
The payment aggregation services of large e-commerce companies all have this kind of scenario:
Call the verification service to verify whether the order to be generated is legal
The order service generates the order (the verification service and the order service have no dependency)
Call 1 and 2, the payment service implements the payment core function
Combine steps 1 to 3 to complete the aggregation call of the payment service
If step 1 takes 5 seconds, step 2 takes 3 seconds, and step 3 takes 2 seconds, if you are an architect, the requirements are:
1. Please implement the synchronization of microservices Call
2. Please implement asynchronous calling of microservices (implemented using CompletableFuture)
Compare the performance of 1 and 2.
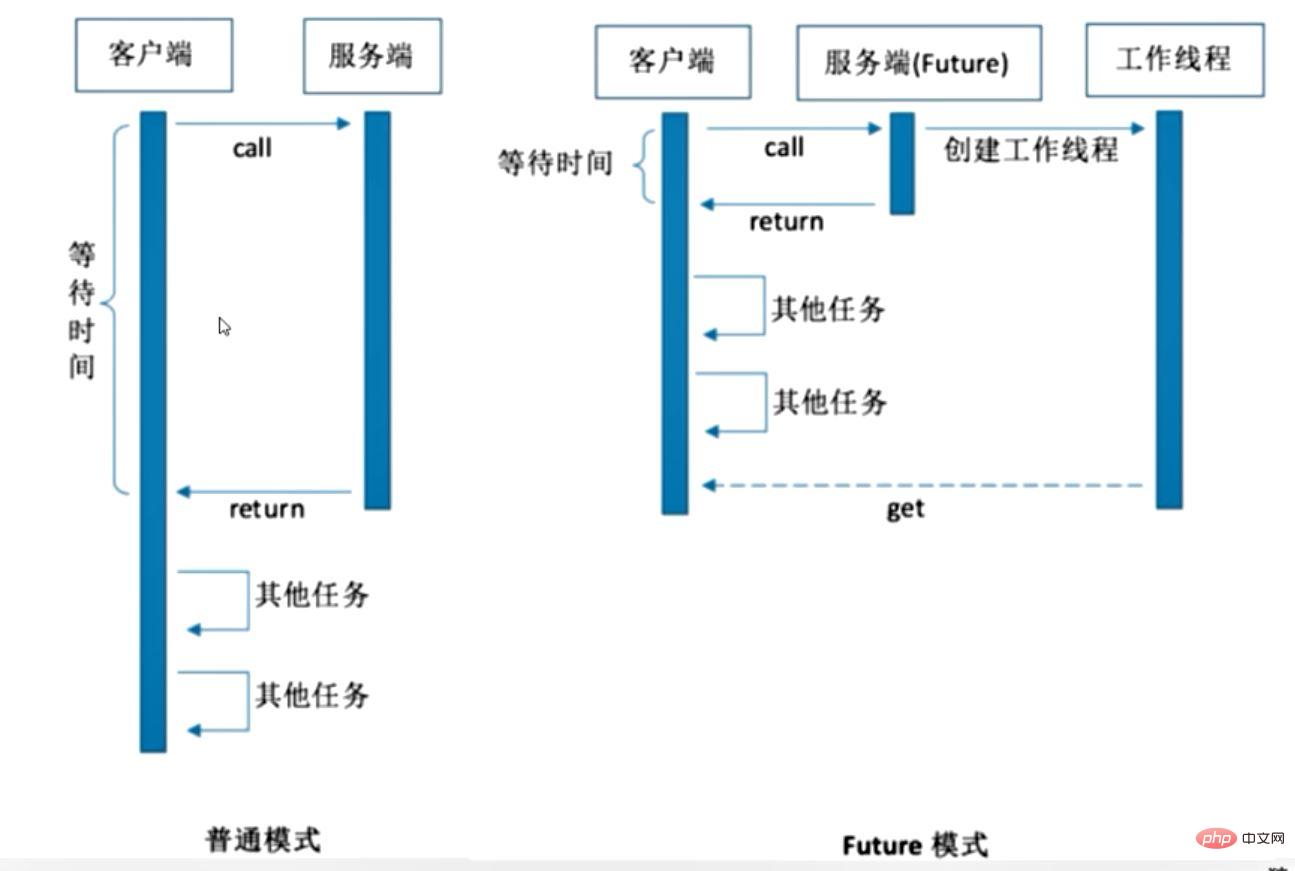
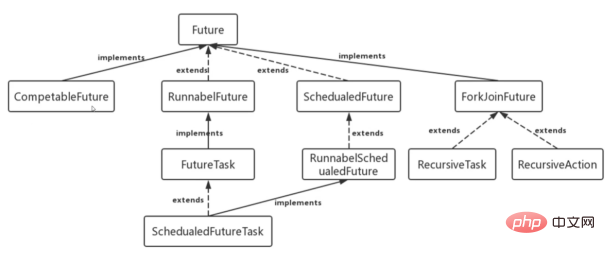
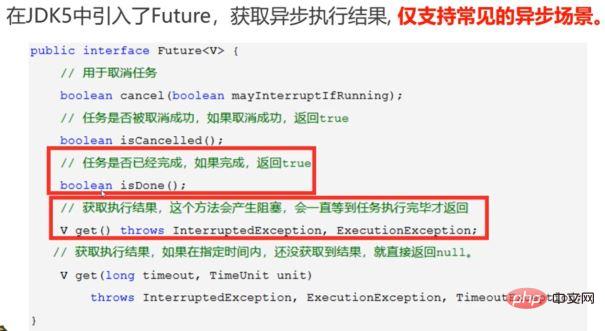
Future has many direct expressions There are certain flaws in the dependency between Future results:
1. Merge two asynchronous calculations into one (the second asynchronous calculation depends on the result of the first one). This is not easy to use Future. Easy to implement.
2. Wait for all tasks in the Future collection to be completed
Only wait for the fastest completed task in the Future collection to complete and return its result
https://gitee.com/zjvngvn/mutil-thread
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 同步调用
long start1 = System.currentTimeMillis();
PaymentService.syncPay();
System.out.println("同步支付耗时:" + (System.currentTimeMillis() - start1)+" ms");
System.out.println("=========================");
// 异步调用
long start2 = System.currentTimeMillis();
PaymentService.asyncPay();
System.out.println("异步支付耗时:" + (System.currentTimeMillis() - start2)+" ms");
}
}import java.util.concurrent.CompletableFuture;
import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;
public class PaymentService {
/**
* 异步支付的入口方法
*
* @return
*/
public static boolean asyncPay() {
//校验
CompletableFuture<Boolean> isValid = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> CheckService.isValid());
//创建订单
CompletableFuture<Integer> orderSum = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> OrderService.createOrder());
//支付
CompletableFuture<Integer> money = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> basePay());
// 上面三个都完成之后,再进行下面匿名内部类的代码
CompletableFuture.allOf(isValid, orderSum, money)
.thenRun(() -> System.out.println("完成异步支付"))
.join();
return true;
}
/**
* 同步支付的入口方法
*
* @return
*/
public static boolean syncPay() {
CheckService.isValid();
OrderService.createOrder();
basePay();
System.out.println("同步支付成功");
//假设支付成功
return true;
}
public static int basePay() {
int money = 1000;
try {
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(2);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("支付");
//假设支付成功
return money;
}
}import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;
public class CheckService {
/**
* 返回true说明订单流程才会往下走
*/
public static boolean isValid() {
System.out.println("订单生成前,检验订单是否合法" );
try {
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(5);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
//假设订单合法,通过校验
return true;
}
}import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;
public class OrderService {
public static int createOrder() {
int orderSum=1;
System.out.println("生成订单" );
try {
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(3);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
//假设订单数量为1
return orderSum;
}
}The above is the detailed content of How to tune the performance of Java multi-threaded asynchronous calls. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!




