Example analysis of dynamic proxy and static proxy in Java
0. Agent mode
Why should we learn the agent mode? This is the bottom layer of SpringAOP [SpringAOP and SpringMVC]
Classification of proxy mode:
Static proxy
-
Dynamic proxy
1. Static proxy
In static proxy, our enhancement of each method of the target object is done manually ( The code will be demonstrated in detail later_), very inflexible (for example, once a new method is added to the interface, the target object and proxy object must be modified) and troublesome (_need to write a separate proxy class for each target class). There are very few actual application scenarios, and there are almost no scenarios where static proxies are used in daily development.
Role analysis:
Abstract role: Generally, interfaces or abstract classes are used to solve the problem
Real role: Acted role
Agent role: Act as the real role. After acting as the real role, we usually do some subsidiary operations
Customer: The person who accesses the proxy object!
Code steps:
1. Interface
public interface Rent {
public void rent();
}2. Real character
//房东
public class Host implements Rent {
public void rent() {
System.out.println("房东要租房子");
}
}3. Agent role
public class Proxy implements Rent{
private Host host;
public Proxy() {
}
public Proxy(Host host) {
this.host = host;
}
public void rent(){
seeHouse();
host.rent();
fare();
}
//看房
public void seeHouse(){
System.out.println("中介带你看房");
}
//收中介费
public void fare(){
System.out.println("中介收费");
}
}4. Client access to the agent role
public class Client {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Host host = new Host();
//代理,代理角色一般会有附属操作!
Proxy proxy = new Proxy(host);
proxy.rent();
}
}Benefits of the agent mode:
can make real roles The operation is more pure! There is no need to pay attention to some public business
The public will be left to the agent role! Realize the division of labor in business!
When public services expand, centralized management is convenient!
Disadvantages:
A real role will generate a proxy role; from a JVM perspective, a static proxy changes the interface, Implementation classes and proxy classes have become actual class files.
2. Deepen understanding of
AOP, the underlying proxy model
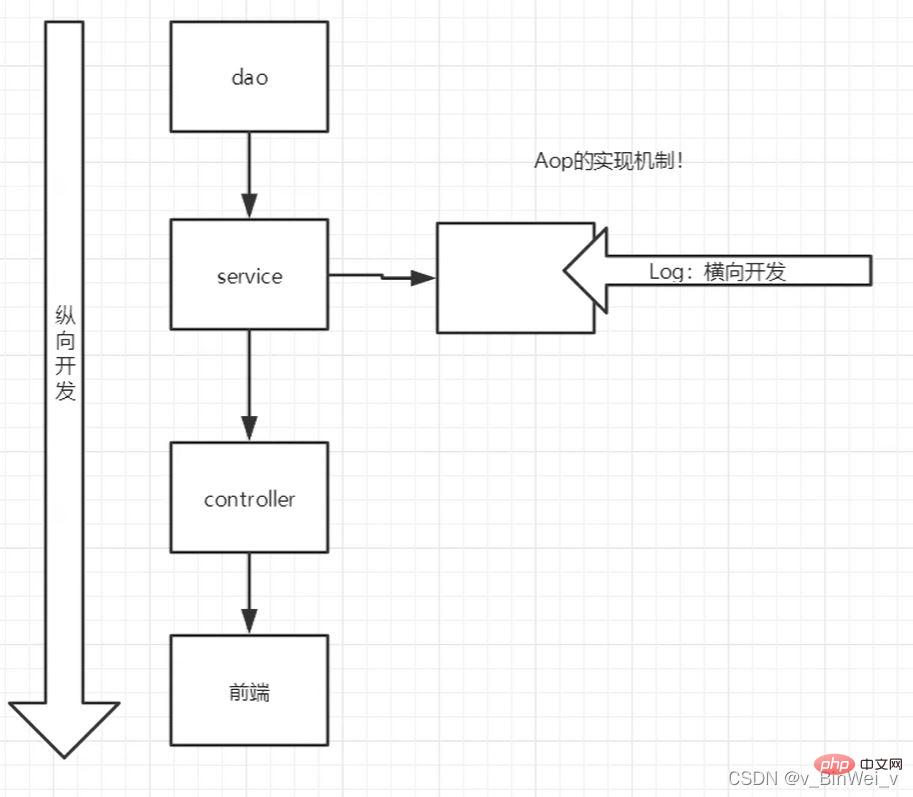
3. Dynamic proxy
-
The role of dynamic proxy is the same as that of static proxy
The proxy class of dynamic proxy is dynamically generated, not written directly by us!
Dynamic agents are divided into two categories: interface-based dynamic agents and class-based dynamic agents
Interface-based— —JDK dynamic proxy
Based on class: cglib dynamic proxy
java bytecode implementation: javasist
You need to understand two classes: Proxy: proxy class, InvocationHandler: call handler
From the JVM perspective, dynamic proxy dynamically generates class bytecode at runtime , and loaded into the JVM.
//Proxy是生成动态代理类,提供了创建动态代理类和实例的静态方法,它也是由这些方法创建的所有动态代理类的超类。 //InvocationHandler-- invoke 调用处理程序并返回接口, 是由代理实例的调用处理程序实现的接口 。
Benefits of dynamic proxy:
can make the operation of real characters more pure! There is no need to deal with some public business
The public will be left to the agent role! Implementation
public static Object newProxyInstance(ClassLoader loader, Class<?>[] interfaces, InvocationHandler h){
}1.loader : Class loader, used to load proxy objects.
2.interfaces : Some interfaces implemented by the proxy class;
3.h : An object that implements the InvocationHandler interface;
To implement a dynamic proxy, you must also implement InvocationHandler to customize the processing logic. When our dynamic proxy object calls a method, the call to this method will be forwarded to the invoke method of the class that implements the InvocationHandler interface.
public interface InvocationHandler {
Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable;
}1.proxy: dynamically generated proxy class
2.method: corresponds to the method called by the proxy class object
3.args: Parameters of the current method method
Example of dynamic proxy
1. Define the interface
public interface Rent {
public void rent();
}2. Implement rental Interface
public class Host implements Rent {
@Override
public void rent() {
System.out.println("房东要租房");
}
}3. Define a JDK dynamic proxy class
public class DebugInvocationHandler implements InvocationHandler {
/**
* 代理类中的真实对象
*/
private final Object target;
public DebugInvocationHandler(Object target){
this.target = target;
}
/**
* 当你使用代理对象调用方法的时候实际会调用到这个方法
*/
@Override
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable {
//调用方法前
System.out.println("before method" + method.getName());
Object res = method.invoke(target, args);
//调用方法后
System.out.println("after method" + method.getName());
return res;
}
}invoke() Method: When our dynamic proxy object calls the native method, it will actually be called What we get is the invoke() method, and then the invoke() method calls the native method of the proxy object on our behalf.
4. Get the factory class of the proxy object
public class JdkProxyFactory {
public static Object getProxy(Object target){
return Proxy.newProxyInstance(
target.getClass().getClassLoader(),
target.getClass().getInterfaces(),
new DebugInvocationHandler(target)
);
}
}getProxy(): Mainly obtain the factory class of a certain class through the Proxy.newProxyInstance() method Proxy object
5. Actual use
public static void main(String[] args) {
//Rent rent = new Host();
//Rent rentProxy= (Rent) Proxy.newProxyInstance(rent.getClass().getClassLoader(), rent.getClass().getInterfaces(),new DebugInvocationHandler(rent));
Rent rentProxy = (Rent)JdkProxyFactory.getProxy(new Host());
rentProxy.rent();
}The output of running the above agent
before methodrent
The landlord wants to rent a house
after methodrent
The above is the detailed content of Example analysis of dynamic proxy and static proxy in Java. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1376
1376
 52
52
 Square Root in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:26 PM
Square Root in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:26 PM
Guide to Square Root in Java. Here we discuss how Square Root works in Java with example and its code implementation respectively.
 Perfect Number in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:28 PM
Perfect Number in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:28 PM
Guide to Perfect Number in Java. Here we discuss the Definition, How to check Perfect number in Java?, examples with code implementation.
 Armstrong Number in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:26 PM
Armstrong Number in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:26 PM
Guide to the Armstrong Number in Java. Here we discuss an introduction to Armstrong's number in java along with some of the code.
 Random Number Generator in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:27 PM
Random Number Generator in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:27 PM
Guide to Random Number Generator in Java. Here we discuss Functions in Java with examples and two different Generators with ther examples.
 Weka in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:28 PM
Weka in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:28 PM
Guide to Weka in Java. Here we discuss the Introduction, how to use weka java, the type of platform, and advantages with examples.
 Smith Number in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:28 PM
Smith Number in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:28 PM
Guide to Smith Number in Java. Here we discuss the Definition, How to check smith number in Java? example with code implementation.
 Java Spring Interview Questions
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:29 PM
Java Spring Interview Questions
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:29 PM
In this article, we have kept the most asked Java Spring Interview Questions with their detailed answers. So that you can crack the interview.
 Break or return from Java 8 stream forEach?
Feb 07, 2025 pm 12:09 PM
Break or return from Java 8 stream forEach?
Feb 07, 2025 pm 12:09 PM
Java 8 introduces the Stream API, providing a powerful and expressive way to process data collections. However, a common question when using Stream is: How to break or return from a forEach operation? Traditional loops allow for early interruption or return, but Stream's forEach method does not directly support this method. This article will explain the reasons and explore alternative methods for implementing premature termination in Stream processing systems. Further reading: Java Stream API improvements Understand Stream forEach The forEach method is a terminal operation that performs one operation on each element in the Stream. Its design intention is




