, showing the pollution situation more intuitively. The highest and lowest air quality index are also marked, and the average air quality index is drawn with a dotted line. The figure below is the result of the drawing. :
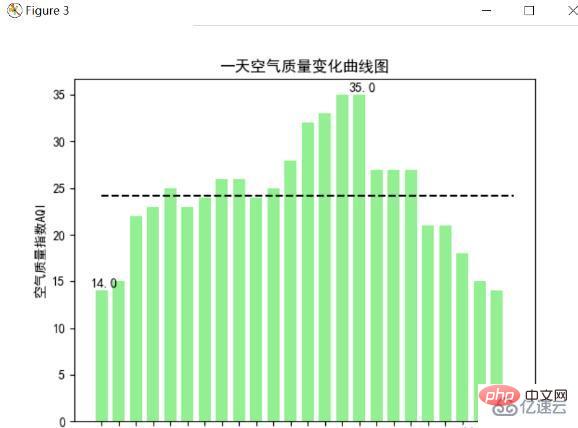
The above picture is the control quality chart of Zhuhai in the south. It can be seen that the maximum air quality index is also in the healthy range, indicating that the air in Zhuhai is very good. Analysis can find that on this day The highest air quality index reaches 35, the lowest is only 14, and the average is around 25. It can also be found by time that the air is basically the best in the early morning (4-9 o'clock), and the air pollution is the most serious in the afternoon. time, so you can usually go outside to breathe fresh air in the early morning, when the pollution is minimal.
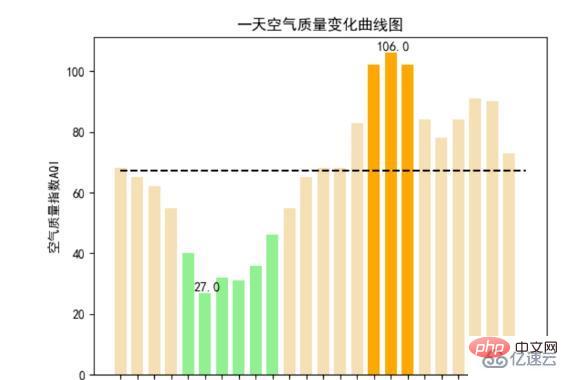
The air quality map below is from a city in the north. You can see that the environment here is far inferior to Zhuhai.
Wind direction and wind level radar chart
Statistics of wind power and wind direction for a day. Since the wind power and direction are better displayed using polar coordinates, the one used here is The polar coordinates display the wind force and direction diagram of the day. The circle is divided into 8 parts, each part represents a wind direction, and the radius represents the average wind force. As the wind level increases, the blue color deepens. The final result is as follows:
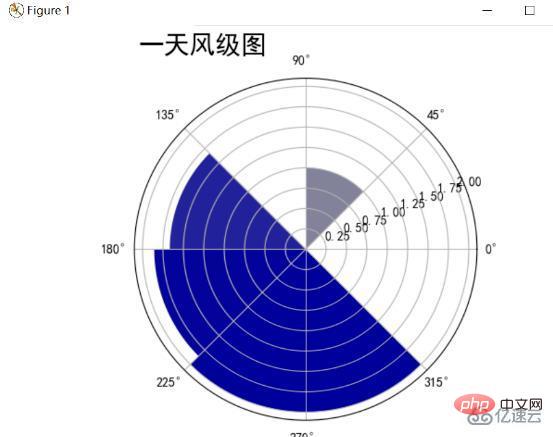
Analysis can be found that on this day, the southwest wind was the strongest, with the average wind level reaching 1.75. The northeast wind also had a small amount of 1.0 level, and there was no wind in the other blank directions.
High and low temperature change curve chart for the next 14 days
Statistics on the high and low temperature changes for the next 14 days, and draw their change curve charts, using dotted lines to draw their average temperature lines, The final results are as follows:
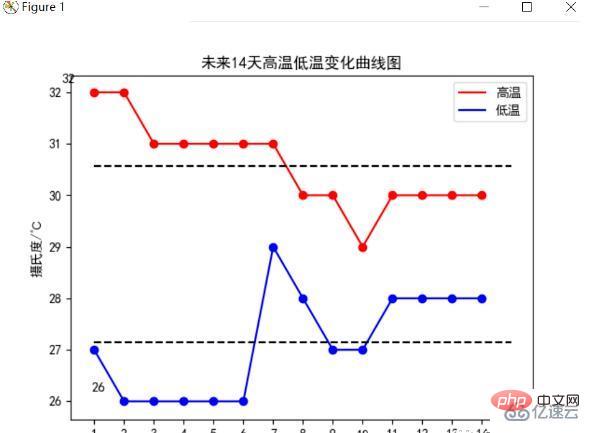
The analysis can find that the average high temperature in the next 14 days is 30.5℃. The temperature is still relatively high, but there will be cooling in the next 8 days, which needs to be done. It is good to be prepared for cooling. The low temperature is on a stable trend before it starts to drop on the 8th day. Along with the high temperature, the overall temperature drops, and the average low temperature is around 27°C.
Wind direction and wind level radar chart for the next 14 days
Statistics the wind direction and average wind force for the next 14 days, and uses polar coordinates as before, dividing the circle into 8 parts, representing 8 direction, the darker the color, the higher the wind level. The final results are as follows:
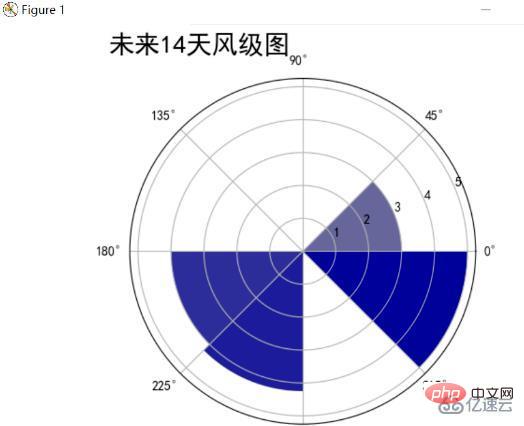
The analysis can find the main wind direction and wind level of southeasterly and southwesterly winds in the next 14 days. The highest level reached level 5, and the lowest average westerly wind level was level 3.
Climate distribution pie chart for the next 14 days
Count the climate for the next 14 days, find the total number of days for each climate, and finally draw the pie chart for each climate. The results are as follows:
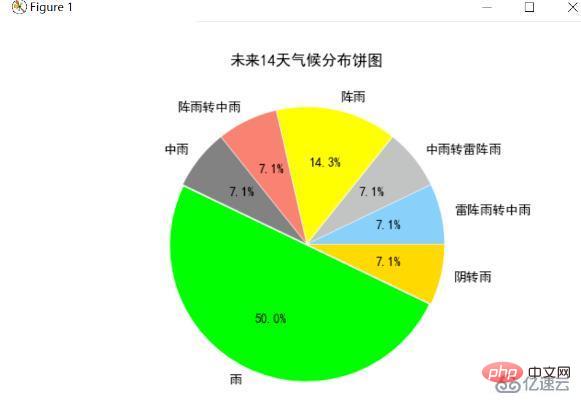
The analysis can find that the climate in the next 14 days will basically be "rain", "overcast to rain" and "showers". There will be more rainy days. Combined with the previous temperature distribution It can be seen from the figure that the temperature dropped on the 8th and 9th days. It can be speculated that it rained that day, causing the temperature to drop.
3. Conclusion
1. First, based on the analysis of the crawled temperature and humidity data, the temperature ranges from low in the morning to high at noon and then low in the evening. The trends of humidity and temperature are opposite. Through correlation The coefficient found that temperature and humidity have a strong negative correlation. After reviewing the data, it was found that as the temperature increases, the evaporation of water vapor intensifies, and the moisture in the air decreases and the humidity decreases. Of course, humidity is affected by both air pressure and rain, and the humidity will increase significantly when it rains.
2.经查阅资料空气质量不仅跟工厂、汽车等排放的烟气、废气等有关,更为重要的是与气象因素有关。由于昼夜温差明显变化,当地面温度高于高空温度时,空气上升,污染物易被带到高空扩散;当地面温度低于一定高度的温度时,天空形成逆温层,它像一个大盖子一样压在地面上空,使地表空气中各种污染物不易扩散。一般在晚间和清晨影响较大,而当太阳出来后,地面迅速升温,逆温层就会逐渐消散,于是污染空气也就扩散了。
3.风是由气压在水平方向分布的不均匀导致的。风受大气环流、地形、水域等不同因素的综合影响,表现形式多种多样,如季风、地方性的海陆风、山谷风等,一天的风向也有不同的变化,根据未来14天的风向雷达图可以发现未来所有风向基本都有涉及,并且没有特别的某个风向,原因可能是近期没有降水和气文变化不大,导致风向也没有太大的变化规律。
4.天气是指某一个地区距离地表较近的大气层在短时间内的具体状态。跟某瞬时内大气中各种气象要素分布的综合表现。根据未来14天的天气和温度变化可以大致推断出某个时间的气候,天气和温度之间也是有联系的。
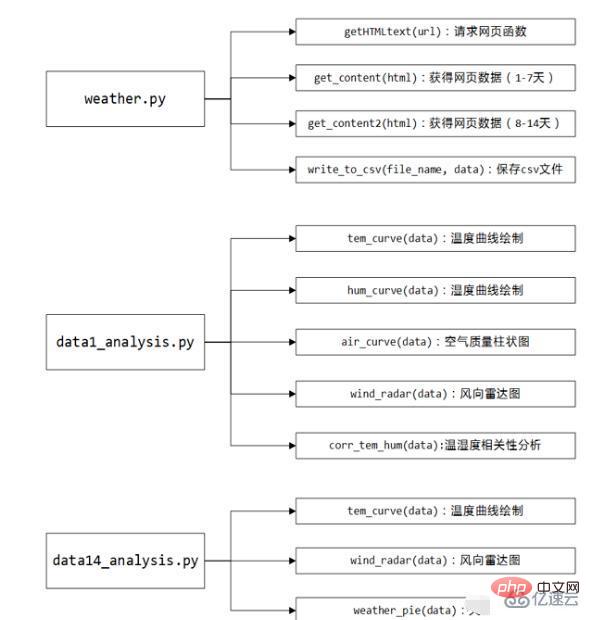
4、代码框架
代码主要分为weather.py:对中国天气网进行爬取天气数据并保存csv文件;data1_analysis.py:对当天的天气信息进行可视化处理;data14_analysis.py:对未来14天的天气信息进行可视化处理。下面是代码的结构图:
附源代码
weather.py
# weather.py
import requests
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup
import csv
import json
def getHTMLtext(url):
"""请求获得网页内容"""
try:
r = requests.get(url, timeout = 30)
r.raise_for_status()
r.encoding = r.apparent_encoding
print("成功访问")
return r.text
except:
print("访问错误")
return" "
def get_content(html):
"""处理得到有用信息保存数据文件"""
final = []# 初始化一个列表保存数据
bs = BeautifulSoup(html, "html.parser")# 创建BeautifulSoup对象
body = bs.body
data = body.find('div', {'id': '7d'})# 找到div标签且id = 7d
# 下面爬取当天的数据
data2 = body.find_all('div',{'class':'left-div'})
text = data2[2].find('script').string
text = text[text.index('=')+1 :-2] # 移除改var data=将其变为json数据
jd = json.loads(text)
dayone = jd['od']['od2'] # 找到当天的数据
final_day = [] # 存放当天的数据
count = 0
for i in dayone:
temp = []
if count <=23:
temp.append(i['od21']) # 添加时间
temp.append(i['od22']) # 添加当前时刻温度
temp.append(i['od24']) # 添加当前时刻风力方向
temp.append(i['od25']) # 添加当前时刻风级
temp.append(i['od26']) # 添加当前时刻降水量
temp.append(i['od27']) # 添加当前时刻相对湿度
temp.append(i['od28']) # 添加当前时刻控制质量
#print(temp)
final_day.append(temp)
count = count +1
# 下面爬取7天的数据
ul = data.find('ul')# 找到所有的ul标签
li = ul.find_all('li')# 找到左右的li标签
i = 0 # 控制爬取的天数
for day in li:# 遍历找到的每一个li
if i < 7 and i > 0:
temp = []# 临时存放每天的数据
date = day.find('h2').string # 得到日期
date = date[0:date.index('日')] # 取出日期号
temp.append(date)
inf = day.find_all('p')# 找出li下面的p标签,提取第一个p标签的值,即天气
temp.append(inf[0].string)
tem_low = inf[1].find('i').string # 找到最低气温
if inf[1].find('span') is None: # 天气预报可能没有最高气温
tem_high = None
else:
tem_high = inf[1].find('span').string# 找到最高气温
temp.append(tem_low[:-1])
if tem_high[-1] == '℃':
temp.append(tem_high[:-1])
else:
temp.append(tem_high)
wind = inf[2].find_all('span')# 找到风向
for j in wind:
temp.append(j['title'])
wind_scale = inf[2].find('i').string # 找到风级
index1 = wind_scale.index('级')
temp.append(int(wind_scale[index1-1:index1]))
final.append(temp)
i = i + 1
return final_day,final
#print(final)
def get_content2(html):
"""处理得到有用信息保存数据文件"""
final = []# 初始化一个列表保存数据
bs = BeautifulSoup(html, "html.parser")# 创建BeautifulSoup对象
body = bs.body
data = body.find('div', {'id': '15d'})# 找到div标签且id = 15d
ul = data.find('ul')# 找到所有的ul标签
li = ul.find_all('li')# 找到左右的li标签
final = []
i = 0 # 控制爬取的天数
for day in li: # 遍历找到的每一个li
if i < 8:
temp = [] # 临时存放每天的数据
date = day.find('span',{'class':'time'}).string# 得到日期
date = date[date.index('(')+1:-2]# 取出日期号
temp.append(date)
weather = day.find('span',{'class':'wea'}).string# 找到天气
temp.append(weather)
tem = day.find('span',{'class':'tem'}).text# 找到温度
temp.append(tem[tem.index('/')+1:-1]) # 找到最低气温
temp.append(tem[:tem.index('/')-1])# 找到最高气温
wind = day.find('span',{'class':'wind'}).string# 找到风向
if '转' in wind: # 如果有风向变化
temp.append(wind[:wind.index('转')])
temp.append(wind[wind.index('转')+1:])
else: # 如果没有风向变化,前后风向一致
temp.append(wind)
temp.append(wind)
wind_scale = day.find('span',{'class':'wind1'}).string# 找到风级
index1 = wind_scale.index('级')
temp.append(int(wind_scale[index1-1:index1]))
final.append(temp)
return final
def write_to_csv(file_name, data, day=14):
"""保存为csv文件"""
with open(file_name, 'a', errors='ignore', newline='') as f:
if day == 14:
header = ['日期','天气','最低气温','最高气温','风向1','风向2','风级']
else:
header = ['小时','温度','风力方向','风级','降水量','相对湿度','空气质量']
f_csv = csv.writer(f)
f_csv.writerow(header)
f_csv.writerows(data)
def main():
"""主函数"""
print("Weather test")
# 珠海
url1 = 'http://www.weather.com.cn/weather/101280701.shtml'# 7天天气中国天气网
url2 = 'http://www.weather.com.cn/weather15d/101280701.shtml' # 8-15天天气中国天气网
html1 = getHTMLtext(url1)
data1, data1_7 = get_content(html1)# 获得1-7天和当天的数据
html2 = getHTMLtext(url2)
data8_14 = get_content2(html2) # 获得8-14天数据
data14 = data1_7 + data8_14
#print(data)
write_to_csv('weather14.csv',data14,14) # 保存为csv文件
write_to_csv('weather1.csv',data1,1)
if __name__ == '__main__':
main()data1_analysis.py:
# data1_analysis.py
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
import math
def tem_curve(data):
"""温度曲线绘制"""
hour = list(data['小时'])
tem = list(data['温度'])
for i in range(0,24):
if math.isnan(tem[i]) == True:
tem[i] = tem[i-1]
tem_ave = sum(tem)/24 # 求平均温度
tem_max = max(tem)
tem_max_hour = hour[tem.index(tem_max)] # 求最高温度
tem_min = min(tem)
tem_min_hour = hour[tem.index(tem_min)] # 求最低温度
x = []
y = []
for i in range(0, 24):
x.append(i)
y.append(tem[hour.index(i)])
plt.figure(1)
plt.plot(x,y,color='red',label='温度') # 画出温度曲线
plt.scatter(x,y,color='red') # 点出每个时刻的温度点
plt.plot([0, 24], [tem_ave, tem_ave], c='blue', linestyle='--',label='平均温度')# 画出平均温度虚线
plt.text(tem_max_hour+0.15, tem_max+0.15, str(tem_max), ha='center', va='bottom', fontsize=10.5)# 标出最高温度
plt.text(tem_min_hour+0.15, tem_min+0.15, str(tem_min), ha='center', va='bottom', fontsize=10.5)# 标出最低温度
plt.xticks(x)
plt.legend()
plt.title('一天温度变化曲线图')
plt.xlabel('时间/h')
plt.ylabel('摄氏度/℃')
plt.show()
def hum_curve(data):
"""相对湿度曲线绘制"""
hour = list(data['小时'])
hum = list(data['相对湿度'])
for i in range(0,24):
if math.isnan(hum[i]) == True:
hum[i] = hum[i-1]
hum_ave = sum(hum)/24 # 求平均相对湿度
hum_max = max(hum)
hum_max_hour = hour[hum.index(hum_max)] # 求最高相对湿度
hum_min = min(hum)
hum_min_hour = hour[hum.index(hum_min)] # 求最低相对湿度
x = []
y = []
for i in range(0, 24):
x.append(i)
y.append(hum[hour.index(i)])
plt.figure(2)
plt.plot(x,y,color='blue',label='相对湿度') # 画出相对湿度曲线
plt.scatter(x,y,color='blue') # 点出每个时刻的相对湿度
plt.plot([0, 24], [hum_ave, hum_ave], c='red', linestyle='--',label='平均相对湿度')# 画出平均相对湿度虚线
plt.text(hum_max_hour+0.15, hum_max+0.15, str(hum_max), ha='center', va='bottom', fontsize=10.5)# 标出最高相对湿度
plt.text(hum_min_hour+0.15, hum_min+0.15, str(hum_min), ha='center', va='bottom', fontsize=10.5)# 标出最低相对湿度
plt.xticks(x)
plt.legend()
plt.title('一天相对湿度变化曲线图')
plt.xlabel('时间/h')
plt.ylabel('百分比/%')
plt.show()
def air_curve(data):
"""空气质量曲线绘制"""
hour = list(data['小时'])
air = list(data['空气质量'])
print(type(air[0]))
for i in range(0,24):
if math.isnan(air[i]) == True:
air[i] = air[i-1]
air_ave = sum(air)/24 # 求平均空气质量
air_max = max(air)
air_max_hour = hour[air.index(air_max)] # 求最高空气质量
air_min = min(air)
air_min_hour = hour[air.index(air_min)] # 求最低空气质量
x = []
y = []
for i in range(0, 24):
x.append(i)
y.append(air[hour.index(i)])
plt.figure(3)
for i in range(0,24):
if y[i] <= 50:
plt.bar(x[i],y[i],color='lightgreen',width=0.7)# 1等级
elif y[i] <= 100:
plt.bar(x[i],y[i],color='wheat',width=0.7) # 2等级
elif y[i] <= 150:
plt.bar(x[i],y[i],color='orange',width=0.7) # 3等级
elif y[i] <= 200:
plt.bar(x[i],y[i],color='orangered',width=0.7)# 4等级
elif y[i] 300:
plt.bar(x[i],y[i],color='maroon',width=0.7) # 6等级
plt.plot([0, 24], [air_ave, air_ave], c='black', linestyle='--')# 画出平均空气质量虚线
plt.text(air_max_hour+0.15, air_max+0.15, str(air_max), ha='center', va='bottom', fontsize=10.5)# 标出最高空气质量
plt.text(air_min_hour+0.15, air_min+0.15, str(air_min), ha='center', va='bottom', fontsize=10.5)# 标出最低空气质量
plt.xticks(x)
plt.title('一天空气质量变化曲线图')
plt.xlabel('时间/h')
plt.ylabel('空气质量指数AQI')
plt.show()
def wind_radar(data):
"""风向雷达图"""
wind = list(data['风力方向'])
wind_speed = list(data['风级'])
for i in range(0,24):
if wind[i] == "北风":
wind[i] = 90
elif wind[i] == "南风":
wind[i] = 270
elif wind[i] == "西风":
wind[i] = 180
elif wind[i] == "东风":
wind[i] = 360
elif wind[i] == "东北风":
wind[i] = 45
elif wind[i] == "西北风":
wind[i] = 135
elif wind[i] == "西南风":
wind[i] = 225
elif wind[i] == "东南风":
wind[i] = 315
degs = np.arange(45,361,45)
temp = []
for deg in degs:
speed = []
# 获取 wind_deg 在指定范围的风速平均值数据
for i in range(0,24):
if wind[i] == deg:
speed.append(wind_speed[i])
if len(speed) == 0:
temp.append(0)
else:
temp.append(sum(speed)/len(speed))
print(temp)
N = 8
theta = np.arange(0.+np.pi/8,2*np.pi+np.pi/8,2*np.pi/8)
# 数据极径
radii = np.array(temp)
# 绘制极区图坐标系
plt.axes(polar=True)
# 定义每个扇区的RGB值(R,G,B),x越大,对应的颜色越接近蓝色
colors = [(1-x/max(temp), 1-x/max(temp),0.6) for x in radii]
plt.bar(theta,radii,width=(2*np.pi/N),bottom=0.0,color=colors)
plt.title('一天风级图',x=0.2,fontsize=20)
plt.show()
def calc_corr(a, b):
"""计算相关系数"""
a_avg = sum(a)/len(a)
b_avg = sum(b)/len(b)
cov_ab = sum([(x - a_avg)*(y - b_avg) for x,y in zip(a, b)])
sq = math.sqrt(sum([(x - a_avg)**2 for x in a])*sum([(x - b_avg)**2 for x in b]))
corr_factor = cov_ab/sq
return corr_factor
def corr_tem_hum(data):
"""温湿度相关性分析"""
tem = data['温度']
hum = data['相对湿度']
plt.scatter(tem,hum,color='blue')
plt.title("温湿度相关性分析图")
plt.xlabel("温度/℃")
plt.ylabel("相对湿度/%")
plt.text(20,40,"相关系数为:"+str(calc_corr(tem,hum)),fontdict={'size':'10','color':'red'})
plt.show()
print("相关系数为:"+str(calc_corr(tem,hum)))
def main():
plt.rcParams['font.sans-serif']=['SimHei'] # 解决中文显示问题
plt.rcParams['axes.unicode_minus'] = False# 解决负号显示问题
data1 = pd.read_csv('weather1.csv',encoding='gb2312')
print(data1)
tem_curve(data1)
hum_curve(data1)
air_curve(data1)
wind_radar(data1)
corr_tem_hum(data1)
if __name__ == '__main__':
main()
data14_analysis.py:
# data14_analysis.py
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
import math
def tem_curve(data):
"""温度曲线绘制"""
date = list(data['日期'])
tem_low = list(data['最低气温'])
tem_high = list(data['最高气温'])
for i in range(0,14):
if math.isnan(tem_low[i]) == True:
tem_low[i] = tem_low[i-1]
if math.isnan(tem_high[i]) == True:
tem_high[i] = tem_high[i-1]
tem_high_ave = sum(tem_high)/14 # 求平均高温
tem_low_ave = sum(tem_low)/14 # 求平均低温
tem_max = max(tem_high)
tem_max_date = tem_high.index(tem_max) # 求最高温度
tem_min = min(tem_low)
tem_min_date = tem_low.index(tem_min) # 求最低温度
x = range(1,15)
plt.figure(1)
plt.plot(x,tem_high,color='red',label='高温')# 画出高温度曲线
plt.scatter(x,tem_high,color='red') # 点出每个时刻的温度点
plt.plot(x,tem_low,color='blue',label='低温')# 画出低温度曲线
plt.scatter(x,tem_low,color='blue') # 点出每个时刻的温度点
plt.plot([1, 15], [tem_high_ave, tem_high_ave], c='black', linestyle='--')# 画出平均温度虚线
plt.plot([1, 15], [tem_low_ave, tem_low_ave], c='black', linestyle='--')# 画出平均温度虚线
plt.legend()
plt.text(tem_max_date+0.15, tem_max+0.15, str(tem_max), ha='center', va='bottom', fontsize=10.5)# 标出最高温度
plt.text(tem_min_date+0.15, tem_min+0.15, str(tem_min), ha='center', va='bottom', fontsize=10.5)# 标出最低温度
plt.xticks(x)
plt.title('未来14天高温低温变化曲线图')
plt.xlabel('未来天数/天')
plt.ylabel('摄氏度/℃')
plt.show()
def change_wind(wind):
"""改变风向"""
for i in range(0,14):
if wind[i] == "北风":
wind[i] = 90
elif wind[i] == "南风":
wind[i] = 270
elif wind[i] == "西风":
wind[i] = 180
elif wind[i] == "东风":
wind[i] = 360
elif wind[i] == "东北风":
wind[i] = 45
elif wind[i] == "西北风":
wind[i] = 135
elif wind[i] == "西南风":
wind[i] = 225
elif wind[i] == "东南风":
wind[i] = 315
return wind
def wind_radar(data):
"""风向雷达图"""
wind1 = list(data['风向1'])
wind2 = list(data['风向2'])
wind_speed = list(data['风级'])
wind1 = change_wind(wind1)
wind2 = change_wind(wind2)
degs = np.arange(45,361,45)
temp = []
for deg in degs:
speed = []
# 获取 wind_deg 在指定范围的风速平均值数据
for i in range(0,14):
if wind1[i] == deg:
speed.append(wind_speed[i])
if wind2[i] == deg:
speed.append(wind_speed[i])
if len(speed) == 0:
temp.append(0)
else:
temp.append(sum(speed)/len(speed))
print(temp)
N = 8
theta = np.arange(0.+np.pi/8,2*np.pi+np.pi/8,2*np.pi/8)
# 数据极径
radii = np.array(temp)
# 绘制极区图坐标系
plt.axes(polar=True)
# 定义每个扇区的RGB值(R,G,B),x越大,对应的颜色越接近蓝色
colors = [(1-x/max(temp), 1-x/max(temp),0.6) for x in radii]
plt.bar(theta,radii,width=(2*np.pi/N),bottom=0.0,color=colors)
plt.title('未来14天风级图',x=0.2,fontsize=20)
plt.show()
def weather_pie(data):
"""绘制天气饼图"""
weather = list(data['天气'])
dic_wea = { }
for i in range(0,14):
if weather[i] in dic_wea.keys():
dic_wea[weather[i]] += 1
else:
dic_wea[weather[i]] = 1
print(dic_wea)
explode=[0.01]*len(dic_wea.keys())
color = ['lightskyblue','silver','yellow','salmon','grey','lime','gold','red','green','pink']
plt.pie(dic_wea.values(),explode=explode,labels=dic_wea.keys(),autopct='%1.1f%%',colors=color)
plt.title('未来14天气候分布饼图')
plt.show()
def main():
plt.rcParams['font.sans-serif']=['SimHei'] # 解决中文显示问题
plt.rcParams['axes.unicode_minus'] = False# 解决负号显示问题
data14 = pd.read_csv('weather14.csv',encoding='gb2312')
print(data14)
tem_curve(data14)
wind_radar(data14)
weather_pie(data14)
if __name__ == '__main__':
main()The above is the detailed content of What is the method for crawling weather data and visual analysis in Python?. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1389
1389
 52
52
 Choosing Between PHP and Python: A Guide
Apr 18, 2025 am 12:24 AM
Choosing Between PHP and Python: A Guide
Apr 18, 2025 am 12:24 AM
PHP is suitable for web development and rapid prototyping, and Python is suitable for data science and machine learning. 1.PHP is used for dynamic web development, with simple syntax and suitable for rapid development. 2. Python has concise syntax, is suitable for multiple fields, and has a strong library ecosystem.
 PHP and Python: Different Paradigms Explained
Apr 18, 2025 am 12:26 AM
PHP and Python: Different Paradigms Explained
Apr 18, 2025 am 12:26 AM
PHP is mainly procedural programming, but also supports object-oriented programming (OOP); Python supports a variety of paradigms, including OOP, functional and procedural programming. PHP is suitable for web development, and Python is suitable for a variety of applications such as data analysis and machine learning.
 Can vs code run in Windows 8
Apr 15, 2025 pm 07:24 PM
Can vs code run in Windows 8
Apr 15, 2025 pm 07:24 PM
VS Code can run on Windows 8, but the experience may not be great. First make sure the system has been updated to the latest patch, then download the VS Code installation package that matches the system architecture and install it as prompted. After installation, be aware that some extensions may be incompatible with Windows 8 and need to look for alternative extensions or use newer Windows systems in a virtual machine. Install the necessary extensions to check whether they work properly. Although VS Code is feasible on Windows 8, it is recommended to upgrade to a newer Windows system for a better development experience and security.
 Is the vscode extension malicious?
Apr 15, 2025 pm 07:57 PM
Is the vscode extension malicious?
Apr 15, 2025 pm 07:57 PM
VS Code extensions pose malicious risks, such as hiding malicious code, exploiting vulnerabilities, and masturbating as legitimate extensions. Methods to identify malicious extensions include: checking publishers, reading comments, checking code, and installing with caution. Security measures also include: security awareness, good habits, regular updates and antivirus software.
 How to run programs in terminal vscode
Apr 15, 2025 pm 06:42 PM
How to run programs in terminal vscode
Apr 15, 2025 pm 06:42 PM
In VS Code, you can run the program in the terminal through the following steps: Prepare the code and open the integrated terminal to ensure that the code directory is consistent with the terminal working directory. Select the run command according to the programming language (such as Python's python your_file_name.py) to check whether it runs successfully and resolve errors. Use the debugger to improve debugging efficiency.
 Can visual studio code be used in python
Apr 15, 2025 pm 08:18 PM
Can visual studio code be used in python
Apr 15, 2025 pm 08:18 PM
VS Code can be used to write Python and provides many features that make it an ideal tool for developing Python applications. It allows users to: install Python extensions to get functions such as code completion, syntax highlighting, and debugging. Use the debugger to track code step by step, find and fix errors. Integrate Git for version control. Use code formatting tools to maintain code consistency. Use the Linting tool to spot potential problems ahead of time.
 Can vscode be used for mac
Apr 15, 2025 pm 07:36 PM
Can vscode be used for mac
Apr 15, 2025 pm 07:36 PM
VS Code is available on Mac. It has powerful extensions, Git integration, terminal and debugger, and also offers a wealth of setup options. However, for particularly large projects or highly professional development, VS Code may have performance or functional limitations.
 Can vscode run ipynb
Apr 15, 2025 pm 07:30 PM
Can vscode run ipynb
Apr 15, 2025 pm 07:30 PM
The key to running Jupyter Notebook in VS Code is to ensure that the Python environment is properly configured, understand that the code execution order is consistent with the cell order, and be aware of large files or external libraries that may affect performance. The code completion and debugging functions provided by VS Code can greatly improve coding efficiency and reduce errors.



