 Technology peripherals
Technology peripherals
 AI
AI
 As long as the model is large enough and the samples are large enough, AI can become smarter!
As long as the model is large enough and the samples are large enough, AI can become smarter!
As long as the model is large enough and the samples are large enough, AI can become smarter!
There is no difference in mathematical mechanism between the AI model and the human brain.
As long as the model is large enough and the samples are large enough, AI can become smarter!
The emergence of chatGPT has actually proved this point.
1. The underlying details of AI and the human brain are based on if else statements
logical operations, which are the basic operations that generate intelligence.
The basic logic of the programming language is if else, which divides the code into two branches based on conditional expressions.
On this basis, programmers can write very complex codes and implement various business logics.
The basic logic of the human brain is also if else. The two words if else come from English, and the corresponding Chinese vocabulary is if...else...
When the human brain thinks about problems It’s also such a logical idea, and it’s no different from a computer in this regard.
if else statement, the core of logic
The "if else statement" of the AI model is the activation function!
A computing node of the AI model, we can also call it a "neuron".
It has an input vector X, a weight matrix W, a bias vector b, and an activation function.
The activation function is actually an if else statement, and the linear operation WX b is a conditional expression.
After activation, the code of the AI model is equivalent to running in the if branch, and when not activated, it is equivalent to running in the else branch.
The different activation states of multi-layer neural networks are actually binary encodings of sample information.
Deep learning is also a binary encoding of sample information
The encoding of sample information by the AI model is dynamic and parallel, not the same as the CPU code They are static and serial, but their underlying basis is if else.
It is not difficult to implement if else at the circuit level. It can be implemented with a triode.
2. The human brain is smarter than computers because humans obtain more information.
The human brain is acquiring information from the outside world all the time and updating its own information all the time. "Sample database", but the program code cannot update itself, which is why many people can do it but computers cannot.
The code of the human brain is alive, but the code of the computer is dead.
Of course "dead code" cannot be smarter than "live code", because "live code" can actively find the bugs of "dead code".
According to the continuity of real numbers, as long as the information encoded by "dead code" is countable, then it will always have bug points that cannot be encoded.
This can be mathematically supported by Cantor's three-point set.
No matter how many ternary decimal digits we use to encode real numbers in the interval [0, 1], there is always at least one point that cannot be encoded.
So when two people argue, they can always find points to argue with.
But once the computer code is written, it cannot be updated automatically, so programmers can come up with various ideas. A way to trick the CPU.
For example, Intel's CPU originally required switching task gates when switching processes, but Linux came up with a way to only switch the page directory and RSP register
In the view of Intel CPU , the Linux system has been running the same process, but it is not. This is called process soft switching.
So, as long as the circuit of the CPU is fixed, the information encoded by the CPU will also be fixed.
The information encoded by the CPU is fixed, so the information it cannot encode is unlimited and can be used by programmers.
The reason why programmers can use this information is because the programmer's brain is alive and can dynamically update samples.
3. The emergence of neural network has changed this situation.
Neural network is really a great invention. It realizes dynamic information update on fixed circuits.
The information that all written programs can process is fixed, including CPU circuits and codes of various systems.
But this is not the case with neural networks. Although its code is written, it only needs to update the weight data to change the logical context of the model.
In fact, as long as new samples are continuously input, the AI model can continuously update the weight data using the BP algorithm (gradient descent algorithm) to adapt to new business scenarios.
Updating the AI model does not require modifying the code, but only requires modifying the data, so the same CNN model can recognize different objects if it is trained with different samples.
In this process, both the code of the tensorflow framework and the network structure of the AI model remain unchanged. What changes is the weight data of each node.
Theoretically, as long as an AI model can crawl data through the network, it can become smarter.
Is this fundamentally different from people watching things through a browser (thus becoming smarter)? It seems not.
4, as long as the model is large enough and the samples are large enough, maybe ChatGPT can really challenge the human brain
The human brain has 15 billion neurons, and human eyes and ears are constantly changing Of course, the AI model can also do this by providing it with new data.
Perhaps compared to AI, the advantage of humans is that the "industrial chain" is shorter
The birth of a baby only requires its parents, but the birth of an AI model obviously does not require one or two programs Members can do it.
There are more than tens of thousands of people manufacturing GPUs alone.
The CUDA program on the GPU is not difficult to write, but the industry chain of GPU manufacturing is too long, far inferior to the birth and growth of human beings.
This may be the real disadvantage of AI compared to humans.
The above is the detailed content of As long as the model is large enough and the samples are large enough, AI can become smarter!. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1386
1386
 52
52
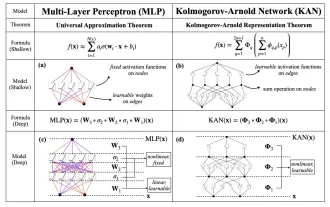 KAN, which replaces MLP, has been extended to convolution by open source projects
Jun 01, 2024 pm 10:03 PM
KAN, which replaces MLP, has been extended to convolution by open source projects
Jun 01, 2024 pm 10:03 PM
Earlier this month, researchers from MIT and other institutions proposed a very promising alternative to MLP - KAN. KAN outperforms MLP in terms of accuracy and interpretability. And it can outperform MLP running with a larger number of parameters with a very small number of parameters. For example, the authors stated that they used KAN to reproduce DeepMind's results with a smaller network and a higher degree of automation. Specifically, DeepMind's MLP has about 300,000 parameters, while KAN only has about 200 parameters. KAN has a strong mathematical foundation like MLP. MLP is based on the universal approximation theorem, while KAN is based on the Kolmogorov-Arnold representation theorem. As shown in the figure below, KAN has
 Comprehensively surpassing DPO: Chen Danqi's team proposed simple preference optimization SimPO, and also refined the strongest 8B open source model
Jun 01, 2024 pm 04:41 PM
Comprehensively surpassing DPO: Chen Danqi's team proposed simple preference optimization SimPO, and also refined the strongest 8B open source model
Jun 01, 2024 pm 04:41 PM
In order to align large language models (LLMs) with human values and intentions, it is critical to learn human feedback to ensure that they are useful, honest, and harmless. In terms of aligning LLM, an effective method is reinforcement learning based on human feedback (RLHF). Although the results of the RLHF method are excellent, there are some optimization challenges involved. This involves training a reward model and then optimizing a policy model to maximize that reward. Recently, some researchers have explored simpler offline algorithms, one of which is direct preference optimization (DPO). DPO learns the policy model directly based on preference data by parameterizing the reward function in RLHF, thus eliminating the need for an explicit reward model. This method is simple and stable
 No OpenAI data required, join the list of large code models! UIUC releases StarCoder-15B-Instruct
Jun 13, 2024 pm 01:59 PM
No OpenAI data required, join the list of large code models! UIUC releases StarCoder-15B-Instruct
Jun 13, 2024 pm 01:59 PM
At the forefront of software technology, UIUC Zhang Lingming's group, together with researchers from the BigCode organization, recently announced the StarCoder2-15B-Instruct large code model. This innovative achievement achieved a significant breakthrough in code generation tasks, successfully surpassing CodeLlama-70B-Instruct and reaching the top of the code generation performance list. The unique feature of StarCoder2-15B-Instruct is its pure self-alignment strategy. The entire training process is open, transparent, and completely autonomous and controllable. The model generates thousands of instructions via StarCoder2-15B in response to fine-tuning the StarCoder-15B base model without relying on expensive manual annotation.
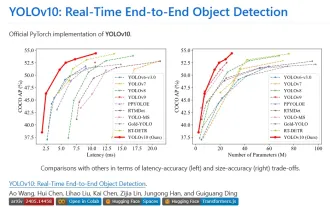 Yolov10: Detailed explanation, deployment and application all in one place!
Jun 07, 2024 pm 12:05 PM
Yolov10: Detailed explanation, deployment and application all in one place!
Jun 07, 2024 pm 12:05 PM
1. Introduction Over the past few years, YOLOs have become the dominant paradigm in the field of real-time object detection due to its effective balance between computational cost and detection performance. Researchers have explored YOLO's architectural design, optimization goals, data expansion strategies, etc., and have made significant progress. At the same time, relying on non-maximum suppression (NMS) for post-processing hinders end-to-end deployment of YOLO and adversely affects inference latency. In YOLOs, the design of various components lacks comprehensive and thorough inspection, resulting in significant computational redundancy and limiting the capabilities of the model. It offers suboptimal efficiency, and relatively large potential for performance improvement. In this work, the goal is to further improve the performance efficiency boundary of YOLO from both post-processing and model architecture. to this end
 Tsinghua University took over and YOLOv10 came out: the performance was greatly improved and it was on the GitHub hot list
Jun 06, 2024 pm 12:20 PM
Tsinghua University took over and YOLOv10 came out: the performance was greatly improved and it was on the GitHub hot list
Jun 06, 2024 pm 12:20 PM
The benchmark YOLO series of target detection systems has once again received a major upgrade. Since the release of YOLOv9 in February this year, the baton of the YOLO (YouOnlyLookOnce) series has been passed to the hands of researchers at Tsinghua University. Last weekend, the news of the launch of YOLOv10 attracted the attention of the AI community. It is considered a breakthrough framework in the field of computer vision and is known for its real-time end-to-end object detection capabilities, continuing the legacy of the YOLO series by providing a powerful solution that combines efficiency and accuracy. Paper address: https://arxiv.org/pdf/2405.14458 Project address: https://github.com/THU-MIG/yo
 Li Feifei reveals the entrepreneurial direction of 'spatial intelligence': visualization turns into insight, seeing becomes understanding, and understanding leads to action
Jun 01, 2024 pm 02:55 PM
Li Feifei reveals the entrepreneurial direction of 'spatial intelligence': visualization turns into insight, seeing becomes understanding, and understanding leads to action
Jun 01, 2024 pm 02:55 PM
After Stanford's Feifei Li started his business, he unveiled the new concept "spatial intelligence" for the first time. This is not only her entrepreneurial direction, but also the "North Star" that guides her. She considers it "the key puzzle piece to solve the artificial intelligence problem." Visualization leads to insight; seeing leads to understanding; understanding leads to action. Based on Li Feifei's 15-minute TED talk, which is fully open to the public, it starts from the origin of life evolution hundreds of millions of years ago, to how humans are not satisfied with what nature has given them and develops artificial intelligence, to how to build spatial intelligence in the next step. Nine years ago, Li Feifei introduced the newly born ImageNet to the world on the same stage - one of the starting points for this round of deep learning explosion. She herself also encouraged netizens: If you watch both videos, you will be able to understand the computer vision of the past 10 years.
 Beating GPT-4o in seconds, beating Llama 3 70B in 22B, Mistral AI opens its first code model
Jun 01, 2024 pm 06:32 PM
Beating GPT-4o in seconds, beating Llama 3 70B in 22B, Mistral AI opens its first code model
Jun 01, 2024 pm 06:32 PM
French AI unicorn MistralAI, which is targeting OpenAI, has made a new move: Codestral, the first large code model, was born. As an open generative AI model designed specifically for code generation tasks, Codestral helps developers write and interact with code by sharing instructions and completion API endpoints. Codestral's proficiency in coding and English allows software developers to design advanced AI applications. The parameter size of Codestral is 22B, it complies with the new MistralAINon-ProductionLicense, and can be used for research and testing purposes, but commercial use is prohibited. Currently, the model is available for download on HuggingFace. download link
 Google Gemini 1.5 technical report: Easily prove Mathematical Olympiad questions, the Flash version is 5 times faster than GPT-4 Turbo
Jun 13, 2024 pm 01:52 PM
Google Gemini 1.5 technical report: Easily prove Mathematical Olympiad questions, the Flash version is 5 times faster than GPT-4 Turbo
Jun 13, 2024 pm 01:52 PM
In February this year, Google launched the multi-modal large model Gemini 1.5, which greatly improved performance and speed through engineering and infrastructure optimization, MoE architecture and other strategies. With longer context, stronger reasoning capabilities, and better handling of cross-modal content. This Friday, Google DeepMind officially released the technical report of Gemini 1.5, which covers the Flash version and other recent upgrades. The document is 153 pages long. Technical report link: https://storage.googleapis.com/deepmind-media/gemini/gemini_v1_5_report.pdf In this report, Google introduces Gemini1



