How to use Steam streaming in Java and examples
一. 流的常用创建方法
1-1 使用Collection下的 stream() 和 parallelStream() 方法
List<String> list = new ArrayList<>(); Stream<String> stream = list.stream(); //获取一个顺序流 Stream<String> parallelStream = list.parallelStream(); //获取一个并行流
1-2 使用Arrays 中的 stream() 方法,将数组转成流
Integer[] nums = new Integer[10]; Stream<Integer> stream = Arrays.stream(nums);
1-3 使用Stream中的静态方法:of()、iterate()、generate()
// 1. of() Stream<Integer> stream = Stream.of(1,2,3,4,5,6); // 2. iterate() Stream<Integer> stream2 = Stream.iterate(0, (x) -> x + 2).limit(6); stream2.forEach(System.out::println); // 0 2 4 6 8 10 // 3. generate() Stream<Double> stream3 = Stream.generate(Math::random).limit(2); stream3.forEach(System.out::println);
1-4 使用 BufferedReader.lines() 方法,将每行内容转成流
BufferedReader reader = new BufferedReader(new FileReader("F:\\test_stream.txt"));
Stream<String> lineStream = reader.lines();
lineStream.forEach(System.out::println);1-5 使用 Pattern.splitAsStream() 方法,将字符串分隔成流
Pattern pattern = Pattern.compile(",");
Stream<String> stringStream = pattern.splitAsStream("a,b,c,d");
stringStream.forEach(System.out::println);二、流的中间操作
// 1. 筛选与切片 filter:过滤流中的某些元素 limit skip distinct sorted 都是有状态操作,这些操作只有拿到前面处理后的所有元素之后才能继续下去。 limit(n):获取前n个元素 skip(n):跳过前n元素,配合limit(n)可实现分页 distinct:通过流中元素的 hashCode() 和 equals() 去除重复元素 // 2. 映射 map:接收一个函数作为参数,该函数会被应用到每个元素上,并将其映射成一个新的元素。 flatMap:接收一个函数作为参数,将流中的每个值都换成另一个流,然后把所有流连接成一个流。 // 3. 消费 peek , 类似map, // map接收的是一个Function表达式,有返回值; // 而peek接收的是Consumer表达式,没有返回值。 // 4. 排序 sorted():自然排序,流中元素需实现Comparable接口 sorted(Comparator com):定制排序,自定义Comparator排序器 // 5.
2-1 筛选、去重与切片:filter、distinct、skip、limit
// 实例:集合内元素>5,去重,跳过前两位,取剩下元素的两个返回为新集合 Stream<Integer> stream = Stream.of(6, 4, 6, 7, 3, 9, 8, 10, 12, 14, 14); Stream<Integer> newStream = stream.filter(s -> s > 5) //6 6 7 9 8 10 12 14 14 .distinct() //6 7 9 8 10 12 14 .skip(2) //9 8 10 12 14 .limit(2); //9 8 newStream.forEach(System.out::println);
2-2 映射:map、flatMap
// 1. Map可以看成一个转换器,传入一个对象,返回新的对象
// map的使用实例 stream.map(x->x.getId());
List<String> list = Arrays.asList("a,b,c", "1,2,3");
// 去掉字符串中所有的,
List<String> collect = list.stream().map(s -> s.replaceAll(",", "")).collect(Collectors.toList());
// collect集合内容为:{abc,123}
System.out.println(collect);
// 2. flatMap 效果:结果展平 ,即把嵌套集合,按照子集合的形式,统一放入到新的一个集合中
// 接收一个函数作为参数,将流中的每个值都换成另一个流,
// 然后把所有流连接成一个流。
Stream<String> stringStream = list.stream().flatMap(s -> {
// 将字符串以,分割后得到一个字符串数组
String[] split = s.split(",");
// 然后将每个字符串数组对应流返回,flatMap会自动把返回的所有流连接成一个流
Stream<String> stream = Arrays.stream(split);
return stream;
});
// stringStream.collect(Collectors.toList())的集合内容为:{a,b,c,1,2,3}
System.out.println(stringStream.collect(Collectors.toList()));2-3 归约:统计-计算-逻辑处理:reduce
// 说明:reduce看似效果和map相似,
// 但reduce返回的是函数经过执行运算后的结果,
// 而map返回的是处理后新的集合
List<String> memberNames = new ArrayList<>();
memberNames.add("Amitabh");
memberNames.add("Shekhar");
memberNames.add("Aman");
memberNames.add("Rahul");
memberNames.add("Shahrukh");
memberNames.add("Salman");
memberNames.add("Yana");
memberNames.add("Lokesh");
// 将集合中的元素按照#连接成字符串,并返回放置在Optional<String>中
Optional<String> reduced = memberNames.stream()
.reduce((s1,s2) -> s1 + "#" + s2);
// 有值则取出打印显示
reduced.ifPresent(System.out::println);
// 输出内容: Amitabh#Shekhar#Aman#Rahul#Shahrukh#Salman#Yana#Lokesh
// 计算统计实例:
/**
* T reduce(T identity, BinaryOperator<T> accumulator);
* identity:它允许用户提供一个循环计算的初始值。
* accumulator:计算的累加器,
*/
private static void testReduce() {
//T reduce(T identity, BinaryOperator<T> accumulator);
System.out.println("给定个初始值,求和");
System.out.println(Stream.of(1, 2, 3, 4).reduce(100, (sum, item) -> sum + item));
System.out.println(Stream.of(1, 2, 3, 4).reduce(100, Integer::sum));
// 输出:110
System.out.println("给定个初始值,求min");
System.out.println(Stream.of(1, 2, 3, 4).reduce(100, (min, item) -> Math.min(min, item)));
System.out.println(Stream.of(1, 2, 3, 4).reduce(100, Integer::min));
// 输出:1
System.out.println("给定个初始值,求max");
System.out.println(Stream.of(1, 2, 3, 4).reduce(100, (max, item) -> Math.max(max, item)));
System.out.println(Stream.of(1, 2, 3, 4).reduce(100, Integer::max));
// 输出:100
//Optional<T> reduce(BinaryOperator<T> accumulator);
// 注意返回值,上面的返回是T,泛型,传进去啥类型,返回就是啥类型。
// 下面的返回的则是Optional类型
System.out.println("无初始值,求和");
System.out.println(Stream.of(1, 2, 3, 4).reduce(Integer::sum).orElse(0));
// 输出:10
Integer sum=Stream.of(1, 2, 3, 4).reduce((x,y)->x+y).get();
System.out.println(sum); // 输出:10
System.out.println("无初始值,求max");
System.out.println(Stream.of(1, 2, 3, 4).reduce(Integer::max).orElse(0));
// 输出:4
System.out.println("无初始值,求min");
System.out.println(Stream.of(1, 2, 3, 4).reduce(Integer::min).orElse(0));
// 输出:1
}2-4 排序:sorted
// 按照默认字典顺序排序 stream.sorted(); // 按照sortNo排序 stream.sorted((x,y)->Integer.compare(x.getSortNo(),y.getSortNo())); 2-4-1 函数式接口排序 // 正向排序(默认) pendingPeriod.stream().sorted(Comparator.comparingInt(ReservoirPeriodResult::getId)); // 逆向排序 pendingPeriod.stream().sorted(Comparator.comparingInt(ReservoirPeriodResult::getId).reversed()); 2-4-2 LocalDate 和 LocalDateTime 排序 // 准备测试数据 Stream<DateModel> stream = Stream.of(new DateModel(LocalDate.of(2020, 1, 1)) , new DateModel(LocalDate.of(2021, 1, 1)), new DateModel(LocalDate.of(2022, 1, 1))); // 正向排序(默认) stream.sorted(Comparator.comparing(DateModel::getLocalDate)) .forEach(System.out::println); // 逆向排序 stream.sorted(Comparator.comparing(DateModel::getLocalDate).reversed()) .forEach(System.out::println);
三. 流的终止操作 allMatch,noneMatch,anyMatch,findFirst,findAny,count,max,min
// 匹配和聚合
allmatch,noneMatch,anyMatch用于对集合中对象的某一个属性值是否存在判断。
allMatch全部符合该条件返回true,
noneMatch全部不符合该断言返回true
anyMatch 任意一个元素符合该断言返回true
// 实例:
List<Integer> list = Arrays.asList(1, 2, 3, 4, 5);
boolean allMatch = list.stream().allMatch(e -> e > 10); //false
boolean noneMatch = list.stream().noneMatch(e -> e > 10); //true
boolean anyMatch = list.stream().anyMatch(e -> e > 4); //true
// 其他一些方法
findFirst:返回流中第一个元素
String firstMatchedName = memberNames.stream()
.filter((s) -> s.startsWith("L"))
.findFirst().get();
findAny:返回流中的任意元素
count:返回流中元素的总个数
long totalMatched = memberNames.stream()
.filter((s) -> s.startsWith("A"))
.count();
max:返回流中元素最大值
min:返回流中元素最小值3-1 普通收集 – 收集为List
// 默认返回的类型为ArrayList,可通过Collectors.toCollection(LinkedList::new)
// 显示指明使用其它数据结构作为返回值容器。
List<String> collect = stream.collect(Collectors.toList());
// 由集合创建流的收集需注意:仅仅修改流字段中的内容,没有返回新类型,
// 如下操作直接修改原始集合,无需处理返回值。
userVos.stream().map(e -> e.setDeptName(hashMap.get(e.getDeptId())))
.collect(Collectors.toList());
// 收集偶数集合的实例:
List<Integer> list = new ArrayList<Integer>();
for(int i = 1; i< 10; i++){
list.add(i);
}
Stream<Integer> stream = list.stream();
List<Integer> evenNumbersList = stream.filter(i -> i%2 == 0)
.collect(Collectors.toList());
System.out.print(evenNumbersList);3-2 普通收集 – 收集流为数组(Array)
// list 为 {1,2,3,.....100}
Stream<Integer> stream = list.stream();
Integer[] evenNumbersArr = stream.filter(i -> i%2 == 0).toArray(Integer[]::new);3-3 普通收集 – 收集为Set
// 默认返回类型为HashSet,可通过Collectors.toCollection(TreeSet::new) // 显示指明使用其它数据结构作为返回值容器。 Set<String> collect = stream.collect(Collectors.toSet());
3-4 高级收集 – 收集为Map
// 默认返回类型为HashMap,可通过Collectors.toCollection(LinkedHashMap::new)
// 显示指明使用其它数据结构作为返回值容器
// 测试实体类
@Data
public class Entity {
private Integer id;
private String name;
}
// 模拟从数据库中查询批量的数据
List<Entity> entityList = Stream.of(new Entity(1,"A"),
new Entity(2,"B"), new Entity(3,"C")).collect(Collectors.toList());
// 将集合数据转化成id与name的Map
Map<Integer, String> hashMap = entityList.stream()
.collect(Collectors.toMap(Entity::getId, Entity::getName));3-5 高级收集 – 分组收集
// 默认使用List作为分组后承载容器 Map<Integer, List<XUser>> hashMap = xUsers.stream().collect(Collectors.groupingBy(XUser::getDeptId)); // 显示指明使用List作为分组后承载容器 Map<Integer, List<XUser>> hashMap = xUsers.stream().collect(Collectors.groupingBy(XUser::getDeptId, Collectors.toList())); // 映射后再分组 Map<Integer, List<String>> hashMap = xUsers.stream().collect(Collectors.groupingBy(XUser::getDeptId,Collectors.mapping(XUser::getUserName,Collectors.toList())));
四. Steam拓展
4-1 集合与对象互转
/**
* 将单个对象转化为集合
*
* @param t 对象实例
* @param <T> 对象类型
* @param <C> 集合类型
* @return 包含对象的集合实例
*/
public static <T, C extends Collection<T>> Collection<T> toCollection(T t) {
return toCollection(t, ArrayList::new);
}
/**
* 用户自定义返回的集合实例类型: 将单个对象转化为集合
*
* @param t 对象实例
* @param supplier 集合工厂
* @param <T> 对象类型
* @param <C> 集合类型
* @return 包含对象的集合实例
*/
public static <T, C extends Collection<T>> Collection<T> toCollection(T t, Supplier<C> supplier) {
return Stream.of(t).collect(Collectors.toCollection(supplier));
}4-2 集合转对象
/**
* 取出集合中第一个元素
*
* @param collection 集合实例
* @param <E> 集合中元素类型
* @return 泛型类型
*/
public static <E> E toObject(Collection<E> collection) {
// 处理集合空指针异常
Collection<E> coll = Optional.ofNullable(collection).orElseGet(ArrayList::new);
// 此处可以对流进行排序,然后取出第一个元素
return coll.stream().findFirst().orElse(null);
}4-3 Java Steam中的并发操作实例
List<Integer> list = new ArrayList<Integer>();
for(int i = 1; i< 10; i++){
list.add(i);
}
Stream<Integer> stream = list.parallelStream(); // 创建并发流
Integer[] evenNumbersArr = stream.filter(i -> i%2 == 0).toArray(Integer[]::new);
System.out.print(evenNumbersArr); // 打印出的偶数为无规则排序的The above is the detailed content of How to use Steam streaming in Java and examples. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1378
1378
 52
52
 Java Spring Interview Questions
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:29 PM
Java Spring Interview Questions
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:29 PM
In this article, we have kept the most asked Java Spring Interview Questions with their detailed answers. So that you can crack the interview.
 Break or return from Java 8 stream forEach?
Feb 07, 2025 pm 12:09 PM
Break or return from Java 8 stream forEach?
Feb 07, 2025 pm 12:09 PM
Java 8 introduces the Stream API, providing a powerful and expressive way to process data collections. However, a common question when using Stream is: How to break or return from a forEach operation? Traditional loops allow for early interruption or return, but Stream's forEach method does not directly support this method. This article will explain the reasons and explore alternative methods for implementing premature termination in Stream processing systems. Further reading: Java Stream API improvements Understand Stream forEach The forEach method is a terminal operation that performs one operation on each element in the Stream. Its design intention is
 TimeStamp to Date in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:28 PM
TimeStamp to Date in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:28 PM
Guide to TimeStamp to Date in Java. Here we also discuss the introduction and how to convert timestamp to date in java along with examples.
 Java Program to Find the Volume of Capsule
Feb 07, 2025 am 11:37 AM
Java Program to Find the Volume of Capsule
Feb 07, 2025 am 11:37 AM
Capsules are three-dimensional geometric figures, composed of a cylinder and a hemisphere at both ends. The volume of the capsule can be calculated by adding the volume of the cylinder and the volume of the hemisphere at both ends. This tutorial will discuss how to calculate the volume of a given capsule in Java using different methods. Capsule volume formula The formula for capsule volume is as follows: Capsule volume = Cylindrical volume Volume Two hemisphere volume in, r: The radius of the hemisphere. h: The height of the cylinder (excluding the hemisphere). Example 1 enter Radius = 5 units Height = 10 units Output Volume = 1570.8 cubic units explain Calculate volume using formula: Volume = π × r2 × h (4
 How to Run Your First Spring Boot Application in Spring Tool Suite?
Feb 07, 2025 pm 12:11 PM
How to Run Your First Spring Boot Application in Spring Tool Suite?
Feb 07, 2025 pm 12:11 PM
Spring Boot simplifies the creation of robust, scalable, and production-ready Java applications, revolutionizing Java development. Its "convention over configuration" approach, inherent to the Spring ecosystem, minimizes manual setup, allo
 Create the Future: Java Programming for Absolute Beginners
Oct 13, 2024 pm 01:32 PM
Create the Future: Java Programming for Absolute Beginners
Oct 13, 2024 pm 01:32 PM
Java is a popular programming language that can be learned by both beginners and experienced developers. This tutorial starts with basic concepts and progresses through advanced topics. After installing the Java Development Kit, you can practice programming by creating a simple "Hello, World!" program. After you understand the code, use the command prompt to compile and run the program, and "Hello, World!" will be output on the console. Learning Java starts your programming journey, and as your mastery deepens, you can create more complex applications.
 Java Made Simple: A Beginner's Guide to Programming Power
Oct 11, 2024 pm 06:30 PM
Java Made Simple: A Beginner's Guide to Programming Power
Oct 11, 2024 pm 06:30 PM
Java Made Simple: A Beginner's Guide to Programming Power Introduction Java is a powerful programming language used in everything from mobile applications to enterprise-level systems. For beginners, Java's syntax is simple and easy to understand, making it an ideal choice for learning programming. Basic Syntax Java uses a class-based object-oriented programming paradigm. Classes are templates that organize related data and behavior together. Here is a simple Java class example: publicclassPerson{privateStringname;privateintage;
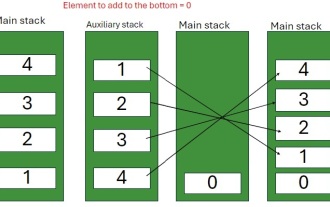 Java Program to insert an element at the Bottom of a Stack
Feb 07, 2025 am 11:59 AM
Java Program to insert an element at the Bottom of a Stack
Feb 07, 2025 am 11:59 AM
A stack is a data structure that follows the LIFO (Last In, First Out) principle. In other words, The last element we add to a stack is the first one to be removed. When we add (or push) elements to a stack, they are placed on top; i.e. above all the




