
For example, I have an entity class User, and User has an attribute Name
public class User {
public User(String name, String age, int height) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
this.height = height;
}
private String name;
private String age;
private int height;
// setter、getter方法我就不写了
}
// 创建三个user
User user1 = new User("111", "18", 180);
User user2 = new User("222", "18", 175);
User user3 = new User("333", "19", 170);Now I want to create 3 users and put them in the list:
List<User> userList = new ArrayList<>(); userList.add(user1); userList.add(user2); userList.add(user3);
// stream流,创建的是动态数组,可以添加元素 List<User> userList = Stream.of(user1, user2, user3).collect(Collectors.toList());
The essence is to convert an array into a list. The size of the array is fixed, so elements cannot be added to this list.
If you call the add method to add a new element, an exception will be reported: java.lang.UnsupportedOperationException
When the element is fixed, you can use this;
// 本质是将一个数组转成list,数组的大小是固定的,所以此list不能添加元素
// 如果调用add方法增加新的元素,会报异常:java.lang.UnsupportedOperationException
List<String> s = Arrays.asList("1","2","3")Take the userList above as an example. I take out the name attributes of all users in the list and put them into a new list:
// 遍历
List<String> userNameList = new ArrayList<>();
for (User user : userList) {
userNameList.add(user.getName());
}// Stream流 List<String> userNameList = userList.stream().map(User::getName).collect(Collectors.toList());
Also take the userList above, for example, I want to filter out the name in the userList is not empty user
List<User> newUserList = new ArrayList<>();
// if判断
for (User user : userList) {
if(user.getName() != null) {
newUserList.add(user);
}
}// 获取userName不为空的user的List List<User> userList = userList.stream().filter(user-> user.getName() != null).collect(Collectors.toList());
User grouping according to age:
Map<String, List<User>> map = new HashMap<>();
// if判断
for (User user : userList) {
if (map.get(user.getAge()) == null) {
map.put(user.getAge(), new ArrayList());
}
map.get(user.getAge()).add(user);
}Map<String, List<User>> map =userList.stream().collect( Collectors.groupingBy(User::getAge, Collectors.toList()));
The ordinary traversal method for summation is similar to the above, so I won’t give an example;
// int、double、long: double max = userList.stream().mapToDouble(User::getHeight).sum();
a, traversal:
Map<String, User> userMap = new Map<>();
for (User user : userList) {
userMap.put(user.getName(), user);
}b, stream:
Use Collectors’ toMap method to convert List, you will generally encounter two problems a question.
(1) Convert map, key duplication problem;
Using (key1, key2)->key2 expression in the code can solve this kind of problem. If there are duplicate keys, use key2 To overwrite the previous key1, it can also be defined as (key1, key2)->key1, retain key1, and adjust it according to your own business scenario.
(2) Null pointer exception, that is, the value converted to map is null. This can be filtered with filter;
Map<String, User> userMap= userList.stream().collect(Collectors.toMap(User::getName, Function.identity(),(key1, key2)->key2));
a, traversal:
List<User> userList = new List<>();
for (String userName : userMap.keySet()) {
userList.add(userMap.get(userName));
}b, stream:
List<User> userList = userMap.entrySet().stream().map(e ->e.getValue()).collect(Collectors.toList());
If any element succeeds in the judgment conditions, true will be returned;
For example, in the userlList above, I think Determine whether there is a height > 175:
userList.stream().anyMatch(user -> user.getHeight() > 175);
allMatch: Judgment of the elements in the condition, all of them are, return true;
For example, in the userlList above, I want to determine whether all height > 175:
userList.stream().allMatch(user -> user.getHeight() > 175);
Contrary to allMatch, all elements in the condition are judged. None, return true
userList.stream().noneMatch(user -> user.getHeight() > 175);
userList.stream().filter(user -> user.getHeight() > 175).count();
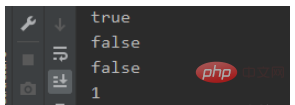
All print results:
System.out.println(userList. stream().anyMatch(user -> user.getHeight() > 175));
System.out.println(userList.stream().allMatch(user -> user.getHeight() > 175 ));
System.out.println(userList.stream().noneMatch(user -> user.getHeight() > 175));
System.out.println(userList.stream(). filter(user -> user.getHeight() > 175).count());
The above is the detailed content of What are the common methods of Java8 Stream?. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!




