What are the practical operations of Python?
1)映射代理(不可变字典)
映射代理是创建后无法更改的字典。如果我们不希望用户能够更改我们的值,就可以使用它。
from types import MappingProxyType
mp = MappingProxyType({'apple':4, 'orange':5})
print(mp)
# {'apple': 4, 'orange': 5}如果我们尝试更改映射代理中的内容,就会出现错误。
from types import MappingProxyType
mp = MappingProxyType({'apple':4, 'orange':5})
print(mp)
'''
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "some/path/a.py", line 4, in <module>
mp['apple'] = 10
~~^^^^^^^^^
TypeError: 'mappingproxy' object does not support item assignment
'''2) dict 对于类和对象是不同的
class Dog:
def __init__(self, name, age):
self.name = name
self.age = age
rocky = Dog('rocky', 5)
print(type(rocky.__dict__)) # <class 'dict'>
print(rocky.__dict__) # {'name': 'rocky', 'age': 5}
print(type(Dog.__dict__)) # <class 'mappingproxy'>
print(Dog.__dict__)
# {'__module__': '__main__',
# '__init__': <function Dog.__init__ at 0x108f587c0>,
# '__dict__': <attribute '__dict__' of 'Dog' objects>,
# '__weakref__': <attribute '__weakref__' of 'Dog' objects>,
# '__doc__': None}对象的 dict 属性是普通字典,而类的 dict 属性是映射代理,它们本质上是不可变字典(无法更改)。
3) any() 和 all()
any([True, False, False]) # True any([False, False, False]) # False all([True, False, False]) # False all([True, True, True]) # True
any() 和 all() 函数都接受可迭代对象(例如列表)。
any() 如果至少有一个元素为 True,则返回 True。
all() 只有当所有元素都为 True 时才返回 True。
4) divmod()
内置的divmod()函数可以同时执行//和%运算符。
quotient, remainder = divmod(27, 10) print(quotient) # 2 print(remainder) # 7
这里,27 // 10 的值为2,而 27 % 10 的值为7。因此,返回元组2,7。
5) 使用格式化字符串轻松检查变量
name = 'rocky'
age = 5
string = f'{name=} {age=}'
print(string)
# name='rocky' age=5在格式化字符串中,我们可以在变量后面添加 = 以使用 var_name=var_value 的语法打印它。
6) 我们可以将浮点数转换为比率
print(float.as_integer_ratio(0.5)) # (1, 2) print(float.as_integer_ratio(0.25)) # (1, 4) print(float.as_integer_ratio(1.5)) # (3, 2)
内置的 float.as_integer_ratio() 函数允许我们将浮点数转换为表示分数的元组。但有时它会表现得很奇怪。
print(float.as_integer_ratio(0.1)) # (3602879701896397, 36028797018963968) print(float.as_integer_ratio(0.2)) # (3602879701896397, 18014398509481984)
7) 用globals()和locals()显示现有的全局/本地变量
x = 1
print(globals())
# {'__name__': '__main__', '__doc__': None, ..., 'x': 1}内置的 globals() 函数返回一个包含所有全局变量及其值的字典。
def test():
x = 1
y = 2
print(locals())
test()
# {'x': 1, 'y': 2}内置函数 locals() 返回一个包含所有局部变量及其值的字典。
8) import() 函数
import numpy as np import pandas as pd
^ 导入模块的常规方式。
np = __import__('numpy') pd = __import__('pandas')
^ 这与上面的代码块执行相同的操作。
9) Python中的无限值
a = float('inf') b = float('-inf')
^ 我们可以定义正无穷和负无穷。 正无穷大于所有其他数字,而负无穷小于所有其他数字。
10) 我们可以使用 ‘pprint’ 来漂亮地打印东西
from pprint import pprint
d = {"A":{"apple":1, "orange":2, "pear":3},
"B":{"apple":4, "orange":5, "pear":6},
"C":{"apple":7, "orange":8, "pear":9}}
pprint(d)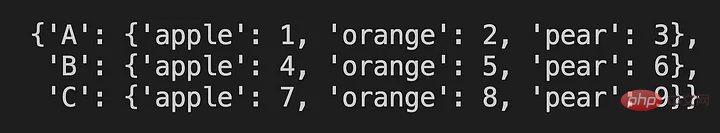
11) 我们可以在Python中打印彩色输出
我们需要先安装colorama。
from colorama import Fore print(Fore.RED + "hello world") print(Fore.BLUE + "hello world") print(Fore.GREEN + "hello world")
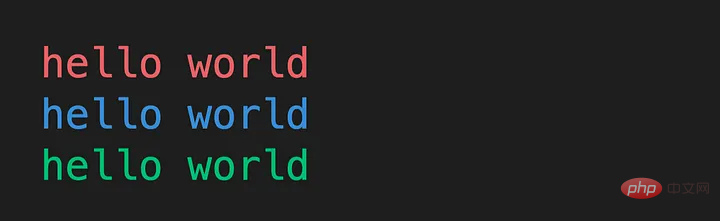
12) 创建字典的更快方法
d1 = {'apple':'pie', 'orange':'juice', 'pear':'cake'}^ 正常的方式
d2 = dict(apple='pie', orange='juice', pear='cake')
^更快的方法。这与上面的代码块完全相同,但我们输入较少的引号。
13) 我们可以在Python中取消打印的内容
CURSOR_UP = '\033[1A' CLEAR = '\x1b[2K' print('apple') print('orange') print('pear') print((CURSOR_UP + CLEAR)*2, end='') # this unprints 2 lines print('pineapple')

14) 对象中的私有变量并不是真正的私有
class Dog:
def __init__(self, name):
self.__name = name
@property
def name(self):
return self.__name这里,self.__name变量应该是私有的。我们不应该能够从类外部访问它。但实际上我们可以。
rocky = Dog('rocky')
print(rocky.__dict__) # {'_Dog__name': 'rocky'}我们可以使用 dict 属性来访问或编辑这些属性。
15) 我们可以使用’type()'创建类
classname = type(name, bases, dict)
name 是一个字符串,代表类的名称
bases 是包含类父类的元组
dict 是包含属性和方法的字典
class Dog:
def __init__(self, name, age):
self.name = name
self.age = age
def bark(self):
print(f'Dog({self.name}, {self.age})')^ 以正常方式创建一个 Dog 类
def __init__(self, name, age):
self.name = name
self.age = age
def bark(self):
print(f'Dog({self.name}, {self.age})')
Dog = type('Dog', (), {'__init__':__init__, 'bark':bark})^ 使用 type() 创建与上面完全相同的 Dog 类
The above is the detailed content of What are the practical operations of Python?. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 How to efficiently integrate Node.js or Python services under LAMP architecture?
Apr 01, 2025 pm 02:48 PM
How to efficiently integrate Node.js or Python services under LAMP architecture?
Apr 01, 2025 pm 02:48 PM
Many website developers face the problem of integrating Node.js or Python services under the LAMP architecture: the existing LAMP (Linux Apache MySQL PHP) architecture website needs...
 How to solve the permissions problem encountered when viewing Python version in Linux terminal?
Apr 01, 2025 pm 05:09 PM
How to solve the permissions problem encountered when viewing Python version in Linux terminal?
Apr 01, 2025 pm 05:09 PM
Solution to permission issues when viewing Python version in Linux terminal When you try to view Python version in Linux terminal, enter python...
 What is the reason why pipeline persistent storage files cannot be written when using Scapy crawler?
Apr 01, 2025 pm 04:03 PM
What is the reason why pipeline persistent storage files cannot be written when using Scapy crawler?
Apr 01, 2025 pm 04:03 PM
When using Scapy crawler, the reason why pipeline persistent storage files cannot be written? Discussion When learning to use Scapy crawler for data crawler, you often encounter a...
 What is the reason why the Python process pool handles concurrent TCP requests and causes the client to get stuck?
Apr 01, 2025 pm 04:09 PM
What is the reason why the Python process pool handles concurrent TCP requests and causes the client to get stuck?
Apr 01, 2025 pm 04:09 PM
Python process pool handles concurrent TCP requests that cause client to get stuck. When using Python for network programming, it is crucial to efficiently handle concurrent TCP requests. ...
 How to view the original functions encapsulated internally by Python functools.partial object?
Apr 01, 2025 pm 04:15 PM
How to view the original functions encapsulated internally by Python functools.partial object?
Apr 01, 2025 pm 04:15 PM
Deeply explore the viewing method of Python functools.partial object in functools.partial using Python...
 Python Cross-platform Desktop Application Development: Which GUI Library is the best for you?
Apr 01, 2025 pm 05:24 PM
Python Cross-platform Desktop Application Development: Which GUI Library is the best for you?
Apr 01, 2025 pm 05:24 PM
Choice of Python Cross-platform desktop application development library Many Python developers want to develop desktop applications that can run on both Windows and Linux systems...
 Python hourglass graph drawing: How to avoid variable undefined errors?
Apr 01, 2025 pm 06:27 PM
Python hourglass graph drawing: How to avoid variable undefined errors?
Apr 01, 2025 pm 06:27 PM
Getting started with Python: Hourglass Graphic Drawing and Input Verification This article will solve the variable definition problem encountered by a Python novice in the hourglass Graphic Drawing Program. Code...
 Do Google and AWS provide public PyPI image sources?
Apr 01, 2025 pm 05:15 PM
Do Google and AWS provide public PyPI image sources?
Apr 01, 2025 pm 05:15 PM
Many developers rely on PyPI (PythonPackageIndex)...






