How to merge and join data using DataFrame in Python?
May 07, 2023 pm 09:04 PMmerge()
1. Conventional merge
①Method 1
Specify a reference column , based on this column, merge other columns.
import pandas as pd
df1 = pd.DataFrame({'id': ['001', '002', '003'],
'num1': [120, 101, 104],
'num2': [110, 102, 121],
'num3': [105, 120, 113]})
df2 = pd.DataFrame({'id': ['001', '002', '003'],
'num4': [80, 86, 79]})
print(df1)
print("=======================================")
print(df2)
print("=======================================")
df_merge = pd.merge(df1, df2, on='id')
print(df_merge)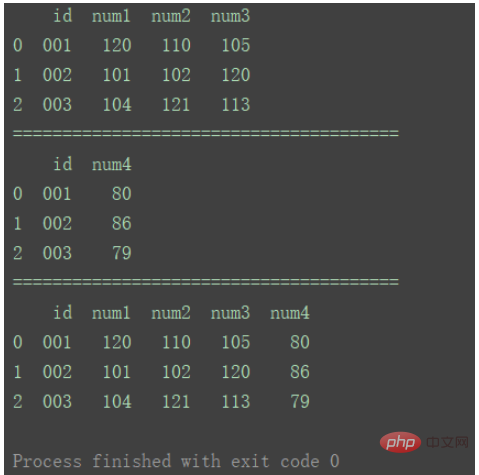
②Method 2
To achieve this merge, you can also merge through the index, that is, based on the index column. Just set both left_index and right_index to True
. (Both left_index and right_index default to False. left_index means that the left table is based on the index of the left table data, and right_index means that the right table is based on the index of the right table data.)
import pandas as pd
df1 = pd.DataFrame({'id': ['001', '002', '003'],
'num1': [120, 101, 104],
'num2': [110, 102, 121],
'num3': [105, 120, 113]})
df2 = pd.DataFrame({'id': ['001', '002', '003'],
'num4': [80, 86, 79]})
print(df1)
print("=======================================")
print(df2)
print("=======================================")
df_merge = pd.merge(df1, df2, left_index=True, right_index=True)
print(df_merge)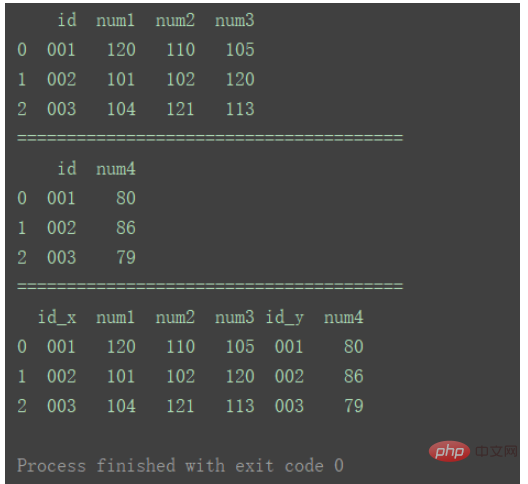
Compared with method ①, the difference is that, as shown in the figure, there are duplicate columns in the data merged by method ②.
Important parameters
pd.merge(right,how=‘inner’, on=“None”, left_on=“None”, right_on=“None”, left_index= False, right_index=False )
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| left | Left table, merged object, DataFrame or Series |
| right | Right table, merged object, DataFrame or Series |
| how | The merging method can be left (left merging), right (right merging), outer (outer merging), inner (inner merging) |
| on | Column name of the base column |
| left_on | Column name of the base column of the left table |
| right_on | Right table base column column name |
| left_index | Whether the left column is based on index, the default is False, no |
| right_index | Whether the right column is based on index, the default is False, no |
Among them, left_index and right_index Cannot be specified together with on.
Merge method left right outer inner
Prepare data‘
Prepare a new set of data:
import pandas as pd
df1 = pd.DataFrame({'id': ['001', '002', '003'],
'num1': [120, 101, 104],
'num2': [110, 102, 121],
'num3': [105, 120, 113]})
df2 = pd.DataFrame({'id': ['001', '004', '003'],
'num4': [80, 86, 79]})
print(df1)
print("=======================================")
print(df2)
print("=======================================") 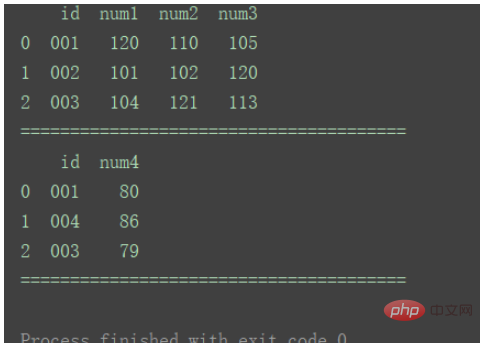
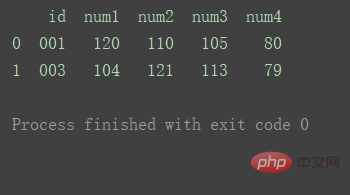
inner (default)
Uses the intersection of keys from both datasets
df_merge = pd.merge(df1, df2, on='id') print(df_merge)
outer
Using the union of keys from both datasets
df_merge = pd.merge(df1, df2, on='id', how="outer") print(df_merge)
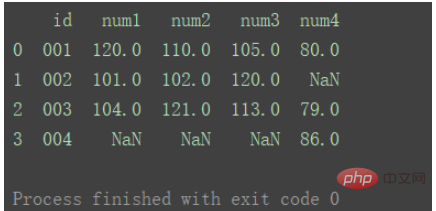
left
Use keys from left data set
df_merge = pd.merge(df1, df2, on='id', how='left') print(df_merge)
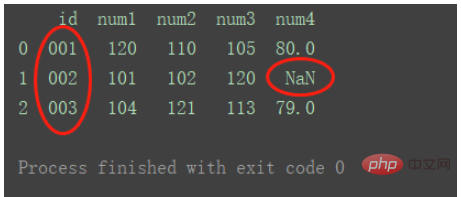
right
Use keys from right data set
df_merge = pd.merge(df1, df2, on='id', how='right') print(df_merge)
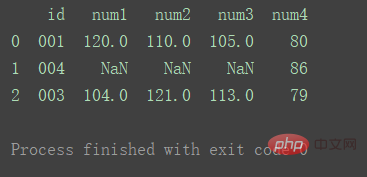
2. Many-to-one merge
import pandas as pd
df1 = pd.DataFrame({'id': ['001', '002', '003'],
'num1': [120, 101, 104],
'num2': [110, 102, 121],
'num3': [105, 120, 113]})
df2 = pd.DataFrame({'id': ['001', '001', '003'],
'num4': [80, 86, 79]})
print(df1)
print("=======================================")
print(df2)
print("=======================================")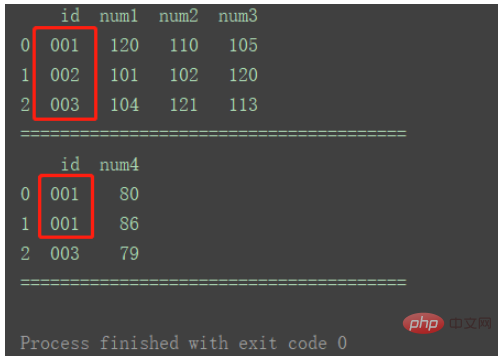
As shown in the figure, there is duplicate id1 data in df2.
Merge
df_merge = pd.merge(df1, df2, on='id') print(df_merge)
The merged result is as shown in the figure:
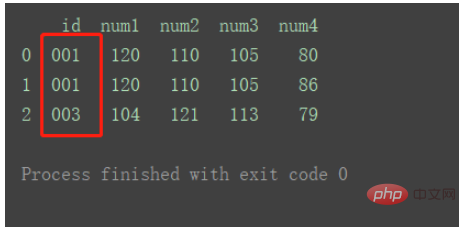
Still according to the default Inner method, using the data from the two data sets The intersection of keys. And rows with duplicate keys will be reflected as multiple rows in the merged result.
3. Many-to-many merge
For example, there are multiple rows with duplicate IDs in both Chart 1 and Table 2.
import pandas as pd
df1 = pd.DataFrame({'id': ['001', '002', '002', '002', '003'],
'num1': [120, 101, 104, 114, 123],
'num2': [110, 102, 121, 113, 126],
'num3': [105, 120, 113, 124, 128]})
df2 = pd.DataFrame({'id': ['001', '001', '002', '003', '001'],
'num4': [80, 86, 79, 88, 93]})
print(df1)
print("=======================================")
print(df2)
print("=======================================")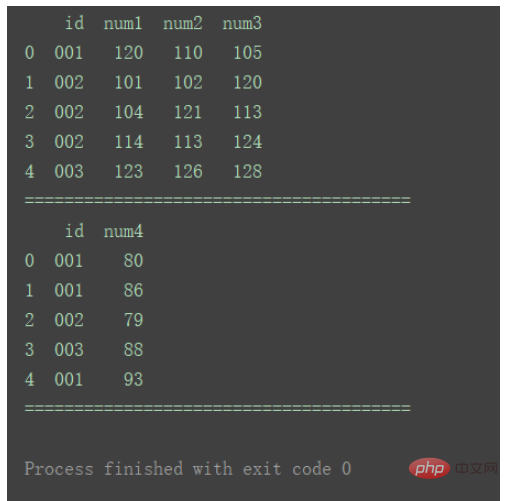
df_merge = pd.merge(df1, df2, on='id') print(df_merge)
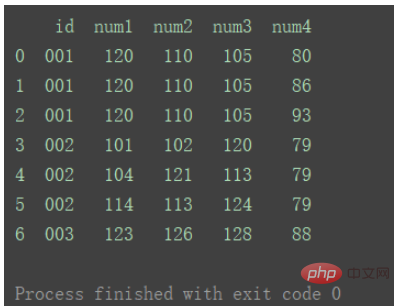
concat()
pd.concat(objs, axis=0, join= ‘outer’, ignore_index:bool=False,keys=None,levels=None,names=None, verify_integrity:bool=False,sort:bool=False,copy:bool=True)
| Parameters | Description |
|---|---|
| objs | A sequence of Series, DataFrame or Panel objects Or mapping |
| axis | Default is 0, indicating columns. If 1 it means row. |
| #join | The default is "outer", it can also be "inner" |
| ignore_index | The default is False, which means the index is retained (not ignored). Set to True to ignore the index. |
其他重要参数通过实例说明。
1.相同字段的表首位相连
首先准备三组DataFrame数据:
import pandas as pd
df1 = pd.DataFrame({'id': ['001', '002', '003'],
'num1': [120, 114, 123],
'num2': [110, 102, 121],
'num3': [113, 124, 128]})
df2 = pd.DataFrame({'id': ['004', '005'],
'num1': [120, 101],
'num2': [113, 126],
'num3': [105, 128]})
df3 = pd.DataFrame({'id': ['007', '008', '009'],
'num1': [120, 101, 125],
'num2': [113, 126, 163],
'num3': [105, 128, 114]})
print(df1)
print("=======================================")
print(df2)
print("=======================================")
print(df3)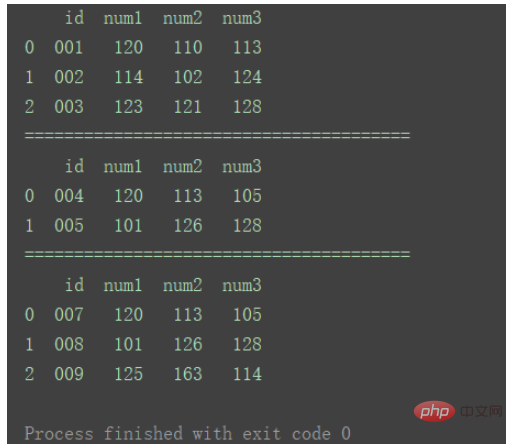
合并
dfs = [df1, df2, df3] result = pd.concat(dfs) print(result)
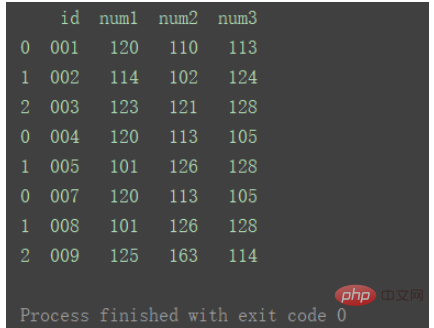
如果想要在合并后,标记一下数据都来自于哪张表或者数据的某类别,则也可以给concat加上 参数keys 。
result = pd.concat(dfs, keys=['table1', 'table2', 'table3']) print(result)
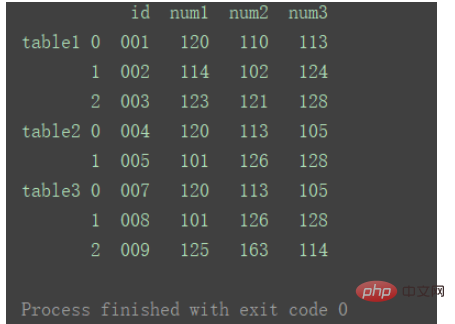
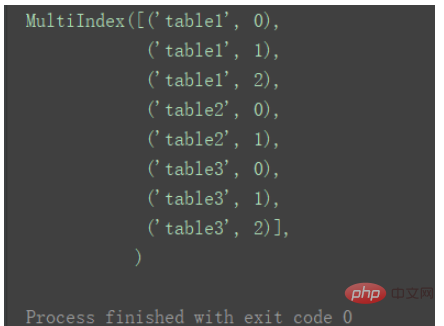
此时,添加的keys与原来的index组成元组,共同成为新的index。
print(result.index)
2.横向表合并(行对齐)
准备两组DataFrame数据:
import pandas as pd
df1 = pd.DataFrame({'num1': [120, 114, 123],
'num2': [110, 102, 121],
'num3': [113, 124, 128]}, index=['001', '002', '003'])
df2 = pd.DataFrame({'num3': [117, 120, 101, 126],
'num5': [113, 125, 126, 133],
'num6': [105, 130, 128, 128]}, index=['002', '003', '004', '005'])
print(df1)
print("=======================================")
print(df2)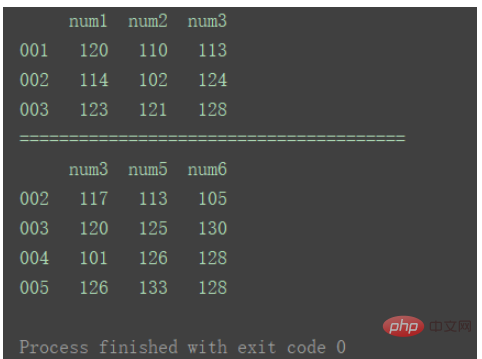
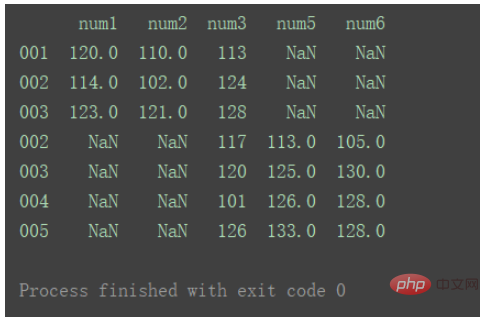
当axis为默认值0时:
result = pd.concat([df1, df2]) print(result)
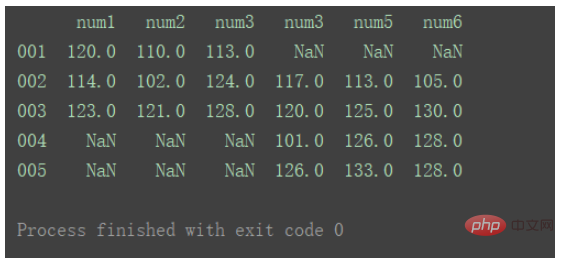
横向合并需要将axis设置为1 :
result = pd.concat([df1, df2], axis=1) print(result)
对比以上输出差异。
axis=0时,即默认纵向合并时,如果出现重复的行,则会同时体现在结果中
axis=1时,即横向合并时,如果出现重复的列,则会同时体现在结果中。
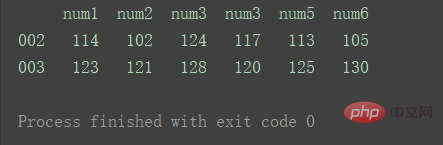
3.交叉合并
result = pd.concat([df1, df2], axis=1, join='inner') print(result)
The above is the detailed content of How to merge and join data using DataFrame in Python?. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot Article

Hot tools Tags

Hot Article

Hot Article Tags

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 What are the advantages and disadvantages of templating?
May 08, 2024 pm 03:51 PM
What are the advantages and disadvantages of templating?
May 08, 2024 pm 03:51 PM
What are the advantages and disadvantages of templating?
 Google AI announces Gemini 1.5 Pro and Gemma 2 for developers
Jul 01, 2024 am 07:22 AM
Google AI announces Gemini 1.5 Pro and Gemma 2 for developers
Jul 01, 2024 am 07:22 AM
Google AI announces Gemini 1.5 Pro and Gemma 2 for developers
 For only $250, Hugging Face's technical director teaches you how to fine-tune Llama 3 step by step
May 06, 2024 pm 03:52 PM
For only $250, Hugging Face's technical director teaches you how to fine-tune Llama 3 step by step
May 06, 2024 pm 03:52 PM
For only $250, Hugging Face's technical director teaches you how to fine-tune Llama 3 step by step
 Share several .NET open source AI and LLM related project frameworks
May 06, 2024 pm 04:43 PM
Share several .NET open source AI and LLM related project frameworks
May 06, 2024 pm 04:43 PM
Share several .NET open source AI and LLM related project frameworks
 A complete guide to golang function debugging and analysis
May 06, 2024 pm 02:00 PM
A complete guide to golang function debugging and analysis
May 06, 2024 pm 02:00 PM
A complete guide to golang function debugging and analysis










