 Java
Java
 javaTutorial
javaTutorial
 Differences in interface syntax between Java versions and similarities and differences between abstract classes and interfaces
Differences in interface syntax between Java versions and similarities and differences between abstract classes and interfaces
Differences in interface syntax between Java versions and similarities and differences between abstract classes and interfaces
What is an interface?
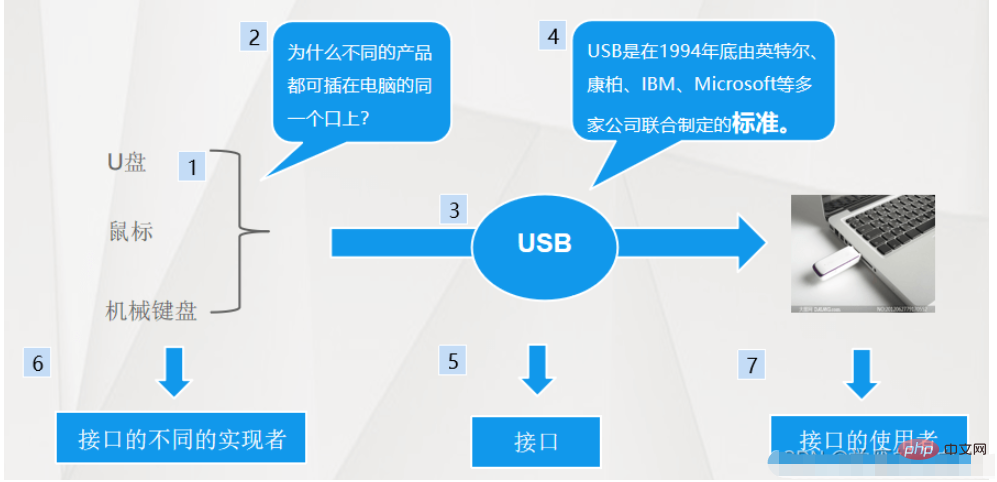
Speaking of interfaces, USB is certainly familiar to everyone~
The interface is a standard and specification.
Note: Once the interface is formulated, both users and implementers must follow the standard.
Interface syntax: (JDK7.0)
(1) Keyword: interface
(2) Syntax: interface interface name{}
(3) After the interface is compiled, the corresponding .class file will be generated
(4) The interface cannot create objects, but it can declare a reference to the interface name;
(5) There is no constructor method in the interface
(6 ) All properties in the interface are public static constants
(Default is: public static final)
(7) All methods in the interface are public abstract methods
(Default is: public abstract modification)
Note: The default access permission for methods in the interface is public;
The default access permission for methods in the class is default
Implementation class of the interface:
Syntax:
class class name implements interface name {}
Note: The keyword of implementation is implements
(1) If the implementation class does not want to become an abstract class, it must overwrite (implement) the interface All methods
(2) When an implementation class overrides a method in an interface, the access permission must be public
Use:
(1) In the reference of the interface type, only objects of the corresponding implementation class can be stored. Reflecting polymorphic applications
(2) Syntax:
Interface name reference name = new implementation class name (actual parameter);
Note: an interface Multiple implementation classes can be defined
Inheritance of interface: (very important~)
The relationship between interfaces is multiple inheritance
(1) An interface You can inherit multiple parent interfaces at the same time
(2) Syntax:
interface interface name extends parent interface name 1, parent interface name 2{}
The relationship between classes and interfaces is multi-implementation
(1) A class can implement multiple interfaces at the same time
(2) Syntax:
class class Name implements interface name 1, interface name 2 {}
(3) If a class implements multiple interfaces at the same time, and does not want to become an abstract class, it needs to implement all methods in all interfaces
(including all Methods in the parent interface that implement the interface)
A class can implement multiple interfaces and inherit a class at the same time
(1) If a class inherits a parent class and implements multiple interfaces at the same time , must be inherited first, and then implemented
(2) Syntax:
class class name extends parent class name implements parent interface 1, parent interface 2{}
Note: Must extend first, then implements
Existence between classes: single inheritance------extends
Existence between classes and interfaces: multiple implementations-- ----implements
Exists between interfaces: multiple inheritance------extends
The impact of interfaces:
1. Since the interfaces are The relationship between multiple inheritance and multi-implementation between classes and interfaces makes polymorphism more diversified and complex.
2. If only one of the two parties of forced type conversion is an interface type, the compilation will definitely pass and run There are two situations:
a. If the actual object type stored in the converted reference is one of the types to be converted, run through
b. If the actual object type stored in the converted reference is not the type to be converted One, the compilation is passed, but an error is reported when running, the error message:
Java.lang.ClassCastException (type conversion exception)
The syntax of the interface: (JDK8.0)
(1) Default method:
a. public default return value type method name (formal parameter list) {
// Implementation part of the method
}
b . Note: The method in the interface is represented by the default modification. This method is allowed to have a method implementation part
c. The default method access permission is public
d. The default method is allowed to be overridden, but the access modifier when overridden is public
(2) Static method:
a. public static return value type method name (formal parameter list) {
# b. The access rights of static methods in the interface are public
.
The syntax of the interface: (JDK9.0)—(Private method)
(1) In the interface, from Starting from 9.0, methods can be modified by private
(2) Syntax:
private return value type method name (formal parameter list) {// Method implementation}
(3) Private methods are for internal use of the interface, usually extracting the common logic parts of other methods to reduce code redundancy
Classification of interfaces
Constant interface:
There are only attributes and no methods in the interface, and there are few applications.
Empty interface:
Usually called a mark interface, there are no attributes or abstractions in the interface;
For example: IO Use
Functional interface when serializing objects:
There is only one abstract method in the interface (static and not concerned by default), which is widely used in Lambda expressions
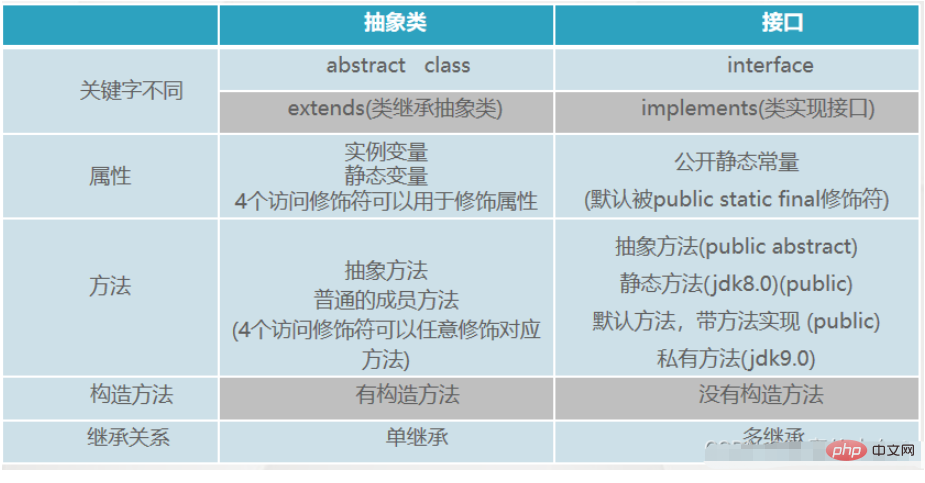
What is the difference between abstract class and interface? (Keep it in mind~)
The above is the detailed content of Differences in interface syntax between Java versions and similarities and differences between abstract classes and interfaces. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 Square Root in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:26 PM
Square Root in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:26 PM
Guide to Square Root in Java. Here we discuss how Square Root works in Java with example and its code implementation respectively.
 Perfect Number in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:28 PM
Perfect Number in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:28 PM
Guide to Perfect Number in Java. Here we discuss the Definition, How to check Perfect number in Java?, examples with code implementation.
 Random Number Generator in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:27 PM
Random Number Generator in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:27 PM
Guide to Random Number Generator in Java. Here we discuss Functions in Java with examples and two different Generators with ther examples.
 Weka in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:28 PM
Weka in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:28 PM
Guide to Weka in Java. Here we discuss the Introduction, how to use weka java, the type of platform, and advantages with examples.
 Armstrong Number in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:26 PM
Armstrong Number in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:26 PM
Guide to the Armstrong Number in Java. Here we discuss an introduction to Armstrong's number in java along with some of the code.
 Smith Number in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:28 PM
Smith Number in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:28 PM
Guide to Smith Number in Java. Here we discuss the Definition, How to check smith number in Java? example with code implementation.
 Java Spring Interview Questions
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:29 PM
Java Spring Interview Questions
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:29 PM
In this article, we have kept the most asked Java Spring Interview Questions with their detailed answers. So that you can crack the interview.
 Break or return from Java 8 stream forEach?
Feb 07, 2025 pm 12:09 PM
Break or return from Java 8 stream forEach?
Feb 07, 2025 pm 12:09 PM
Java 8 introduces the Stream API, providing a powerful and expressive way to process data collections. However, a common question when using Stream is: How to break or return from a forEach operation? Traditional loops allow for early interruption or return, but Stream's forEach method does not directly support this method. This article will explain the reasons and explore alternative methods for implementing premature termination in Stream processing systems. Further reading: Java Stream API improvements Understand Stream forEach The forEach method is a terminal operation that performs one operation on each element in the Stream. Its design intention is





