
pd.MultiIndex, an index with multiple levels. Through multi-level indexes, we can operate the data of the entire index group. This article mainly introduces 6 ways to create multi-level indexes in Pandas:
pd.MultiIndex.from_arrays(): Multi-dimensional arrays are used as parameters, high dimensions specify high-level indexes, and low dimensions specify low-level indexes. index.
pd.MultiIndex.from_tuples(): List of tuples as argument, each tuple specifying each index (high-dimensional and low-dimensional index).
pd.MultiIndex.from_product(): A list of iterable objects as parameters, created based on the Cartesian product (pairwise combination of elements) of multiple iterable object elements index.
pd.MultiIndex.from_frame: directly generated based on the existing data frame
groupby(): obtained through data grouping statistics
pivot_table(): Generate a pivot table to get
In [1] :
import pandas as pd import numpy as np
is generated through an array, usually specifying the elements in the list:
In [2]:
# 列表元素是字符串和数字
array1 = [["xiaoming","guanyu","zhangfei"],
[22,25,27]
]
m1 = pd.MultiIndex.from_arrays(array1)
m1Out[2]:
MultiIndex([('xiaoming', 22), ( 'guanyu', 25), ('zhangfei', 27)],
)In [3]:
type(m1) # 查看数据类型
Use the type function to check the data type and find that it is indeed: MultiIndex
Out[3]:
pandas.core.indexes.multi.MultiIndex
is created At the same time, you can specify the name of each level:
In [4]:
# 列表元素全是字符串
array2 = [["xiaoming","guanyu","zhangfei"],
["male","male","female"]
]
m2 = pd.MultiIndex.from_arrays(
array2,
# 指定姓名和性别
names=["name","sex"])
m2Out[4]:
MultiIndex([('xiaoming', 'male'), ( 'guanyu', 'male'), ('zhangfei', 'female')],
names=['name', 'sex'])The following example generates an index of three levels and Specify name:
In [5]:
array3 = [["xiaoming","guanyu","zhangfei"],
["male","male","female"],
[22,25,27]
]
m3 = pd.MultiIndex.from_arrays(
array3,
names=["姓名","性别","年龄"])
m3Out[5]:
MultiIndex([('xiaoming', 'male', 22), ( 'guanyu', 'male', 25), ('zhangfei', 'female', 27)],
names=['姓名', '性别', '年龄'])Through tuples To generate multi-level indexes in the form:
In [6]:
# 元组的形式
array4 = (("xiaoming","guanyu","zhangfei"),
(22,25,27)
)
m4 = pd.MultiIndex.from_arrays(array4)
m4Out[6]:
MultiIndex([('xiaoming', 22), ( 'guanyu', 25), ('zhangfei', 27)],
)In [7]:
# 元组构成的3层索引
array5 = (("xiaoming","guanyu","zhangfei"),
("male","male","female"),
(22,25,27))
m5 = pd.MultiIndex.from_arrays(array5)
m5Out [7]:
MultiIndex([('xiaoming', 'male', 22), ( 'guanyu', 'male', 25), ('zhangfei', 'female', 27)],
)The outermost layer is the list
All are tuples
In [8]:
array6 = [("xiaoming","guanyu","zhangfei"),
("male","male","female"),
(18,35,27)
]
# 指定名字
m6 = pd.MultiIndex.from_arrays(array6,names=["姓名","性别","年龄"])
m6Out[8]:
MultiIndex([('xiaoming', 'male', 18), ( 'guanyu', 'male', 35), ('zhangfei', 'female', 27)],
names=['姓名', '性别', '年龄'] # 指定名字
)Use a list of iterable objects as parameters to create an index based on the Cartesian product of multiple iterable object elements (a pairwise combination of elements).
In Python, we use the isinstance() function to determine whether a python object is iterable:
# 导入 collections 模块的 Iterable 对比对象 from collections import Iterable


Through the above examples we summarize: Common strings, lists, sets, tuples, and dictionaries are all iterable objects
The following examples are given to illustrate:
In [18 ]:
names = ["xiaoming","guanyu","zhangfei"]
numbers = [22,25]
m7 = pd.MultiIndex.from_product(
[names, numbers],
names=["name","number"]) # 指定名字
m7Out[18]:
MultiIndex([('xiaoming', 22), ('xiaoming', 25), ( 'guanyu', 22), ( 'guanyu', 25), ('zhangfei', 22), ('zhangfei', 25)],
names=['name', 'number'])In [19]:
# 需要展开成列表形式
strings = list("abc")
lists = [1,2]
m8 = pd.MultiIndex.from_product(
[strings, lists],
names=["alpha","number"])
m8Out[19]:
MultiIndex([('a', 1), ('a', 2), ('b', 1), ('b', 2), ('c', 1), ('c', 2)],
names=['alpha', 'number'])In [20]:
# 使用元组形式
strings = ("a","b","c")
lists = [1,2]
m9 = pd.MultiIndex.from_product(
[strings, lists],
names=["alpha","number"])
m9Out[20]:
MultiIndex([('a', 1), ('a', 2), ('b', 1), ('b', 2), ('c', 1), ('c', 2)],
names=['alpha', 'number'])In [21]:
# 使用range函数
strings = ("a","b","c") # 3个元素
lists = range(3) # 0,1,2 3个元素
m10 = pd.MultiIndex.from_product(
[strings, lists],
names=["alpha","number"])
m10Out[21]:
MultiIndex([('a', 0), ('a', 1), ('a', 2), ('b', 0), ('b', 1), ('b', 2), ('c', 0), ('c', 1), ('c', 2)],
names=['alpha', 'number'])In [22]:
# 使用range函数
strings = ("a","b","c")
list1 = range(3) # 0,1,2
list2 = ["x","y"]
m11 = pd.MultiIndex.from_product(
[strings, list1, list2],
names=["name","l1","l2"]
)
m11 # 总个数 3*3*2=18The total number is ``332=18`:
Out[22]:
MultiIndex([('a', 0, 'x'), ('a', 0, 'y'), ('a', 1, 'x'), ('a', 1, 'y'), ('a', 2, 'x'), ('a', 2, 'y'), ('b', 0, 'x'), ('b', 0, 'y'), ('b', 1, 'x'), ('b', 1, 'y'), ('b', 2, 'x'), ('b', 2, 'y'), ('c', 0, 'x'), ('c', 0, 'y'), ('c', 1, 'x'), ('c', 1, 'y'), ('c', 2, 'x'), ('c', 2, 'y')],
names=['name', 'l1', 'l2'])By current Some DataFrames directly generate multi-level indexes:
df = pd.DataFrame({"name":["xiaoming","guanyu","zhaoyun"],
"age":[23,39,34],
"sex":["male","male","female"]})
df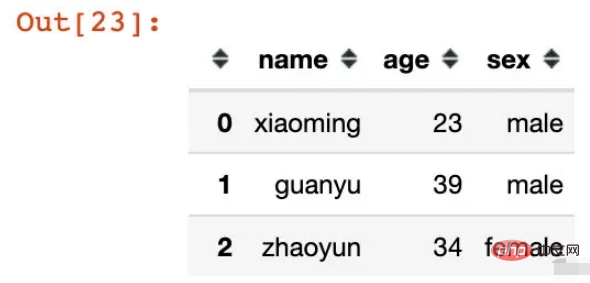
The multi-level indexes are directly generated, and the names are the column fields of the existing data frame:
In [24]:
pd.MultiIndex.from_frame(df)
Out[24]:
MultiIndex([('xiaoming', 23, 'male'), ( 'guanyu', 39, 'male'), ( 'zhaoyun', 34, 'female')],
names=['name', 'age', 'sex'])Specify the name through the names parameter:
In [25]:
# 可以自定义名字 pd.MultiIndex.from_frame(df,names=["col1","col2","col3"])
Out[ 25]:
MultiIndex([('xiaoming', 23, 'male'), ( 'guanyu', 39, 'male'), ( 'zhaoyun', 34, 'female')],
names=['col1', 'col2', 'col3'])is calculated through the grouping function of the groupby function:
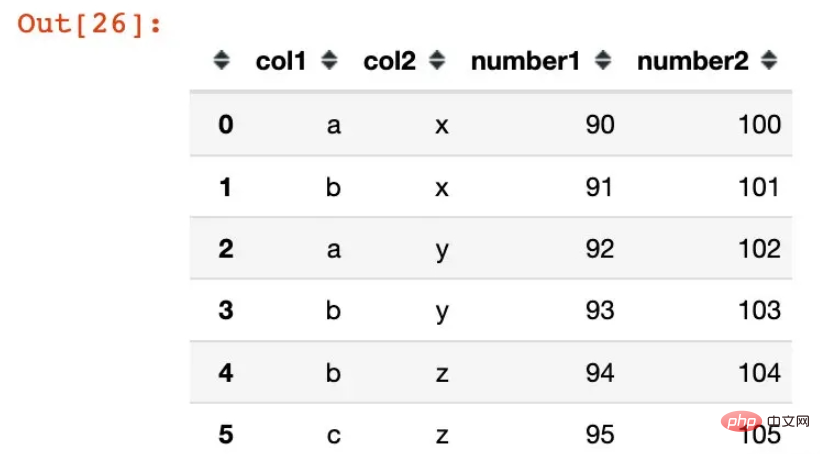
In [26]:
df1 = pd.DataFrame({"col1":list("ababbc"),
"col2":list("xxyyzz"),
"number1":range(90,96),
"number2":range(100,106)})
df1Out[26] :
df2 = df1.groupby(["col1","col2"]).agg({"number1":sum,
"number2":np.mean})
df2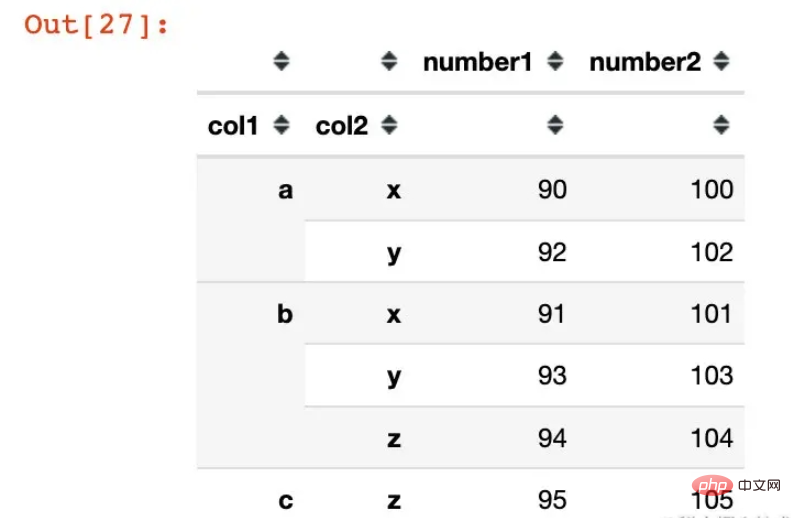
View the index of the data:
In [28]:
df2.index
Out [28]:
MultiIndex([('a', 'x'), ('a', 'y'), ('b', 'x'), ('b', 'y'), ('b', 'z'), ('c', 'z')],
names=['col1', 'col2'])Obtained through the data pivot function:
In [29]:
df3 = df1.pivot_table(values=["col1","col2"],index=["col1","col2"]) df3
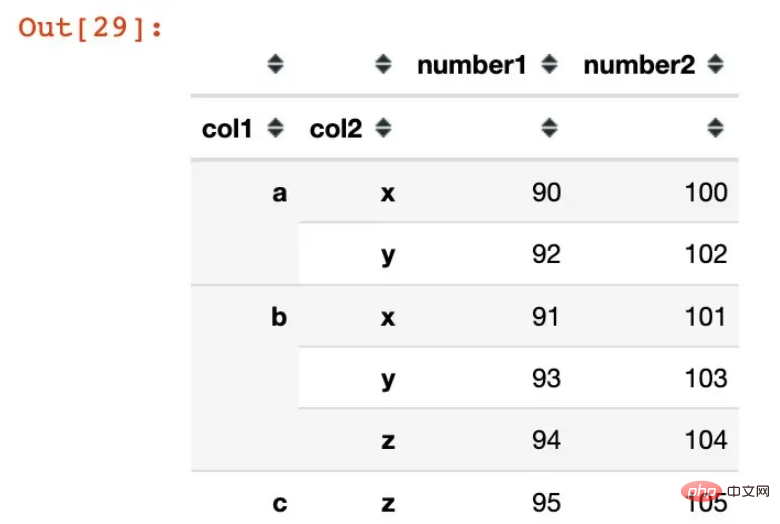
In [30]:
df3.index
Out[30]:
MultiIndex([('a', 'x'), ('a', 'y'), ('b', 'x'), ('b', 'y'), ('b', 'z'), ('c', 'z')],
names=['col1', 'col2'])The above is the detailed content of How to create a multi-level index (MultiIndex) using Python's pandas library?. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!




