Implementation of Java data structure doubly linked list
Doubly linked list
What is a doubly linked list?
Doubly linked list, also called doubly linked list, is a type of linked list. Each data node has two pointers, pointing to the direct successor and direct predecessor respectively. Therefore, starting from any node in the doubly linked list, you can easily access its predecessor nodes and successor nodes.
The main difference between a doubly linked list and a one-way linked list:
Search direction: The search direction of a one-way linked list can only be in one direction, while a doubly linked list can be forward or forward Look backwards.
Delete: Deletion of a one-way linked list requires the use of auxiliary pointers. First find the predecessor of the node to be deleted, and then delete it.
Temp.next = Temp.next.next; (TEMP is auxiliary pointer)
Bidirectional linked list can be deleted by themselves.
The advantages and disadvantages of doubly linked lists and singly linked lists:
Advantages: The doubly linked list structure is more advantageous than the singly linked list structure.
Disadvantages: From the storage structure point of view, the doubly linked list has one more pointer than the one-way linked list, requiring an additional, linear memory usage. (A pointer is 4 bytes in 32-bit operating systems and 8 bytes in 64-bit operating systems).
Illustration of the logical structure of a doubly linked list:
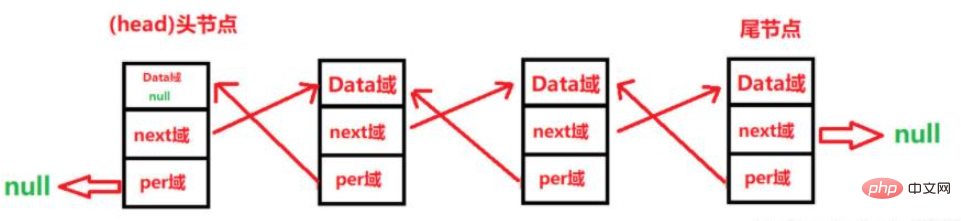
Specific operations of a doubly linked list:
Add:
Illustration:
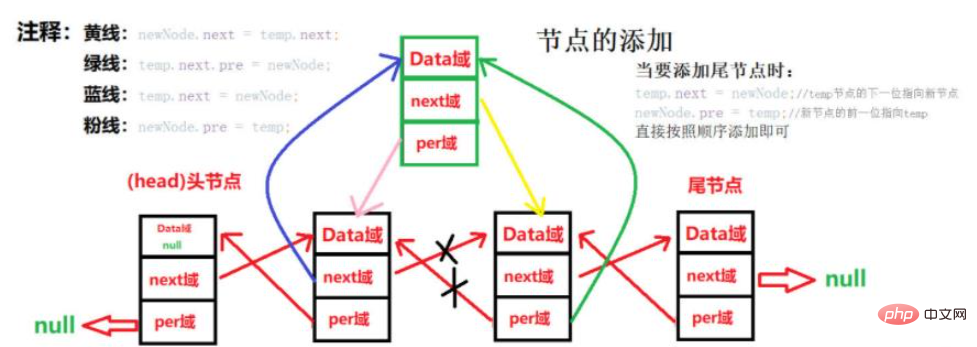
Code:
//添加一个节点到最后
public void add(DoubleNode newNode) {
DoubleNode temp = head;
while (true) {
if (temp.next == null) {
// 当temp.next 为空时,证明temp为最后一个元素。
temp.next = newNode; //temp节点的下一位指向新节点
newNode.pre = temp;//新节点的前一位指向temp
//这两步构成双向链表
break;
}else if (temp.next.ID == newNode.ID) {
//ID相同证明 已经存在该学生。
System.out.printf("要插入学号为%d的学生已经存在。\n", newNode.ID);
break;
}
temp = temp.next;
}
}
//按学号顺序添加节点
public void Sortadd(DoubleNode newNode) {
DoubleNode temp = head;
while (true) {
if (temp.next == null) {
//说明要添加的节点序号在当前链表中最大,因此直接添加在末尾。
temp.next = newNode;//temp节点的下一位指向新节点
newNode.pre = temp;//新节点的前一位指向temp
//这两步构成双向链表
break;
} else if (temp.next.ID > newNode.ID) {
//当前节点的下一位节点的编号大于 要添加的新节点,则证明新节点要添加在temp节点之后
newNode.next = temp.next;//要添加节点的下一位 指向temp当前节点的下一位
temp.next.pre = newNode;//temp当前节点的下一位的前一位 指向 新节点构成双向链表
temp.next = newNode; // 再让当前节点的下一位指向 新节点
newNode.pre = temp;//新节点的前一位 指向 当前节点temp
//这样连接完成后就将 新节点插入 到 原本链表的temp节点与temp.next节点之间
break;
}else if (temp.next.ID == newNode.ID) {
//ID相同证明 已经存在该学生。
System.out.printf("要插入学号为%d的学生已经存在。\n", newNode.ID);
break;
}
temp = temp.next;
}
}Delete:
Illustration:
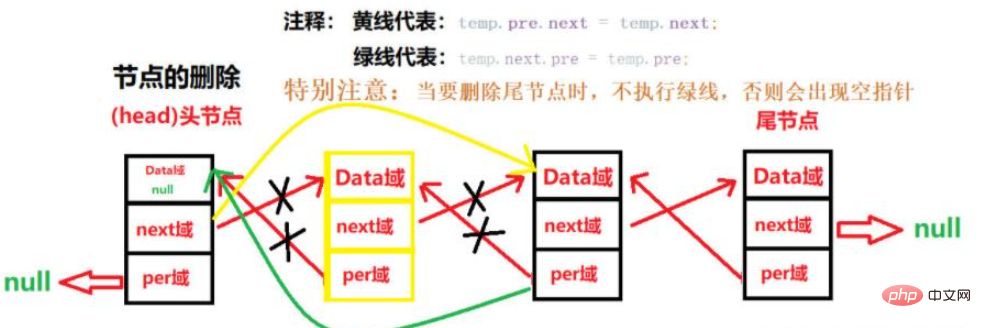
Code :
//删除一个节点。
//自我删除
public void DoubleDelete(int id) {
if (head.next == null) {
System.out.println("链表为空!");
return;
}
DoubleNode temp = head.next;
while (true) {
if (temp == null) {
System.out.printf("要删除的%d节点不存在\n", id);
break;
} else if (temp.ID == id) {
//找到要删除节点
// 此时temp 就代表将要被删除节点
//temp.pre.next 指 当前要被删除节点 的前一位 的后一位
// temp.next 指 当前要被删除节点的后一位
temp.pre.next = temp.next;
// (当前要被删除节点 的前一位 的后一位)指向 (当前要被删除节点的后一位)
//这样就完成了 temp节点的删除操作
// 如果是最后一个节点,就不需要执行下面这句话,否则出现空指针
if (temp.next != null) {
temp.next.pre = temp.pre;
}
break;
}
temp = temp.next;
}
} Modification:
Kankan: It is actually the same as deleting a singly linked list.
Code:
//修改链表节点
public void DoubleUpdate(DoubleNode newNode) {
if (head.next == null) {
System.out.println("链表为空!");
return;
}
DoubleNode temp = head.next;
while (true) {
if (temp == null) {
break;
} else if (temp.ID == newNode.ID) {
//找到要修改的节点
temp.name = newNode.name;
temp.mark = newNode.mark;
return;
}
temp = temp.next;
}
System.out.printf("要修改的%d节点不存在\n", newNode.ID);
}Doubly linked list example:
Use a doubly linked list to create a student information management system to complete the addition, deletion and modification of student information.
package Linkedlist;
//双向链表。
public class DoubleLinkedListDemo {
public static void main(String agrs[]) {
DoubleNode stu1 = new DoubleNode(6, "张三", 99);
DoubleNode stu2 = new DoubleNode(2, "李四", 99);
DoubleNode stu3 = new DoubleNode(3, "王五", 99);
DoubleNode stu4 = new DoubleNode(5, "王二", 99);
DoubleNode stu5 = new DoubleNode(4, "小红", 99);
DoubleNode stu6 = new DoubleNode(1, "小明", 99);
DoubleNode stu7 = new DoubleNode(1, "小明", 99);
DoubleLinkedlist doubleLinkedlist = new DoubleLinkedlist();
/* doubleLinkedlist.add(stu1);
doubleLinkedlist.add(stu2);
doubleLinkedlist.add(stu3);
doubleLinkedlist.add(stu4);
doubleLinkedlist.add(stu5);
doubleLinkedlist.add(stu6);
doubleLinkedlist.add(stu7);*/
doubleLinkedlist.Sortadd(stu1);
doubleLinkedlist.Sortadd(stu2);
doubleLinkedlist.Sortadd(stu3);
doubleLinkedlist.Sortadd(stu4);
doubleLinkedlist.Sortadd(stu5);
doubleLinkedlist.Sortadd(stu6);
doubleLinkedlist.add(stu7);
System.out.println("原链表展示!");
doubleLinkedlist.ShowList();
System.out.println();
doubleLinkedlist.DoubleDelete(6);
doubleLinkedlist.DoubleDelete(15);
System.out.println("删除后链表展示!");
doubleLinkedlist.ShowList();
System.out.println();
DoubleNode stu8 = new DoubleNode(1, "李思成", 100);
DoubleNode stu9 = new DoubleNode(20, "李成", 100);
doubleLinkedlist.DoubleUpdate(stu8);
doubleLinkedlist.DoubleUpdate(stu9);
System.out.println("修改后链表展示!");
doubleLinkedlist.ShowList();
System.out.println();
}
}
class DoubleLinkedlist {
private DoubleNode head = new DoubleNode(0, "", 0);
public DoubleNode getHead() {
return head;
}
//添加一个节点到最后
public void add(DoubleNode newNode) {
DoubleNode temp = head;
while (true) {
if (temp.next == null) {
// 当temp.next 为空时,证明temp为最后一个元素。
temp.next = newNode; //temp节点的下一位指向新节点
newNode.pre = temp;//新节点的前一位指向temp
//这两步构成双向链表
break;
}else if (temp.next.ID == newNode.ID) {
//ID相同证明 已经存在该学生。
System.out.printf("要插入学号为%d的学生已经存在。\n", newNode.ID);
break;
}
temp = temp.next;
}
}
//按学号顺序添加节点
public void Sortadd(DoubleNode newNode) {
DoubleNode temp = head;
while (true) {
if (temp.next == null) {
//说明要添加的节点序号在当前链表中最大,因此直接添加在末尾。
temp.next = newNode;//temp节点的下一位指向新节点
newNode.pre = temp;//新节点的前一位指向temp
//这两步构成双向链表
break;
} else if (temp.next.ID > newNode.ID) {
//当前节点的下一位节点的编号大于 要添加的新节点,则证明新节点要添加在temp节点之后
newNode.next = temp.next;//要添加节点的下一位 指向temp当前节点的下一位
temp.next.pre = newNode;//temp当前节点的下一位的前一位 指向 新节点构成双向链表
temp.next = newNode; // 再让当前节点的下一位指向 新节点
newNode.pre = temp;//新节点的前一位 指向 当前节点temp
//这样连接完成后就将 新节点插入 到 原本链表的temp节点与temp.next节点之间
break;
}else if (temp.next.ID == newNode.ID) {
//ID相同证明 已经存在该学生。
System.out.printf("要插入学号为%d的学生已经存在。\n", newNode.ID);
break;
}
temp = temp.next;
}
}
//删除一个节点。
//自我删除
public void DoubleDelete(int id) {
if (head.next == null) {
System.out.println("链表为空!");
return;
}
DoubleNode temp = head.next;
while (true) {
if (temp == null) {
System.out.printf("要删除的%d节点不存在\n", id);
break;
} else if (temp.ID == id) {
//找到要删除节点
// 此时temp 就代表将要被删除节点
//temp.pre.next 指 当前要被删除节点 的前一位 的后一位
// temp.next 指 当前要被删除节点的后一位
temp.pre.next = temp.next;
// (当前要被删除节点 的前一位 的后一位)指向 (当前要被删除节点的后一位)
//这样就完成了 temp节点的删除操作
// 如果是最后一个节点,就不需要执行下面这句话,否则出现空指针
if (temp.next != null) {
temp.next.pre = temp.pre;
}
break;
}
temp = temp.next;
}
}
//修改链表节点
public void DoubleUpdate(DoubleNode newNode) {
if (head.next == null) {
System.out.println("链表为空!");
return;
}
DoubleNode temp = head.next;
while (true) {
if (temp == null) {
break;
} else if (temp.ID == newNode.ID) {
//找到要修改的节点
temp.name = newNode.name;
temp.mark = newNode.mark;
return;
}
temp = temp.next;
}
System.out.printf("要修改的%d节点不存在\n", newNode.ID);
}
public void ShowList() {
// 判断链表是否为空
if (head.next == null) {
System.out.println("链表为空");
return;
}
// 因为头节点,不能动,因此我们需要一个辅助变量来遍历
DoubleNode temp = head.next;
while (true) {
// 判断是否到链表最后
if (temp == null) {
break;
}
System.out.println(temp);// 输出节点的信息
temp = temp.next;
}
}
}
class DoubleNode {
public int ID; // 编号。
public String name;
public int mark;
public DoubleNode next;
public DoubleNode pre; // 前一个(Previous)
public DoubleNode(int ID, String name, int mark) {
this.ID = ID;
this.name = name;
this.mark = mark;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "DoubleNode{" + "ID=" + ID + ", name='" + name + '\'' + "mark=" + mark + '}';
}
}The above is the detailed content of Implementation of Java data structure doubly linked list. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1377
1377
 52
52
 Perfect Number in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:28 PM
Perfect Number in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:28 PM
Guide to Perfect Number in Java. Here we discuss the Definition, How to check Perfect number in Java?, examples with code implementation.
 Random Number Generator in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:27 PM
Random Number Generator in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:27 PM
Guide to Random Number Generator in Java. Here we discuss Functions in Java with examples and two different Generators with ther examples.
 Weka in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:28 PM
Weka in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:28 PM
Guide to Weka in Java. Here we discuss the Introduction, how to use weka java, the type of platform, and advantages with examples.
 Smith Number in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:28 PM
Smith Number in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:28 PM
Guide to Smith Number in Java. Here we discuss the Definition, How to check smith number in Java? example with code implementation.
 Java Spring Interview Questions
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:29 PM
Java Spring Interview Questions
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:29 PM
In this article, we have kept the most asked Java Spring Interview Questions with their detailed answers. So that you can crack the interview.
 Break or return from Java 8 stream forEach?
Feb 07, 2025 pm 12:09 PM
Break or return from Java 8 stream forEach?
Feb 07, 2025 pm 12:09 PM
Java 8 introduces the Stream API, providing a powerful and expressive way to process data collections. However, a common question when using Stream is: How to break or return from a forEach operation? Traditional loops allow for early interruption or return, but Stream's forEach method does not directly support this method. This article will explain the reasons and explore alternative methods for implementing premature termination in Stream processing systems. Further reading: Java Stream API improvements Understand Stream forEach The forEach method is a terminal operation that performs one operation on each element in the Stream. Its design intention is
 TimeStamp to Date in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:28 PM
TimeStamp to Date in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:28 PM
Guide to TimeStamp to Date in Java. Here we also discuss the introduction and how to convert timestamp to date in java along with examples.
 Create the Future: Java Programming for Absolute Beginners
Oct 13, 2024 pm 01:32 PM
Create the Future: Java Programming for Absolute Beginners
Oct 13, 2024 pm 01:32 PM
Java is a popular programming language that can be learned by both beginners and experienced developers. This tutorial starts with basic concepts and progresses through advanced topics. After installing the Java Development Kit, you can practice programming by creating a simple "Hello, World!" program. After you understand the code, use the command prompt to compile and run the program, and "Hello, World!" will be output on the console. Learning Java starts your programming journey, and as your mastery deepens, you can create more complex applications.




