How to implement Java backend login function
1. Login requirements analysis
Page prototype
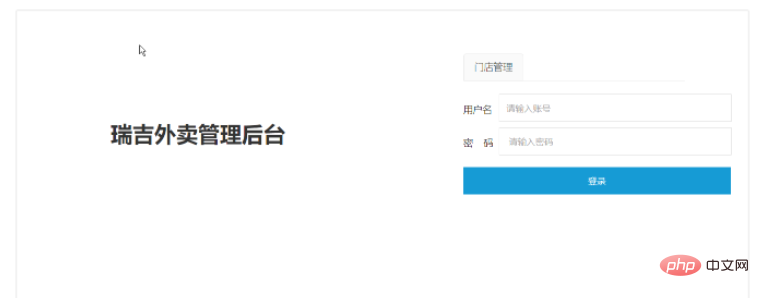
1. Login page display: project path (\resources\backend\page\login\login .html)
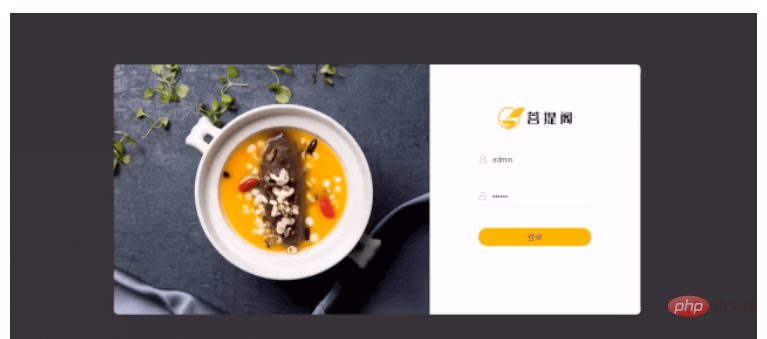
# Employees click the login button to log in to the back-end management platform. Login is not allowed unless the login is correct.
Login processing logic
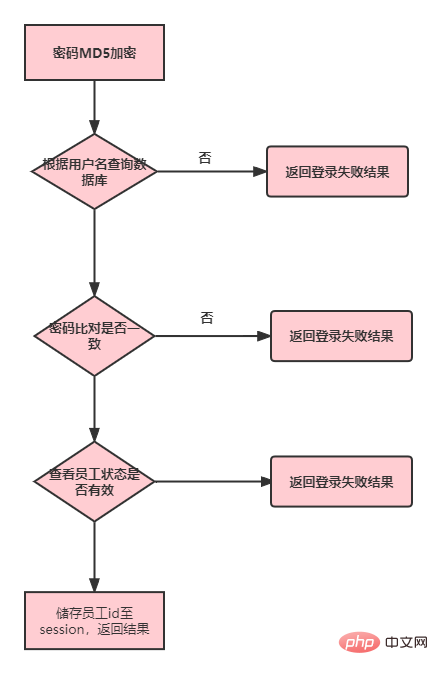
Encrypt the password submitted on the page with MD5
Check the database based on the user name (no result returned)
Compare the password (result returned if the password is incorrect)
Query employee status, employee Login is not allowed when the status is disabled
The login is successful, written to the session, and the result is returned.
2. Configure return general result class
package com.itheima.reggie.common;
import lombok.Data;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
/**
* 返回通用类
* @author jekong
* @date 2022/4/22
*/
@Data
public class R<T> {
/** 编码:1成功,0和其它数字为失败*/
private Integer code;
/** 信息返回*/
private String msg;
/** 信息返回数据*/
private T data;
/** 动态数据*/
private Map map = new HashMap();
public static <T> R<T> success(T object) {
R<T> r = new R<T>();
r.data = object;
r.code = 1;
return r;
}
public static <T> R<T> error(String msg) {
R r = new R();
r.msg = msg;
r.code = 0;
return r;
}
public R<T> add(String key, Object value) {
this.map.put(key, value);
return this;
}
}3. Login request API
| Description | Value |
| Request URL | /employee/login |
| Request data | { "username": "admin", "password": "123456" } |
| Return data | { "code ": 0, "msg": "Login successful", "data": null, "map": {} } |
4. Create entity class and implement login logic
entity: Create entity class
Create Employee.java (employee object)
package com.itheima.reggie.entity;
import com.baomidou.mybatisplus.annotation.FieldFill;
import com.baomidou.mybatisplus.annotation.TableField;
import lombok.Data;
import java.io.Serializable;
import java.time.LocalDateTime;
/**
* 员工实体类
* @author jektong
* @date 2022/4/21
*/
@Data
public class Employee implements Serializable {
/** 序列号*/
private static final long serialVersionUID = 1L;
/**唯一主键*/
private Long id;
/**用户名*/
private String username;
/**姓名*/
private String name;
/**密码*/
private String password;
/**电话*/
private String phone;
/**性别*/
private String sex;
/**身份证号码*/
private String idNumber;
/**状态*/
private Integer status;
/**创建时间*/
private LocalDateTime createTime;
/**更新时间*/
private LocalDateTime updateTime;
/**添加用户时使用*/
@TableField(fill = FieldFill.INSERT)
private Long createUser;
/**更新用户时使用*/
@TableField(fill = FieldFill.INSERT_UPDATE)
private Long updateUser;
}mapper database interaction layer
package com.itheima.reggie.mapper;
import com.baomidou.mybatisplus.core.mapper.BaseMapper;
import com.itheima.reggie.entity.Employee;
import org.apache.ibatis.annotations.Mapper;
/**
* EmployeeMapper
* @author jektong
* @date 2022/4/21
*/
@Mapper
public interface EmployeeMapper extends BaseMapper<Employee> {
}service business layer interface
package com.itheima.reggie.service;
import com.baomidou.mybatisplus.extension.service.IService;
import com.itheima.reggie.entity.Employee;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
/**
* @author jektong
* @date 2022/4/21
*/
public interface EmployeeService extends IService<Employee> {
}Business layer implementation class
package com.itheima.reggie.service.impl;
import com.baomidou.mybatisplus.extension.service.impl.ServiceImpl;
import com.itheima.reggie.entity.Employee;
import com.itheima.reggie.mapper.EmployeeMapper;
import com.itheima.reggie.service.EmployeeService;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
/**
* @author jektong
* @date 2022/4/21
*/
@Service
public class EmployeeServiceImpl extends ServiceImpl<EmployeeMapper, Employee> implements EmployeeService {
}controller control layer
package com.itheima.reggie.controller;
import com.baomidou.mybatisplus.core.conditions.query.LambdaQueryWrapper;
import com.itheima.reggie.common.CommonsConst;
import com.itheima.reggie.common.R;
import com.itheima.reggie.entity.Employee;
import com.itheima.reggie.service.EmployeeService;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.springframework.util.DigestUtils;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.PostMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestBody;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
import javax.annotation.Resource;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
/**
* 员工控制类
*
* @author tongbing
* @date 2022/4/21
*/
@Slf4j
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/employee")
public class EmployeeController {
@Resource
private EmployeeService employeeService = null;
/**
* 登录请求处理
* TODO 后续改进将业务处理的代码放入业务层,这里只做数据请求与返回
* @param request
* @param employee
* @return
*/
@PostMapping("/login")
public R<Employee> login(HttpServletRequest request,
@RequestBody Employee employee) {
// 将页面提交的密码进行MD5加密
String password = employee.getPassword();
password = DigestUtils.md5DigestAsHex(password.getBytes());
// 根据用户名查数据库
LambdaQueryWrapper<Employee> queryWrapper = new LambdaQueryWrapper<Employee>();
queryWrapper.eq(Employee::getUsername, employee.getUsername());
Employee emp = employeeService.getOne(queryWrapper);
// 查不到返回登录失败结果
if(emp == null){
return R.error(CommonsConst.LOGIN_FAIL);
}
// 比对密码
if(!emp.getPassword().equals(password)){
return R.error(CommonsConst.LOGIN_FAIL);
}
// 查看员工状态
if(emp.getStatus() == CommonsConst.EMPLOYEE_STATUS_NO){
return R.error(CommonsConst.LOGIN_ACCOUNT_STOP);
}
// 登录成功将员工的ID放入session中
request.getSession().setAttribute("employeeId",emp.getId());
return R.success(emp);
}
}5. Functional test
Debug test Mainly test the following points:
Verification of user name and password
When the user status is disabled
Whether the data is returned correctly
Appendix
Constant class:
package com.itheima.reggie.common;
/**
* 常量定义
* @author jektong
* @date 2022/4/23
*/
public class CommonsConst {
// 登录失败
public static final String LOGIN_FAIL = "登录失败";
// 账号禁用
public static final String LOGIN_ACCOUNT_STOP = "账号禁止使用";
// 员工账号禁用状态 0:禁用
public static final Integer EMPLOYEE_STATUS_NO = 0;
// 员工账号正常状态 1:正常使用
public static final Integer EMPLOYEE_STATUS_YES = 1;
}The above is the detailed content of How to implement Java backend login function. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 Square Root in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:26 PM
Square Root in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:26 PM
Guide to Square Root in Java. Here we discuss how Square Root works in Java with example and its code implementation respectively.
 Perfect Number in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:28 PM
Perfect Number in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:28 PM
Guide to Perfect Number in Java. Here we discuss the Definition, How to check Perfect number in Java?, examples with code implementation.
 Random Number Generator in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:27 PM
Random Number Generator in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:27 PM
Guide to Random Number Generator in Java. Here we discuss Functions in Java with examples and two different Generators with ther examples.
 Armstrong Number in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:26 PM
Armstrong Number in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:26 PM
Guide to the Armstrong Number in Java. Here we discuss an introduction to Armstrong's number in java along with some of the code.
 Weka in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:28 PM
Weka in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:28 PM
Guide to Weka in Java. Here we discuss the Introduction, how to use weka java, the type of platform, and advantages with examples.
 Smith Number in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:28 PM
Smith Number in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:28 PM
Guide to Smith Number in Java. Here we discuss the Definition, How to check smith number in Java? example with code implementation.
 Java Spring Interview Questions
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:29 PM
Java Spring Interview Questions
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:29 PM
In this article, we have kept the most asked Java Spring Interview Questions with their detailed answers. So that you can crack the interview.
 Break or return from Java 8 stream forEach?
Feb 07, 2025 pm 12:09 PM
Break or return from Java 8 stream forEach?
Feb 07, 2025 pm 12:09 PM
Java 8 introduces the Stream API, providing a powerful and expressive way to process data collections. However, a common question when using Stream is: How to break or return from a forEach operation? Traditional loops allow for early interruption or return, but Stream's forEach method does not directly support this method. This article will explain the reasons and explore alternative methods for implementing premature termination in Stream processing systems. Further reading: Java Stream API improvements Understand Stream forEach The forEach method is a terminal operation that performs one operation on each element in the Stream. Its design intention is






