Java array high-frequency test point example analysis
1. Array theoretical basis
An array is a collection of the same type of data stored in a continuous memory space. The corresponding data under the subscript can be obtained through subscript indexing.
As an example (character array)~
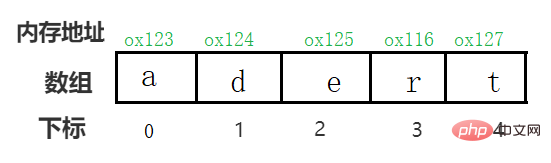
You can see:
1. The subscript of the array starts from 0
2. The addresses of arrays in memory are consecutive
, so when deleting elements, you can only use overwriting.
For example, if you want to delete the element with index 2~, you need to move the elements after 2 to the previous one in order, covering the element to be deleted.
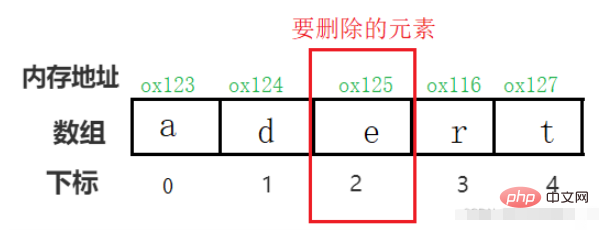
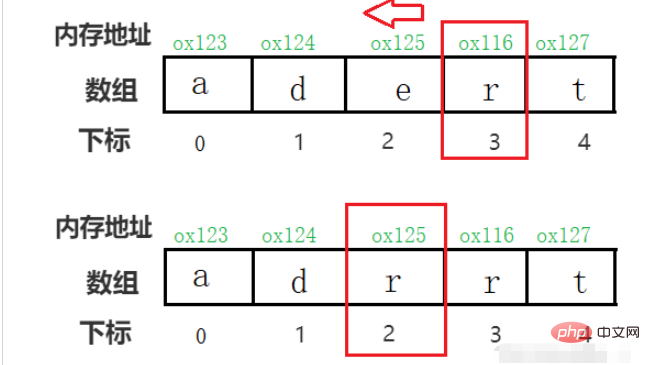
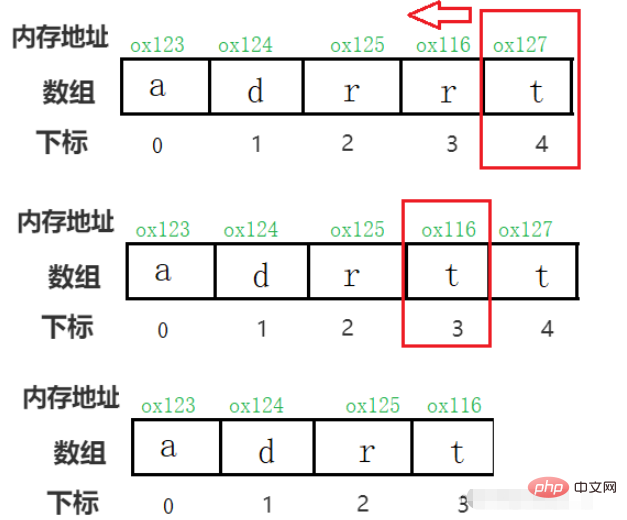
So deleting an element does not release the space of the element, but the space behind it. Move the elements to the front, overwrite the elements to be deleted, and then subtract 1 from the length of the array to get a seemingly new array.
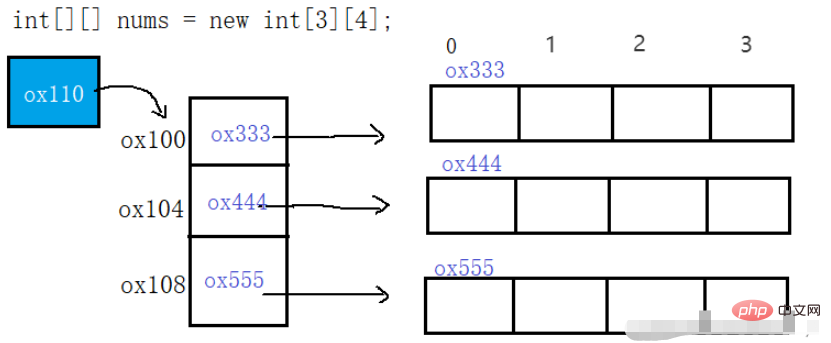
In java, the storage method of two-dimensional array is as follows:
2. Common test points
1.Binary search
Likou question link: Binary search
The premise of this question is an ordered array, because once there are repeated elements, the element subscript returned by the binary search method may not be unique. These are all using Prerequisites for dichotomy.
The idea of binary search is:
Under the premise that the array is ordered (assuming ascending order), if the value in the middle of the array is greater than the value to be found, then the element to be found cannot be in the second half Part, because the values in the second half are greater than the middle value, so through the first comparison, the range can be reduced by half. The same applies later, that is, the time complexity is reduced to O(logN), and the efficiency is greatly improved. When the question When the time complexity of finding elements is required to be O(logN), first think about whether it can be divided into two parts?
class Solution {
public int search(int[] nums, int target) {
// 避免当 target 小于nums[0] nums[nums.length - 1]时多次循环运算
if (target < nums[0] || target > nums[nums.length - 1]) {
return -1;
}
int left = 0, right = nums.length - 1;
while (left <= right) {
int mid = left + ((right - left) >> 1);
if (nums[mid] == target)
return mid;
else if (nums[mid] < target)
left = mid + 1;
else if (nums[mid] > target)
right = mid - 1;
}
return -1;
}
}2. Remove elements
Some students may have said that you can just delete the redundant elements? But you must know that the elements of the array are continuous in the memory address. You cannot delete an element in the array individually, you can only overwrite it.
For example: I give you an array and a val value, and you are required to delete the elements in the array that are equal to the val value. How to do this?
Idea 1: Brutal method
We can use two for loops. When traversing to an element equal to the val value, move the entire following element forward to cover the element to be deleted. element, but this approach obviously has too high time complexity.
class Solution {
public int removeElement(int[] nums, int val) {
int size = nums.length;
for (int i = 0; i < size;i++ ) {
if (nums[i] == val) { // 发现需要移除的元素,就将数组后面集体向前移动一位
for (int j = i + 1; j < size; j++) {
nums[j - 1] = nums[j];
}
i--; // 因为下标i以后的数值都向前移动了一位,所以i也向前移动一位
size--;
}
}
return size;
}
}Idea 2: Double pointer method
Set up a fast and slow pointer respectively, slow fast, and the two move together. When the slow pointer encounters the element to be deleted, it stops and waits for it to be deleted. Delete (overwrite); when the fast pointer reaches the element to be left, assign the element of the fast pointer to the slow pointer, and then the two pointers move backward at the same time until the fast pointer traverses the entire array.
It can be understood like this: define the new length of the array newLength, starting from 0, define a fast pointer to traverse the array fast, when fast reaches the element to be left, it means that the element should be added to the new array (that is, it is added to the newLength subscript, which is equivalent to the part of the array before newLength being regarded as the new array to be returned, which is equivalent to inserting elements into this new array).
class Solution {
public int removeElement(int[] nums, int val) {
int fast = 0;// 定义一个快指针遍历数组
int newLength = 0;// 定义新的数组长度
while(fast < nums.length){
if(nums[fast] != val){
nums[newLength++] = nums[fast];
}
fast++;
}
return newLength;
}
}Recommended questions
1. Delete duplicates in the sorted array
2. Move zeros
3. Compare characters containing backspaces String
4. The square of an ordered array
Many other common array test points are based on these two points. They are nothing more than adding, deleting, modifying, and checking the array, and mastering the search and deletion of the array. , you can start answering questions.
The above is the detailed content of Java array high-frequency test point example analysis. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 Square Root in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:26 PM
Square Root in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:26 PM
Guide to Square Root in Java. Here we discuss how Square Root works in Java with example and its code implementation respectively.
 Perfect Number in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:28 PM
Perfect Number in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:28 PM
Guide to Perfect Number in Java. Here we discuss the Definition, How to check Perfect number in Java?, examples with code implementation.
 Random Number Generator in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:27 PM
Random Number Generator in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:27 PM
Guide to Random Number Generator in Java. Here we discuss Functions in Java with examples and two different Generators with ther examples.
 Armstrong Number in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:26 PM
Armstrong Number in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:26 PM
Guide to the Armstrong Number in Java. Here we discuss an introduction to Armstrong's number in java along with some of the code.
 Weka in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:28 PM
Weka in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:28 PM
Guide to Weka in Java. Here we discuss the Introduction, how to use weka java, the type of platform, and advantages with examples.
 Smith Number in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:28 PM
Smith Number in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:28 PM
Guide to Smith Number in Java. Here we discuss the Definition, How to check smith number in Java? example with code implementation.
 Java Spring Interview Questions
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:29 PM
Java Spring Interview Questions
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:29 PM
In this article, we have kept the most asked Java Spring Interview Questions with their detailed answers. So that you can crack the interview.
 Break or return from Java 8 stream forEach?
Feb 07, 2025 pm 12:09 PM
Break or return from Java 8 stream forEach?
Feb 07, 2025 pm 12:09 PM
Java 8 introduces the Stream API, providing a powerful and expressive way to process data collections. However, a common question when using Stream is: How to break or return from a forEach operation? Traditional loops allow for early interruption or return, but Stream's forEach method does not directly support this method. This article will explain the reasons and explore alternative methods for implementing premature termination in Stream processing systems. Further reading: Java Stream API improvements Understand Stream forEach The forEach method is a terminal operation that performs one operation on each element in the Stream. Its design intention is






