 Technology peripherals
Technology peripherals
 AI
AI
 GPT 4 with 100 trillion parameters has flooded the AI community, it is most likely false news
GPT 4 with 100 trillion parameters has flooded the AI community, it is most likely false news
GPT 4 with 100 trillion parameters has flooded the AI community, it is most likely false news
Today, there must be such a big news in your circle of friends:
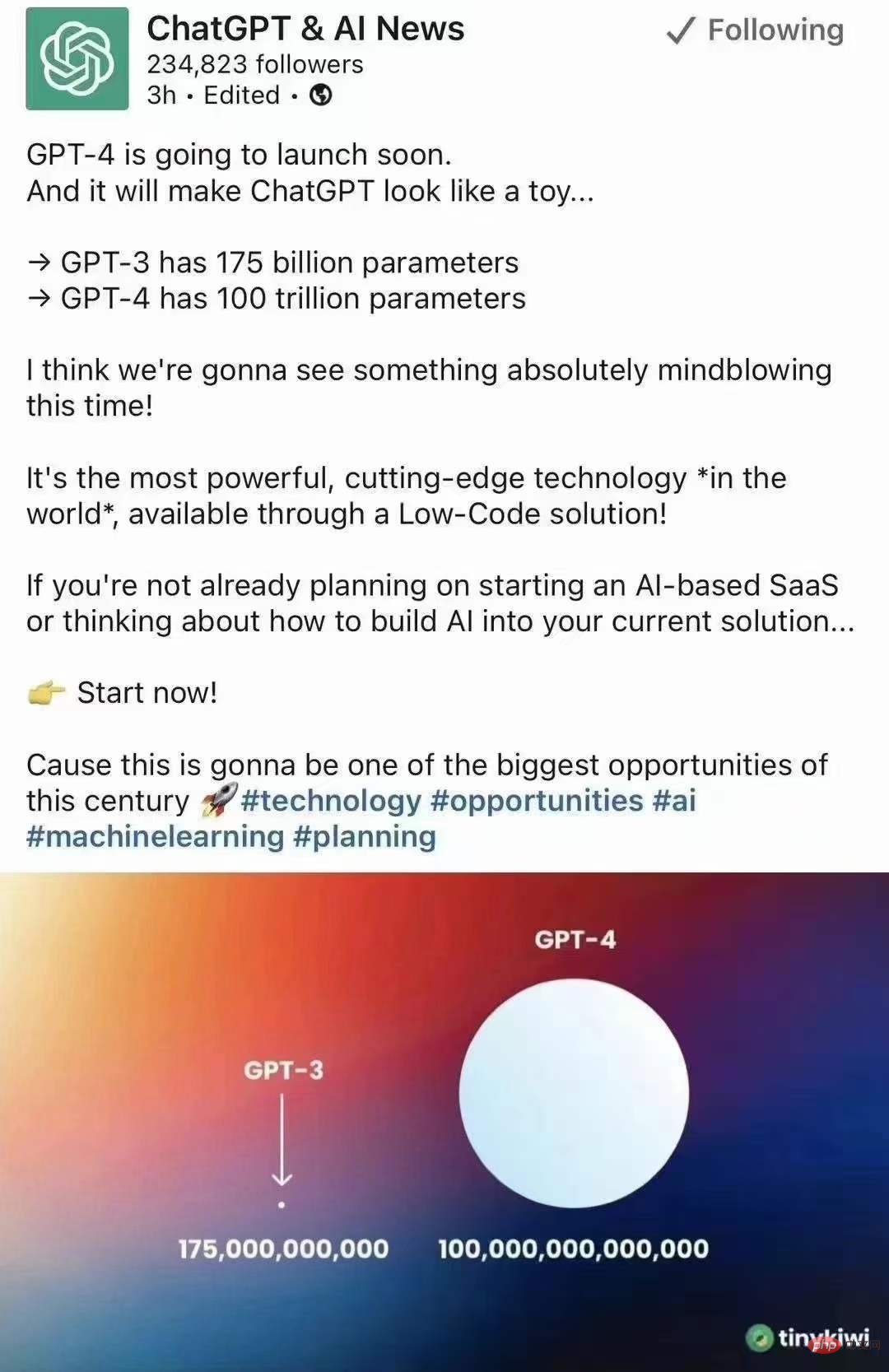
##「GPT 3 has 175 billion parameters, and the following GPT4 has as high as 100 trillion". Such a "big news" detonated the AI community and attracted great attention in Twitter and WeChat Moments. Many netizens shouted: The nuclear bomb is coming, it is unimaginable.
Although we are also amazed by OpenAI's ability to create records, we are still skeptical about "GPT 4 parameters as high as 100 trillion". So I carefully checked the sources of information and their reliability.
Twitter user @Russell Thomas said, "The parameter data of GPT4 is wrong. It was reported a year ago that the parameters of GPT4 would reach 100 trillion, but it was recently confirmed that it was incorrect. Correct. Relevant team members confirmed that the parameter size of GPT4 will only be slightly larger than that of GPT3."
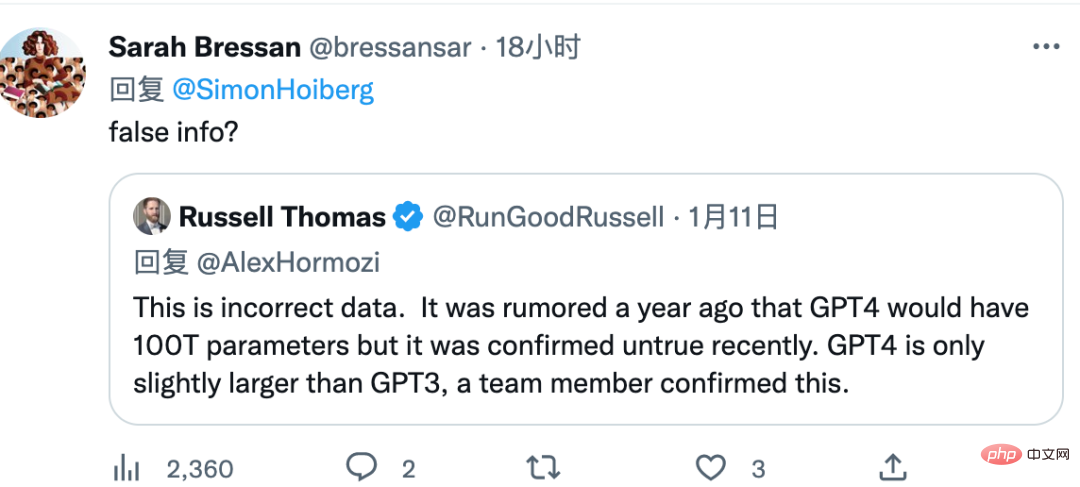
In addition, Twitter user @Omar also said, "The network transmission data of GPT4 is wrong, and OpenAI engineers have confirmed this."
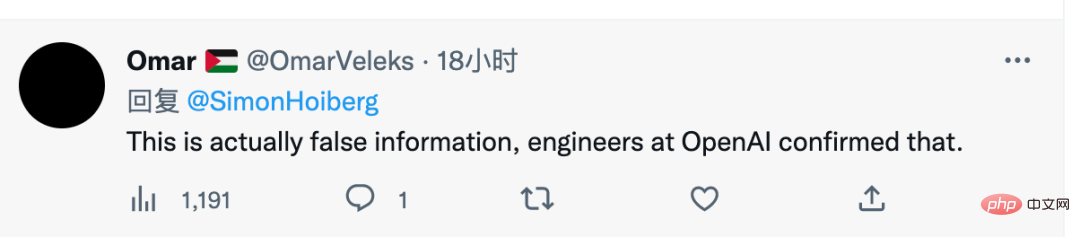
In fact, when it was reported on November 23 last year that the number of GPT4 parameters would reach 100 trillion, OpenAI CEO Sam Altman only said one sentence, "Everyone is too uncool. ". This also seems to indicate OpenAI's attitude towards GPT4 parameter rumors.
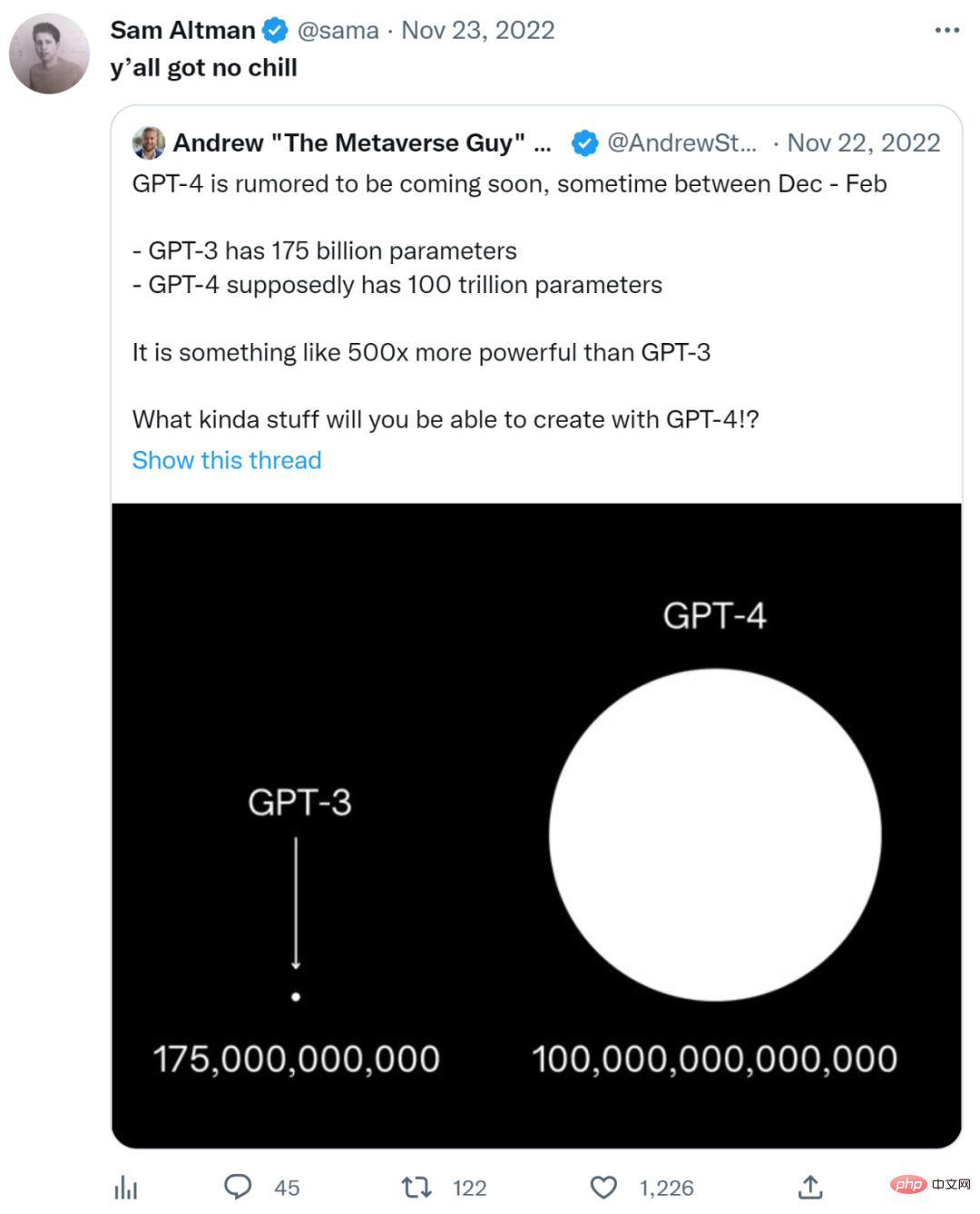
DataCamp’s recent article “Everything We Know About GPT-4” also mentioned the issue of model size, stating that it was confirmed that it would not be larger than GPT 3 is particularly large.

Based on information from all parties, GPT 4 with 100 trillion parameters is most likely false news.
Finally, OpenAI has not officially responded to the number of parameters of GPT 4, allowing rumors to "fly for a while." This is probably also their PR strategy. We won’t know the final data until GPT 4 is released, so let’s wait and see.
The above is the detailed content of GPT 4 with 100 trillion parameters has flooded the AI community, it is most likely false news. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1386
1386
 52
52
 How to check CentOS HDFS configuration
Apr 14, 2025 pm 07:21 PM
How to check CentOS HDFS configuration
Apr 14, 2025 pm 07:21 PM
Complete Guide to Checking HDFS Configuration in CentOS Systems This article will guide you how to effectively check the configuration and running status of HDFS on CentOS systems. The following steps will help you fully understand the setup and operation of HDFS. Verify Hadoop environment variable: First, make sure the Hadoop environment variable is set correctly. In the terminal, execute the following command to verify that Hadoop is installed and configured correctly: hadoopversion Check HDFS configuration file: The core configuration file of HDFS is located in the /etc/hadoop/conf/ directory, where core-site.xml and hdfs-site.xml are crucial. use
 Centos shutdown command line
Apr 14, 2025 pm 09:12 PM
Centos shutdown command line
Apr 14, 2025 pm 09:12 PM
The CentOS shutdown command is shutdown, and the syntax is shutdown [Options] Time [Information]. Options include: -h Stop the system immediately; -P Turn off the power after shutdown; -r restart; -t Waiting time. Times can be specified as immediate (now), minutes ( minutes), or a specific time (hh:mm). Added information can be displayed in system messages.
 What are the backup methods for GitLab on CentOS
Apr 14, 2025 pm 05:33 PM
What are the backup methods for GitLab on CentOS
Apr 14, 2025 pm 05:33 PM
Backup and Recovery Policy of GitLab under CentOS System In order to ensure data security and recoverability, GitLab on CentOS provides a variety of backup methods. This article will introduce several common backup methods, configuration parameters and recovery processes in detail to help you establish a complete GitLab backup and recovery strategy. 1. Manual backup Use the gitlab-rakegitlab:backup:create command to execute manual backup. This command backs up key information such as GitLab repository, database, users, user groups, keys, and permissions. The default backup file is stored in the /var/opt/gitlab/backups directory. You can modify /etc/gitlab
 Centos install mysql
Apr 14, 2025 pm 08:09 PM
Centos install mysql
Apr 14, 2025 pm 08:09 PM
Installing MySQL on CentOS involves the following steps: Adding the appropriate MySQL yum source. Execute the yum install mysql-server command to install the MySQL server. Use the mysql_secure_installation command to make security settings, such as setting the root user password. Customize the MySQL configuration file as needed. Tune MySQL parameters and optimize databases for performance.
 How to operate distributed training of PyTorch on CentOS
Apr 14, 2025 pm 06:36 PM
How to operate distributed training of PyTorch on CentOS
Apr 14, 2025 pm 06:36 PM
PyTorch distributed training on CentOS system requires the following steps: PyTorch installation: The premise is that Python and pip are installed in CentOS system. Depending on your CUDA version, get the appropriate installation command from the PyTorch official website. For CPU-only training, you can use the following command: pipinstalltorchtorchvisiontorchaudio If you need GPU support, make sure that the corresponding version of CUDA and cuDNN are installed and use the corresponding PyTorch version for installation. Distributed environment configuration: Distributed training usually requires multiple machines or single-machine multiple GPUs. Place
 Detailed explanation of docker principle
Apr 14, 2025 pm 11:57 PM
Detailed explanation of docker principle
Apr 14, 2025 pm 11:57 PM
Docker uses Linux kernel features to provide an efficient and isolated application running environment. Its working principle is as follows: 1. The mirror is used as a read-only template, which contains everything you need to run the application; 2. The Union File System (UnionFS) stacks multiple file systems, only storing the differences, saving space and speeding up; 3. The daemon manages the mirrors and containers, and the client uses them for interaction; 4. Namespaces and cgroups implement container isolation and resource limitations; 5. Multiple network modes support container interconnection. Only by understanding these core concepts can you better utilize Docker.
 How to view GitLab logs under CentOS
Apr 14, 2025 pm 06:18 PM
How to view GitLab logs under CentOS
Apr 14, 2025 pm 06:18 PM
A complete guide to viewing GitLab logs under CentOS system This article will guide you how to view various GitLab logs in CentOS system, including main logs, exception logs, and other related logs. Please note that the log file path may vary depending on the GitLab version and installation method. If the following path does not exist, please check the GitLab installation directory and configuration files. 1. View the main GitLab log Use the following command to view the main log file of the GitLabRails application: Command: sudocat/var/log/gitlab/gitlab-rails/production.log This command will display product
 How is the GPU support for PyTorch on CentOS
Apr 14, 2025 pm 06:48 PM
How is the GPU support for PyTorch on CentOS
Apr 14, 2025 pm 06:48 PM
Enable PyTorch GPU acceleration on CentOS system requires the installation of CUDA, cuDNN and GPU versions of PyTorch. The following steps will guide you through the process: CUDA and cuDNN installation determine CUDA version compatibility: Use the nvidia-smi command to view the CUDA version supported by your NVIDIA graphics card. For example, your MX450 graphics card may support CUDA11.1 or higher. Download and install CUDAToolkit: Visit the official website of NVIDIACUDAToolkit and download and install the corresponding version according to the highest CUDA version supported by your graphics card. Install cuDNN library:



