 Backend Development
Backend Development
 Python Tutorial
Python Tutorial
 How to implement hot loading of configuration files in Python
How to implement hot loading of configuration files in Python
How to implement hot loading of configuration files in Python
Background
Due to recent work requirements, it is necessary to add a new function to the existing project to implement the configuration hot reloading function. The so-called configuration hot reloading means that after the service receives the configuration update message, we can use the latest configuration to perform tasks without restarting the service.
How to implement
Below I use multi-process, multi-thread, and coroutine methods to implement hot reloading of configuration.
Use multiple processes to implement configuration hot loading
If we use multiple processes in code implementation, the main process 1 updates the configuration and sends instructions, and the task call is process 2. How to implement configuration hot loading Woolen cloth?
Use signal semaphore to implement hot loading
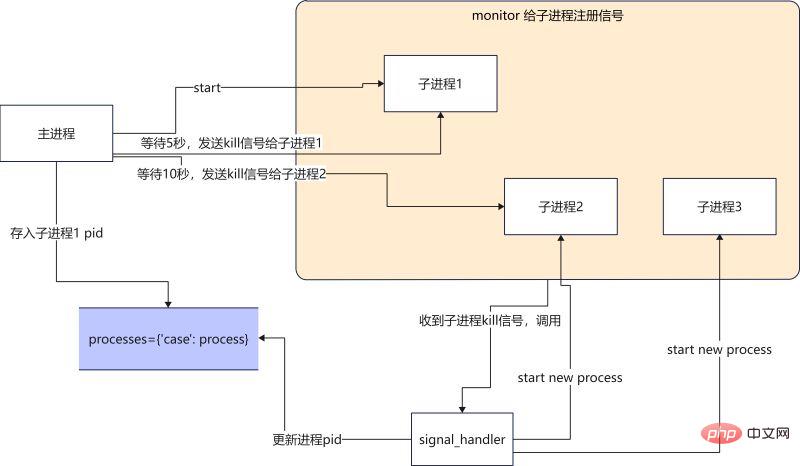
When the main process receives the configuration update message (how does the configuration read receive the configuration update message? ? We won’t discuss it here yet), the main process sends a kill signal to sub-process 1, sub-process 1 exits after receiving the kill signal, and then the signal processing function starts a new process, using the latest configuration file. Continue with the mission.
main function
def main():
# 启动一个进程执行任务
p1 = Process(target=run, args=("p1",))
p1.start()
monitor(p1, run) # 注册信号
processes["case100"] = p1 #将进程pid保存
num = 0
while True: # 模拟获取配置更新
print(
f"{multiprocessing.active_children()=}, count={len(multiprocessing.active_children())}\n")
print(f"{processes=}\n")
sleep(2)
if num == 4:
kill_process(processes["case100"]) # kill 当前进程
if num == 8:
kill_process(processes["case100"]) # kill 当前进程
if num == 12:
kill_process(processes["case100"]) # kill 当前进程
num += 1signal_handler function
def signal_handler(process: Process, func, signum, frame):
# print(f"{signum=}")
global counts
if signum == 17: # 17 is SIGCHILD
# 这个循环是为了忽略SIGTERM发出的信号,避免抢占了主进程发出的SIGCHILD
for signame in [SIGTERM, SIGCHLD, SIGQUIT]:
signal.signal(signame, SIG_DFL)
print("Launch a new process")
p = multiprocessing.Process(target=func, args=(f"p{counts}",))
p.start()
monitor(p, run)
processes["case100"] = p
counts += 1
if signum == 2:
if process.is_alive():
print(f"Kill {process} process")
process.terminate()
signal.signal(SIGCHLD, SIG_IGN)
sys.exit("kill parent process")The complete code is as follows
#! /usr/local/bin/python3.8
from multiprocessing import Process
from typing import Dict
import signal
from signal import SIGCHLD, SIGTERM, SIGINT, SIGQUIT, SIG_DFL, SIG_IGN
import multiprocessing
from multiprocessing import Process
from typing import Callable
from data import processes
import sys
from functools import partial
import time
processes: Dict[str, Process] = {}
counts = 2
def run(process: Process):
while True:
print(f"{process} running...")
time.sleep(1)
def kill_process(process: Process):
print(f"kill {process}")
process.terminate()
def monitor(process: Process, func: Callable):
for signame in [SIGTERM, SIGCHLD, SIGINT, SIGQUIT]:
# SIGTERM is kill signal.
# No SIGCHILD is not trigger singnal_handler,
# No SIGINT is not handler ctrl+c,
# No SIGQUIT is RuntimeError: reentrant call inside <_io.BufferedWriter name='<stdout>'>
signal.signal(signame, partial(signal_handler, process, func))
def signal_handler(process: Process, func, signum, frame):
print(f"{signum=}")
global counts
if signum == 17: # 17 is SIGTERM
for signame in [SIGTERM, SIGCHLD, SIGQUIT]:
signal.signal(signame, SIG_DFL)
print("Launch a new process")
p = multiprocessing.Process(target=func, args=(f"p{counts}",))
p.start()
monitor(p, run)
processes["case100"] = p
counts += 1
if signum == 2:
if process.is_alive():
print(f"Kill {process} process")
process.terminate()
signal.signal(SIGCHLD, SIG_IGN)
sys.exit("kill parent process")
def main():
p1 = Process(target=run, args=("p1",))
p1.start()
monitor(p1, run)
processes["case100"] = p1
num = 0
while True:
print(
f"{multiprocessing.active_children()=}, count={len(multiprocessing.active_children())}\n")
print(f"{processes=}\n")
time.sleep(2)
if num == 4:
kill_process(processes["case100"])
if num == 8:
kill_process(processes["case100"])
if num == 12:
kill_process(processes["case100"])
num += 1
if __name__ == '__main__':
main()The execution results are as follows
multiprocessing.active_children()=[<Process name='Process-1' pid=2533 parent=2532 started>], count=1
processes={'case100': <Process name='Process-1' pid=2533 parent=2532 started>}
p1 running...
p1 running...
kill <Process name='Process-1' pid=2533 parent=2532 started>
multiprocessing.active_children()=[<Process name='Process-1' pid=2533 parent=2532 started>], count=1
processes={'case100': <Process name='Process-1' pid=2533 parent=2532 started>}
signum=17
Launch a new process
p2 running...
p2 running...
multiprocessing.active_children()=[<Process name='Process-2' pid=2577 parent=2532 started>], count=1
processes={'case100': <Process name='Process-2' pid=2577 parent=2532 started>}
p2 running...
p2 running...
multiprocessing.active_children()=[<Process name='Process-2' pid=2577 parent=2532 started>], count=1
processes={'case100': <Process name='Process-2' pid=2577 parent=2532 started>}
p2 running...
p2 running...
multiprocessing.active_children()=[<Process name='Process-2' pid=2577 parent=2532 started>], count=1
processes={'case100': <Process name='Process-2' pid=2577 parent=2532 started>}
p2 running...
p2 running...
kill <Process name='Process-2' pid=2577 parent=2532 started>
signum=17
Launch a new process
multiprocessing.active_children()=[<Process name='Process-2' pid=2577 parent=2532 stopped exitcode=-SIGTERM>], count=1
processes={'case100': <Process name='Process-3' pid=2675 parent=2532 started>}
p3 running...
p3 running...
multiprocessing.active_children()=[<Process name='Process-3' pid=2675 parent=2532 started>], count=1Summary
Benefits: Using semaphores can handle communication problems between multiple processes.
Disadvantages: The code is difficult to write, and the written code is difficult to understand. You must be familiar with the use of semaphores, otherwise it is easy to write a bug for yourself. (All beginners should use it with caution, except experienced drivers.)
Another thing that is not particularly understood isprocess. terminate() The signal sent is SIGTERM number is 15, but the first time signal_handler receives the signal is number=17. If I want to process the signal of 15, This will lead to the problem that the previous process cannot be killed. Anyone who is familiar with semaphores is welcome to give us some advice. Thank you very much.
Use multiprocessing.Event to implement configuration hot loading
The implementation logic is that the main process 1 updates the configuration and sends instructions. Process 2 starts the scheduling task.
At this time, after the main process 1 updates the configuration, it sends an instruction to process 2. The instruction at this time is to use Event to notify an asynchronous event.
Go directly to the code
scheduler function
def scheduler():
while True:
print('wait message...')
case_configurations = scheduler_notify_queue.get()
print(f"Got case configurations {case_configurations=}...")
task_schedule_event.set() # 设置set之后, is_set 为True
print(f"Schedule will start ...")
while task_schedule_event.is_set(): # is_set 为True的话,那么任务就会一直执行
run(case_configurations)
print("Clearing all scheduling job ...")event_scheduler function
def event_scheduler(case_config):
scheduler_notify_queue.put(case_config)
print(f"Put cases config to the Queue ...")
task_schedule_event.clear() # clear之后,is_set 为False
print(f"Clear scheduler jobs ...")
print(f"Schedule job ...")Complete code The execution results are as follows
import multiprocessing
import time
scheduler_notify_queue = multiprocessing.Queue()
task_schedule_event = multiprocessing.Event()
def run(case_configurations: str):
print(f'{case_configurations} running...')
time.sleep(3)
def scheduler():
while True:
print('wait message...')
case_configurations = scheduler_notify_queue.get()
print(f"Got case configurations {case_configurations=}...")
task_schedule_event.set()
print(f"Schedule will start ...")
while task_schedule_event.is_set():
run(case_configurations)
print("Clearing all scheduling job ...")
def event_scheduler(case_config: str):
scheduler_notify_queue.put(case_config)
print(f"Put cases config to the Queue ...")
task_schedule_event.clear()
print(f"Clear scheduler jobs ...")
print(f"Schedule job ...")
def main():
scheduler_notify_queue.put('1')
p = multiprocessing.Process(target=scheduler)
p.start()
count = 1
print(f'{count=}')
while True:
if count == 5:
event_scheduler('100')
if count == 10:
event_scheduler('200')
count += 1
time.sleep(1)
if __name__ == '__main__':
main()The execution results are as follows
wait message... Got case configurations case_configurations='1'... Schedule will start ... 1 running... 1 running... Put cases config to the Queue ... Clear scheduler jobs ... Schedule job ... Clearing all scheduling job ... wait message... Got case configurations case_configurations='100'... Schedule will start ... 100 running... Put cases config to the Queue ... Clear scheduler jobs ... Schedule job ... Clearing all scheduling job ... wait message... Got case configurations case_configurations='200'... Schedule will start ... 200 running... 200 running...
Summary
Using Event event notification, the code is less error-prone, less code is written, and is easier to read. Compared with the previous semaphore method, it is recommended that you use this method more often.
Using multi-threading or coroutine is actually the same as the above implementation method. The only difference is that different libraries are called, queue and event.
# threading scheduler_notify_queue = queue.Queue() task_schedule_event = threading.Event() # async scheduler_notify_queue = asyncio.Queue() task_schedule_event = asyncio.Event()
The above is the detailed content of How to implement hot loading of configuration files in Python. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 Is the conversion speed fast when converting XML to PDF on mobile phone?
Apr 02, 2025 pm 10:09 PM
Is the conversion speed fast when converting XML to PDF on mobile phone?
Apr 02, 2025 pm 10:09 PM
The speed of mobile XML to PDF depends on the following factors: the complexity of XML structure. Mobile hardware configuration conversion method (library, algorithm) code quality optimization methods (select efficient libraries, optimize algorithms, cache data, and utilize multi-threading). Overall, there is no absolute answer and it needs to be optimized according to the specific situation.
 What is the function of C language sum?
Apr 03, 2025 pm 02:21 PM
What is the function of C language sum?
Apr 03, 2025 pm 02:21 PM
There is no built-in sum function in C language, so it needs to be written by yourself. Sum can be achieved by traversing the array and accumulating elements: Loop version: Sum is calculated using for loop and array length. Pointer version: Use pointers to point to array elements, and efficient summing is achieved through self-increment pointers. Dynamically allocate array version: Dynamically allocate arrays and manage memory yourself, ensuring that allocated memory is freed to prevent memory leaks.
 How to convert XML files to PDF on your phone?
Apr 02, 2025 pm 10:12 PM
How to convert XML files to PDF on your phone?
Apr 02, 2025 pm 10:12 PM
It is impossible to complete XML to PDF conversion directly on your phone with a single application. It is necessary to use cloud services, which can be achieved through two steps: 1. Convert XML to PDF in the cloud, 2. Access or download the converted PDF file on the mobile phone.
 Is there any mobile app that can convert XML into PDF?
Apr 02, 2025 pm 08:54 PM
Is there any mobile app that can convert XML into PDF?
Apr 02, 2025 pm 08:54 PM
An application that converts XML directly to PDF cannot be found because they are two fundamentally different formats. XML is used to store data, while PDF is used to display documents. To complete the transformation, you can use programming languages and libraries such as Python and ReportLab to parse XML data and generate PDF documents.
 How to convert xml into pictures
Apr 03, 2025 am 07:39 AM
How to convert xml into pictures
Apr 03, 2025 am 07:39 AM
XML can be converted to images by using an XSLT converter or image library. XSLT Converter: Use an XSLT processor and stylesheet to convert XML to images. Image Library: Use libraries such as PIL or ImageMagick to create images from XML data, such as drawing shapes and text.
 How to control the size of XML converted to images?
Apr 02, 2025 pm 07:24 PM
How to control the size of XML converted to images?
Apr 02, 2025 pm 07:24 PM
To generate images through XML, you need to use graph libraries (such as Pillow and JFreeChart) as bridges to generate images based on metadata (size, color) in XML. The key to controlling the size of the image is to adjust the values of the <width> and <height> tags in XML. However, in practical applications, the complexity of XML structure, the fineness of graph drawing, the speed of image generation and memory consumption, and the selection of image formats all have an impact on the generated image size. Therefore, it is necessary to have a deep understanding of XML structure, proficient in the graphics library, and consider factors such as optimization algorithms and image format selection.
 How to open xml format
Apr 02, 2025 pm 09:00 PM
How to open xml format
Apr 02, 2025 pm 09:00 PM
Use most text editors to open XML files; if you need a more intuitive tree display, you can use an XML editor, such as Oxygen XML Editor or XMLSpy; if you process XML data in a program, you need to use a programming language (such as Python) and XML libraries (such as xml.etree.ElementTree) to parse.
 Recommended XML formatting tool
Apr 02, 2025 pm 09:03 PM
Recommended XML formatting tool
Apr 02, 2025 pm 09:03 PM
XML formatting tools can type code according to rules to improve readability and understanding. When selecting a tool, pay attention to customization capabilities, handling of special circumstances, performance and ease of use. Commonly used tool types include online tools, IDE plug-ins, and command-line tools.





