What is the method for Java to automatically generate trend comparison data?
Background
Pairwise trend comparison between data is a very common application scenario in data analysis applications, as shown below:
| Mock test Batch | Class | Student | Chinese | Mathematics | English |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Class Three Years | 张小明 | 130 | 145 | 133 | |
| 三级一 | 王二小 | 128 | 138 | 140 | |
| Class Three Three Years | Xie Chunhua | 136 | 142 | 139 | |
| Three-Year Class | Zhang Xiaoming | 132 | 140 | 128 | |
| Class Three Three Years | 王二小 | 125 | 146 | 142 | |
| Class Three Three Years | Xie Chunhua | 138 | 143 | 140 | |
| Three-Year Class | Zhang Xiaoming | 135 | 138 | 120 | |
| 三级一级 | 王二小 | 123 | 145 | 138 | |
| Class Three Three Years | Xie Chunhua | 136 | 140 | 142 |
| Class | Student | Chinese | Mathematics | English | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Three-Year Class | Zhang Xiaoming | -2 | 5 | 5 | |
| 三级一级 | 王二小 | 3 | -8 | #-2 | |
| Class Three Three Years | Xie Chunhua | -2 | -1 | -1 | ##Comparison between 202301 and 202212 |
| 张小明 | -3 | 2 | 8 | Comparison between 202301 and 202212 | |
| 王二小 | 2 | 1 | 4 | 202301 and 202212 Comparison | |
| Xie Chunhua | 2 | 3 | -2 |
public class TrendCompare {
/**
* 主体的字段列表(如三年一班的张小明,那么主体字段列表为 班级 + 学生姓名)
*/
private String[] subjectFields;
/**
* 在某个字段的(介词) 如三年一班张晓明在不同考试批次的成绩对比结果
*/
private String atField;
/**
* 参与趋势比较的字段集合
*/
private String[] compareFields;
/**
* 赋值映射集合:给结果数据中指定的key设置指定的值
*/
private Map<String, String> assignValMap;
public String[] subjectFields() {
return this.subjectFields;
}
public TrendCompare subjectFields(String... fields) {
this.subjectFields = fields;
return this;
}
public String atField() {
return this.atField;
}
public TrendCompare atField(String field) {
this.atField = field;
return this;
}
public String[] compareFields() {
return this.compareFields;
}
public TrendCompare compareFields(String... fields) {
this.compareFields = fields;
return this;
}
/**
* 赋值操作
*
* @param field
* @param valueEL 值表达式
* @return
*/
public TrendCompare assignVal(String field, String valueEL) {
if (assignValMap == null) {
assignValMap = new HashMap<>();
}
assignValMap.put(field, valueEL);
return this;
}
public Map<String, String> assignValMap() {
return this.assignValMap;
}
}Copy after login
This class defines the following attributes:The subject's Field listpublic class TrendCompare {
/**
* 主体的字段列表(如三年一班的张小明,那么主体字段列表为 班级 + 学生姓名)
*/
private String[] subjectFields;
/**
* 在某个字段的(介词) 如三年一班张晓明在不同考试批次的成绩对比结果
*/
private String atField;
/**
* 参与趋势比较的字段集合
*/
private String[] compareFields;
/**
* 赋值映射集合:给结果数据中指定的key设置指定的值
*/
private Map<String, String> assignValMap;
public String[] subjectFields() {
return this.subjectFields;
}
public TrendCompare subjectFields(String... fields) {
this.subjectFields = fields;
return this;
}
public String atField() {
return this.atField;
}
public TrendCompare atField(String field) {
this.atField = field;
return this;
}
public String[] compareFields() {
return this.compareFields;
}
public TrendCompare compareFields(String... fields) {
this.compareFields = fields;
return this;
}
/**
* 赋值操作
*
* @param field
* @param valueEL 值表达式
* @return
*/
public TrendCompare assignVal(String field, String valueEL) {
if (assignValMap == null) {
assignValMap = new HashMap<>();
}
assignValMap.put(field, valueEL);
return this;
}
public Map<String, String> assignValMap() {
return this.assignValMap;
}
}- Preposition field
- Compared field list
- For example: The progress and decline of each student
examination batcheseach subjectThe results of mapping the above requirements to the defined class are as follows :
Subject field list (- Class, student
- )
Preposition field (
Exam batch - )
Comparison field list (various subjects:
Chinese, mathematics, English - )
Trend ratio For the execution class
public static <T> List<T> compare(List<T> dataList, TrendCompare trendCompare) {
Map<String, List<T>> groupMap = group(dataList, null, trendCompare.subjectFields());
List<T> resultList = new ArrayList<>();
for (List<T> groupDataList : groupMap.values()) {
List<T> diffValueList = new ArrayList<>();
int size = groupDataList.size();
if (size > 1) {
for (int i = 0; i < size - 1; i++) {
//数据之间两两比较 diffValue = minuend - subtrahend
T minuend = groupDataList.get(i);
T subtrahend = groupDataList.get(i + 1);
T diffValue = minus(trendCompare.compareFields(), minuend, subtrahend);
//设置主体信息
if (trendCompare.subjectFields() != null) {
for (String subjectField : trendCompare.subjectFields()) {
setFieldValue(diffValue, subjectField, getFieldValue(minuend, subjectField));
}
}
//设置介词字段信息
String atField = trendCompare.atField();
if (StringUtils.isNotEmpty(atField)) {
setFieldValue(diffValue, atField, getFieldValue(minuend, atField) + "与" + getFieldValue(subtrahend, atField) + "对比增减");
}
diffValueList.add(diffValue);
}
}
if (diffValueList.size() > 0) {
T firstData = groupDataList.get(0);
Map<String, Object> valMap = new HashMap<>();
//指定的赋值集合进行赋值
if (trendCompare.assignValMap() != null) {
for (Map.Entry<String, String> stringStringEntry : trendCompare.assignValMap().entrySet()) {
String field = stringStringEntry.getKey();
if (!StringUtils.equalsAny(field, trendCompare.compareFields())) {
String valueEL = stringStringEntry.getValue();
valMap.put(field, executeSpEL(valueEL, firstData));
}
}
}
for (Map.Entry<String, Object> entry : valMap.entrySet()) {
for (T diffValue : diffValueList) {
setFieldValue(diffValue, entry.getKey(), entry.getValue());
}
}
}
resultList.addAll(diffValueList);
}
return resultList;
}Copy after login
As you can see, this method requires the incomingdata collection public static <T> List<T> compare(List<T> dataList, TrendCompare trendCompare) {
Map<String, List<T>> groupMap = group(dataList, null, trendCompare.subjectFields());
List<T> resultList = new ArrayList<>();
for (List<T> groupDataList : groupMap.values()) {
List<T> diffValueList = new ArrayList<>();
int size = groupDataList.size();
if (size > 1) {
for (int i = 0; i < size - 1; i++) {
//数据之间两两比较 diffValue = minuend - subtrahend
T minuend = groupDataList.get(i);
T subtrahend = groupDataList.get(i + 1);
T diffValue = minus(trendCompare.compareFields(), minuend, subtrahend);
//设置主体信息
if (trendCompare.subjectFields() != null) {
for (String subjectField : trendCompare.subjectFields()) {
setFieldValue(diffValue, subjectField, getFieldValue(minuend, subjectField));
}
}
//设置介词字段信息
String atField = trendCompare.atField();
if (StringUtils.isNotEmpty(atField)) {
setFieldValue(diffValue, atField, getFieldValue(minuend, atField) + "与" + getFieldValue(subtrahend, atField) + "对比增减");
}
diffValueList.add(diffValue);
}
}
if (diffValueList.size() > 0) {
T firstData = groupDataList.get(0);
Map<String, Object> valMap = new HashMap<>();
//指定的赋值集合进行赋值
if (trendCompare.assignValMap() != null) {
for (Map.Entry<String, String> stringStringEntry : trendCompare.assignValMap().entrySet()) {
String field = stringStringEntry.getKey();
if (!StringUtils.equalsAny(field, trendCompare.compareFields())) {
String valueEL = stringStringEntry.getValue();
valMap.put(field, executeSpEL(valueEL, firstData));
}
}
}
for (Map.Entry<String, Object> entry : valMap.entrySet()) {
for (T diffValue : diffValueList) {
setFieldValue(diffValue, entry.getKey(), entry.getValue());
}
}
}
resultList.addAll(diffValueList);
}
return resultList;
}- Trend comparison defines
- two parameters, and finally returns the result set after trend comparison.
- After grouping, within the group The data is compared pairwise and the comparison result is finally returned.
- Use case
Define a student class: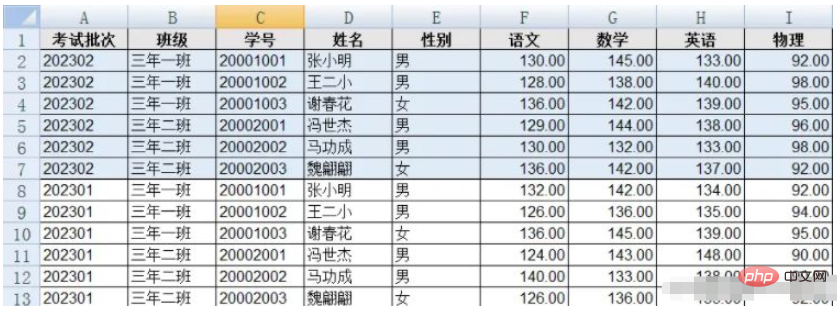
public class Student {
private String batch;
private String banji;
private String studentNo;
private String name;
private String sex;
private Double yuwen;
private Double math;
private Double english;
private Double physics;
//extra
private String maxScoreName1;
public Student(String batch, String banji, String studentNo, String name, String sex, Double yuwen, Double math, Double english, Double physics) {
this.batch = batch;
this.banji = banji;
this.studentNo = studentNo;
this.name = name;
this.sex = sex;
this.yuwen = yuwen;
this.math = math;
this.english = english;
this.physics = physics;
}
}public List<Student> getDataList() {
List<Student> dataList = new ArrayList<>();
dataList.add(new Student("202302", "三年一班", "20001001", "张小明", "男", 130.0, 145.0, 133.0, 92.0));
dataList.add(new Student("202302", "三年一班", "20001002", "王二小", "男", 128.0, 138.0, 140.0, 98.0));
dataList.add(new Student("202302", "三年一班", "20001003", "谢春花", "女", 136.0, 142.0, 139.0, 95.0));
dataList.add(new Student("202302", "三年二班", "20002001", "冯世杰", "男", 129.0, 144.0, 138.0, 96.0));
dataList.add(new Student("202302", "三年二班", "20002002", "马功成", "男", 130.0, 132.0, 133.0, 98.0));
dataList.add(new Student("202302", "三年二班", "20002003", "魏翩翩", "女", 136.0, 142.0, 137.0, 92.0));
dataList.add(new Student("202301", "三年一班", "20001001", "张小明", "男", 132.0, 142.0, 134.0, 92.0));
dataList.add(new Student("202301", "三年一班", "20001002", "王二小", "男", 126.0, 136.0, 135.0, 94.0));
dataList.add(new Student("202301", "三年一班", "20001003", "谢春花", "女", 136.0, 145.0, 139.0, 95.0));
dataList.add(new Student("202301", "三年二班", "20002001", "冯世杰", "男", 124.0, 143.0, 148.0, 90.0));
dataList.add(new Student("202301", "三年二班", "20002002", "马功成", "男", 140.0, 133.0, 138.0, 90.0));
dataList.add(new Student("202301", "三年二班", "20002003", "魏翩翩", "女", 126.0, 136.0, 135.0, 92.0));
return dataList;
}List<Student> dataList = getDataList();
TrendCompare trendCompare = new TrendCompare()
.subjectFields("banji", "name")
.atField("batch")
.compareFields("yuwen", "math", "english")
//.assignVal("batch", "'环比增减'")
;
List<Student> resultList = DataProcessUtil.compare(dataList, trendCompare);
for (Student result : resultList) {
System.out.println(JSON.toJSONString(result));
}{"banji":"三年一班","batch":"202302与202301对比增减","english":-1.0,"math":3.0,"name":"张小明","yuwen":-2.0}
{"banji":"三年一班","batch":"202302与202301对比增减","english":5.0,"math":2.0,"name":"王二小","yuwen":2.0}
{"banji":"三年一班","batch":"202302与202301对比增减","english":0.0,"math":-3.0,"name":"谢春花","yuwen":0.0}
{"banji":"三年二班","batch":"202302与202301对比增减","english":-10.0,"math":1.0,"name":"冯世杰","yuwen":5.0}
{"banji":"三年二班","batch":"202302与202301对比增减","english":-5.0,"math":-1.0,"name":"马功成","yuwen":-10.0}
{"banji":"三年二班","batch":"202302与202301对比增减","english":2.0,"math":6.0,"name":"魏翩翩","yuwen":10.0}The above is the detailed content of What is the method for Java to automatically generate trend comparison data?. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 Square Root in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:26 PM
Square Root in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:26 PM
Guide to Square Root in Java. Here we discuss how Square Root works in Java with example and its code implementation respectively.
 Perfect Number in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:28 PM
Perfect Number in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:28 PM
Guide to Perfect Number in Java. Here we discuss the Definition, How to check Perfect number in Java?, examples with code implementation.
 Random Number Generator in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:27 PM
Random Number Generator in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:27 PM
Guide to Random Number Generator in Java. Here we discuss Functions in Java with examples and two different Generators with ther examples.
 Weka in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:28 PM
Weka in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:28 PM
Guide to Weka in Java. Here we discuss the Introduction, how to use weka java, the type of platform, and advantages with examples.
 Armstrong Number in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:26 PM
Armstrong Number in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:26 PM
Guide to the Armstrong Number in Java. Here we discuss an introduction to Armstrong's number in java along with some of the code.
 Smith Number in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:28 PM
Smith Number in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:28 PM
Guide to Smith Number in Java. Here we discuss the Definition, How to check smith number in Java? example with code implementation.
 Java Spring Interview Questions
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:29 PM
Java Spring Interview Questions
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:29 PM
In this article, we have kept the most asked Java Spring Interview Questions with their detailed answers. So that you can crack the interview.
 Break or return from Java 8 stream forEach?
Feb 07, 2025 pm 12:09 PM
Break or return from Java 8 stream forEach?
Feb 07, 2025 pm 12:09 PM
Java 8 introduces the Stream API, providing a powerful and expressive way to process data collections. However, a common question when using Stream is: How to break or return from a forEach operation? Traditional loops allow for early interruption or return, but Stream's forEach method does not directly support this method. This article will explain the reasons and explore alternative methods for implementing premature termination in Stream processing systems. Further reading: Java Stream API improvements Understand Stream forEach The forEach method is a terminal operation that performs one operation on each element in the Stream. Its design intention is






