Example analysis of Huffman tree in java
Huffman tree
1. Basic introduction

2. Several important concepts and examples of Huffman tree
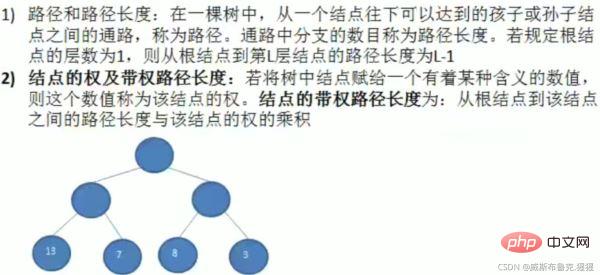
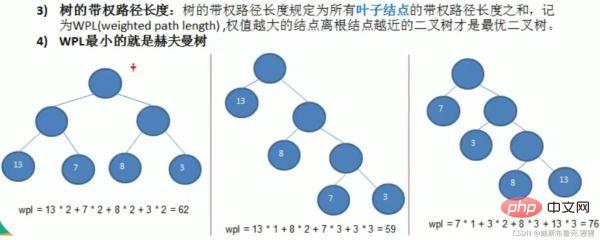
Steps to construct a Huffman tree

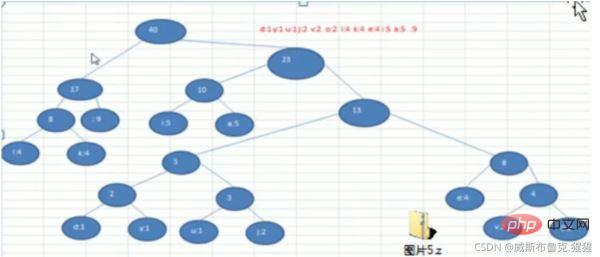
For example: take arr = {1 3 6 7 8 13 29}
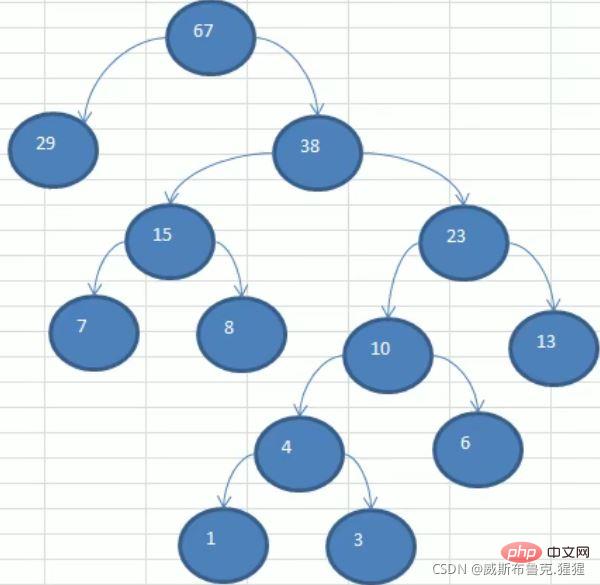
public class HuffmanTree {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] arr = { 13, 7, 8, 3, 29, 6, 1 };
Node root = createHuffmanTree(arr);
preOrder(root);
}
// 编写一个前序遍历的方法
public static void preOrder(Node root) {
if (root != null) {
root.preOrder();
} else {
System.out.println("树是空树,无法遍历~~");
}
}
// 创建赫夫曼树的方法
/**
* @param arr 需要创建成霍夫曼树的数组
* @return 创建好后的霍夫曼树的root节点
*/
public static Node createHuffmanTree(int[] arr) {
// 第一步为了操作方便
// 1.遍历 arr 数组
// 2.将 arr 的每个元素构成一个Node
// 3.将Node 放入到ArrayList中
List<Node> nodes = new ArrayList<Node>();
for (int value : arr) {
nodes.add(new Node(value));
}
while (nodes.size() > 1) {
// 排序从小到大
Collections.sort(nodes);
System.out.println("nodes = " + nodes);
// 取出根节点权值最小的两颗二叉树
//注意:如果是从大到小排列的:就应该取倒数第一个和倒数第二个
// (1) 取出权值最小的节点(二叉树)
Node leftNode = nodes.get(0);
// (2) 取出权值第二小的节点(二叉树)
Node rightNode = nodes.get(1);
// (3) 构建一颗新的二叉树
Node parent = new Node(leftNode.value + rightNode.value);
parent.left = leftNode;
parent.right = rightNode;
// (4) 从ArrayList删除处理过的二叉树
nodes.remove(leftNode);
nodes.remove(rightNode);
// (5) 将parent加入到nodes
nodes.add(parent);
}
// 返回赫夫曼树的root节点
return nodes.get(0);
}
}
//创建节点类
//为了让Node对象支持排序Collections集合排序
//让Node实现Comparable接口
class Node implements Comparable<Node> {
int value;// 节点权值
Node left;// 指向左子节点
Node right;// 指向右子节点
public Node(int value) {
this.value = value;
}
// 写一个前序遍历
public void preOrder() {
System.out.println(this);
if (this.left != null) {
this.left.preOrder();
}
if (this.right != null) {
this.right.preOrder();
}
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Node [value=" + value + "]";
}
@Override
public int compareTo(Node o) {
// 表示从小到大排列
return this.value - o.value;
}
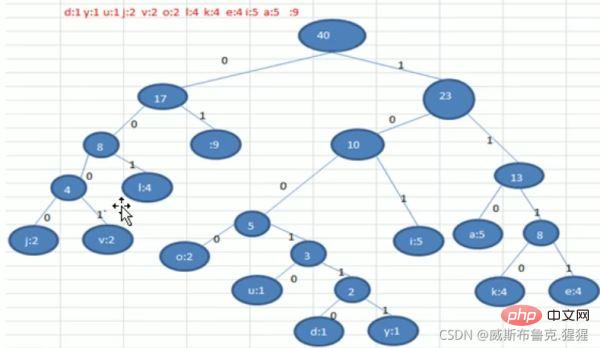
}Huffman coding
1. Basic introduction

2. Principle analysis






The above is the detailed content of Example analysis of Huffman tree in java. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 Square Root in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:26 PM
Square Root in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:26 PM
Guide to Square Root in Java. Here we discuss how Square Root works in Java with example and its code implementation respectively.
 Perfect Number in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:28 PM
Perfect Number in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:28 PM
Guide to Perfect Number in Java. Here we discuss the Definition, How to check Perfect number in Java?, examples with code implementation.
 Random Number Generator in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:27 PM
Random Number Generator in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:27 PM
Guide to Random Number Generator in Java. Here we discuss Functions in Java with examples and two different Generators with ther examples.
 Armstrong Number in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:26 PM
Armstrong Number in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:26 PM
Guide to the Armstrong Number in Java. Here we discuss an introduction to Armstrong's number in java along with some of the code.
 Weka in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:28 PM
Weka in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:28 PM
Guide to Weka in Java. Here we discuss the Introduction, how to use weka java, the type of platform, and advantages with examples.
 Smith Number in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:28 PM
Smith Number in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:28 PM
Guide to Smith Number in Java. Here we discuss the Definition, How to check smith number in Java? example with code implementation.
 Java Spring Interview Questions
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:29 PM
Java Spring Interview Questions
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:29 PM
In this article, we have kept the most asked Java Spring Interview Questions with their detailed answers. So that you can crack the interview.
 Break or return from Java 8 stream forEach?
Feb 07, 2025 pm 12:09 PM
Break or return from Java 8 stream forEach?
Feb 07, 2025 pm 12:09 PM
Java 8 introduces the Stream API, providing a powerful and expressive way to process data collections. However, a common question when using Stream is: How to break or return from a forEach operation? Traditional loops allow for early interruption or return, but Stream's forEach method does not directly support this method. This article will explain the reasons and explore alternative methods for implementing premature termination in Stream processing systems. Further reading: Java Stream API improvements Understand Stream forEach The forEach method is a terminal operation that performs one operation on each element in the Stream. Its design intention is






