How to implement minimum height tree in Java
Question requirements
A tree is an undirected graph in which any two vertices are connected by only one path. In other words, any connected graph without simple cycles is a tree.
You are given a tree containing n nodes, labeled 0 to n - 1 . Given a number n and an edges list with n - 1 undirected edges (each edge is a pair of labels), where edges[i] = [ai, bi] means that there is an edge between nodes ai and bi in the tree Undirected edge.
You can select any node in the tree as the root. When node x is selected as the root node, let the height of the result tree be h. Among all possible trees, the tree with the minimum height (i.e., min(h)) is called the minimum height tree .
Please find all minimum height trees and return their root node label list in any order.
The height of a tree refers to the number of edges on the longest downward path between the root node and leaf nodes.
Example 1:
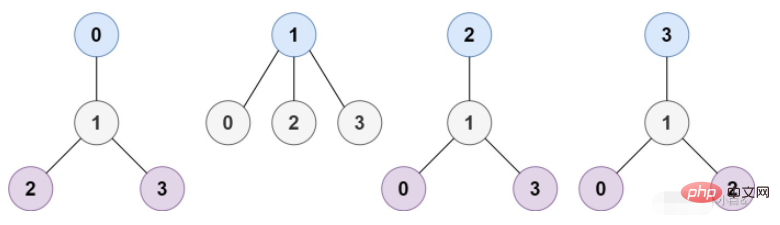
Input: n = 4, edges = [[1,0],[1,2],[1,3] ]
Output: [1]
Explanation: As shown in the figure, when the root is the node with label 1, the height of the tree is 1, which is the only minimum height tree.
Example 2:
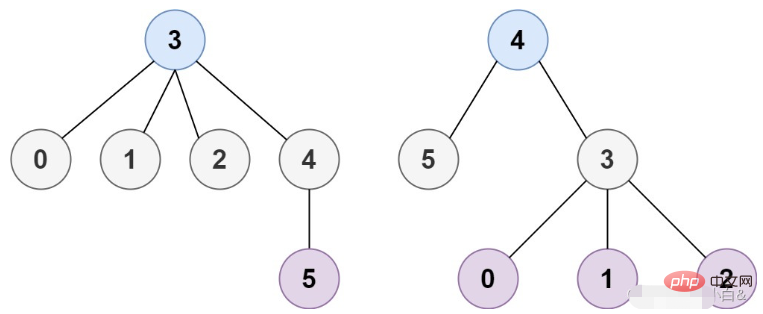
Input: n = 6, edges = [[3,0],[3,1],[3 ,2],[3,4],[5,4]]
Output: [3,4]
##Prompt:Problem-solving ideas From the above two graphs, we can draw the conclusion: What needs to be solved in the problem is the central node in the tree, and each tree will have no more than two central nodes. And if we want to get the central node in the tree, we can FBS layer by layer (that is, pruning the leaf nodes with an out-degree of one layer by layer) until the last layer is cut. , you can output the result! Algorithm1 edges.length == n - 1
0 ai != bi
All (ai, bi) are different from each other
The given input is guaranteed to be a tree, and there will be no duplicate edges
class Solution {
public List<Integer> findMinHeightTrees(int n, int[][] edges) {
List<Integer> res = new ArrayList<Integer>();
//如果只有一个节点,则它就是最小高度树
if(n == 1){
res.add(0);
return res;
}
//每个节点的邻居数量
int [] degree = new int[n];
//每个节点的邻居
HashMap<Integer,List<Integer>> map = new HashMap<>();
for(int [] edge : edges){
int a = edge[0];
int b = edge[1];
degree[a]++;
degree[b]++;
if(map.get(a) == null){
map.put(a,new ArrayList<Integer>());//key:节点 value:邻居
}
if(map.get(b) == null){
map.put(b,new ArrayList<Integer>());//key:节点 value:邻居
}
map.get(a).add(b);
map.get(b).add(a);
}
//建立队列
LinkedList<Integer> leafNodes = new LinkedList<Integer>();//表示叶子节点
//将所有度为1的节点入队
for(int i = 0;i < degree.length;i++){
if(degree[i] == 1){
leafNodes.add(i);
}
}
while(leafNodes.size() > 0){
res.clear();
//每一层节点的数量
int size = leafNodes.size();
for(int i = 0;i < size;i++){
int leaf = leafNodes.poll();
//将当前节点加入到结果集
res.add(leaf);
List<Integer> neighbors = map.get(leaf);
//将出度减一,也就是将最外层的叶子节点剪掉
for(int neighbor : neighbors){
degree[neighbor]--;
if(degree[neighbor] == 1){
//叶子节点入队
leafNodes.add(neighbor);
}
}
}
}
return res;
}
}Copy after login
class Solution {
public List<Integer> findMinHeightTrees(int n, int[][] edges) {
List<Integer> res = new ArrayList<Integer>();
//如果只有一个节点,则它就是最小高度树
if(n == 1){
res.add(0);
return res;
}
//每个节点的邻居数量
int [] degree = new int[n];
//每个节点的邻居
HashMap<Integer,List<Integer>> map = new HashMap<>();
for(int [] edge : edges){
int a = edge[0];
int b = edge[1];
degree[a]++;
degree[b]++;
if(map.get(a) == null){
map.put(a,new ArrayList<Integer>());//key:节点 value:邻居
}
if(map.get(b) == null){
map.put(b,new ArrayList<Integer>());//key:节点 value:邻居
}
map.get(a).add(b);
map.get(b).add(a);
}
//建立队列
LinkedList<Integer> leafNodes = new LinkedList<Integer>();//表示叶子节点
//将所有度为1的节点入队
for(int i = 0;i < degree.length;i++){
if(degree[i] == 1){
leafNodes.add(i);
}
}
while(leafNodes.size() > 0){
res.clear();
//每一层节点的数量
int size = leafNodes.size();
for(int i = 0;i < size;i++){
int leaf = leafNodes.poll();
//将当前节点加入到结果集
res.add(leaf);
List<Integer> neighbors = map.get(leaf);
//将出度减一,也就是将最外层的叶子节点剪掉
for(int neighbor : neighbors){
degree[neighbor]--;
if(degree[neighbor] == 1){
//叶子节点入队
leafNodes.add(neighbor);
}
}
}
}
return res;
}
}The above is the detailed content of How to implement minimum height tree in Java. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1387
1387
 52
52
 Perfect Number in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:28 PM
Perfect Number in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:28 PM
Guide to Perfect Number in Java. Here we discuss the Definition, How to check Perfect number in Java?, examples with code implementation.
 Weka in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:28 PM
Weka in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:28 PM
Guide to Weka in Java. Here we discuss the Introduction, how to use weka java, the type of platform, and advantages with examples.
 Smith Number in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:28 PM
Smith Number in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:28 PM
Guide to Smith Number in Java. Here we discuss the Definition, How to check smith number in Java? example with code implementation.
 Java Spring Interview Questions
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:29 PM
Java Spring Interview Questions
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:29 PM
In this article, we have kept the most asked Java Spring Interview Questions with their detailed answers. So that you can crack the interview.
 Break or return from Java 8 stream forEach?
Feb 07, 2025 pm 12:09 PM
Break or return from Java 8 stream forEach?
Feb 07, 2025 pm 12:09 PM
Java 8 introduces the Stream API, providing a powerful and expressive way to process data collections. However, a common question when using Stream is: How to break or return from a forEach operation? Traditional loops allow for early interruption or return, but Stream's forEach method does not directly support this method. This article will explain the reasons and explore alternative methods for implementing premature termination in Stream processing systems. Further reading: Java Stream API improvements Understand Stream forEach The forEach method is a terminal operation that performs one operation on each element in the Stream. Its design intention is
 TimeStamp to Date in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:28 PM
TimeStamp to Date in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:28 PM
Guide to TimeStamp to Date in Java. Here we also discuss the introduction and how to convert timestamp to date in java along with examples.
 Java Program to Find the Volume of Capsule
Feb 07, 2025 am 11:37 AM
Java Program to Find the Volume of Capsule
Feb 07, 2025 am 11:37 AM
Capsules are three-dimensional geometric figures, composed of a cylinder and a hemisphere at both ends. The volume of the capsule can be calculated by adding the volume of the cylinder and the volume of the hemisphere at both ends. This tutorial will discuss how to calculate the volume of a given capsule in Java using different methods. Capsule volume formula The formula for capsule volume is as follows: Capsule volume = Cylindrical volume Volume Two hemisphere volume in, r: The radius of the hemisphere. h: The height of the cylinder (excluding the hemisphere). Example 1 enter Radius = 5 units Height = 10 units Output Volume = 1570.8 cubic units explain Calculate volume using formula: Volume = π × r2 × h (4
 Create the Future: Java Programming for Absolute Beginners
Oct 13, 2024 pm 01:32 PM
Create the Future: Java Programming for Absolute Beginners
Oct 13, 2024 pm 01:32 PM
Java is a popular programming language that can be learned by both beginners and experienced developers. This tutorial starts with basic concepts and progresses through advanced topics. After installing the Java Development Kit, you can practice programming by creating a simple "Hello, World!" program. After you understand the code, use the command prompt to compile and run the program, and "Hello, World!" will be output on the console. Learning Java starts your programming journey, and as your mastery deepens, you can create more complex applications.




