How to create and call functions in Python?
Create function
The function is created with the def statement. The syntax is as follows:
def 函数名(参数列表): # 具体情况具体对待,参数可有可无
"""函数说明文档字符串"""
函数封装的代码
……The title line consists of the def keyword, the name of the function, and the set of arguments (if any) forming the
def The remainder of the clause includes an optional but strongly recommended docstring, and Required function body
The naming of function name should comply with the naming rules of identifiers
can be composed of letters, underscores and numbers
cannot start with numbers
cannot have the same name as a keyword
def washing_machine(): # 洗衣机可以帮我们完成
print("打水")
print("洗衣服")
print("甩干")Calling a function
Use a pair of parentheses () to call a function. If there are no parentheses, it is just a reference to the function.
Any input parameters All must be placed in brackets
Legend:

Case: Add washing powder
def washing_machine(): # 洗衣机可以帮我们完成
print("打水")
print("加洗衣粉!!!")
print("洗衣服")
print("甩干")
# 早上洗衣服
washing_machine()
# 中午洗衣服
washing_machine()
# 晚上洗衣服
washing_machine()
Summary
After defining the function, it only means that this function encapsulates a piece of code
If you do not actively call the function, the function will not actively execute
Thinking
Can I put function call above function definition?
cannot!
Because before using the function name to call the function, you must ensure that
Pythonalready knows the existence of the functionOtherwise the console will prompt
NameError: name 'menu' is not defined(NameError: the name menu is not defined)
Parameters of function
Formal parameters and actual parameters
##Formal parameters:When defining function , the parameters in parentheses are used to receive parameters. Inside the function is used as a variable
actual parameter : When calling a function, the parameters in parentheses are used to pass data to inside the function
Question
When we want to wash other things, we need to manually change the code inside the method:def washing_machine(): # 洗衣机可以帮我们完成
print("打水")
print("加洗衣粉!!!")
print("洗床单") # 洗被套
print("甩干")def washing_machine(): # 洗衣机可以帮我们完成
print("打水")
print("加洗衣粉!!!")
print("洗衣服")
print("甩干")
washing_machine()
def washing_machine(): # 洗衣机可以帮我们完成
print("打水")
print("加洗衣粉!!!")
print("洗床单")
print("甩干")
washing_machine()
......Thinking What are the problems?
The function can only process fixed dataHow to solve it?
It would be great if the data that needs to be processed can be passed to the inside of the function when calling the function! Pass parameters- Fill in the parentheses after the function name
Parameters
- More Use
,
to separate the parameters - When calling a function, the number of actual parameters needs to be consistent with the number of formal parameters, and the actual parameters will be passed to the formal parameters in turn. Parameter
def washing_machine(something): # 洗衣机可以帮我们完成
print("打水")
print("加洗衣粉!!!")
print("洗" + something)
print("甩干")
# 洗衣服
washing_machine("衣服")
# 洗床单
washing_machine("床单")Legend

def washing_machine(xidiji,something): # 洗衣机可以帮我们完成
print("打水")
print("加" + xidiji)
print("洗衣服" + something)
print("甩干")
#早上洗衣服
#按照参数位置顺序传递参数的方式叫做位置传参
#使用洗衣机,执行洗衣机内部的逻辑
washing_machine("洗衣液","衣服")#something = 衣服
#中午洗被罩
washing_machine("洗衣粉","被罩")# something = 被罩
#晚上洗床单
washing_machine("五粮液","床单")# something = 床单Function
The- function organizes code blocks with independent functions into a small module and calls the parameters of the
- function when needed to increase the versatility of the function and target the same The data processing logic can adapt to more data
shell scripts, program The name and parameters are passed to the python program in the form of positional parameters, using the sys module's argv list to receive
Legend
Default value. Because a default value is assigned to the parameter, when the function is called It is also allowed not to pass a value to the parameter
The return value of the function- In program development, sometimes, you will want
A function to execute After the end, tell the caller a result so that the caller can perform subsequent processing on the specific result
The return value is the function to complete the work After that, Finally gives the caller a result
在函数中使用
return关键字可以返回结果调用函数一方,可以 使用变量 来 接收 函数的返回结果
案例:计算任意两个数字的和
# 函数的返回值: return, 用于对后续逻辑的处理
# 理解: 把结果揣兜里,后续想干啥干啥,想打印打印,想求和就求和
# 注意:
# a. 函数中如果没有return,那么解释器会自动加一个return None
# b. return表示函数的终止,return后的代码都不会执行
# 1 定义一个函数,计算两个数的和
# 2 计算这两个数的和是不是偶数
def get_sum(x, y=100): # 默认参数
he = x + y # sum = 10 + 20
return he # return 30
print("return表示函数的终止,return后的代码都不会执行")
# 将函数return后的结果赋值给变量dc: dc = sum -> dc = 30
dc = get_sum(10, 20) # x = 10, y = 20
print("dc:", dc) # 30
dc1 = get_sum(10) # x = 10, y = 100
print("dc1:", dc1) # 110
# if dc % 2 == 0:
# print("偶数")
# else:
# print("奇数")#默认参数
#注意:具有默认值的参数后面不能跟没有默认值的参数
def get_sum(a=20,b=5,c=10):
he = a + b+ c
return he
dc = get_sum(1,2,3) #a=1 b=2 c=3
print("dc:",dc) # 6
dc1 = get_sum(1,2) # a=1 b=2 c=10
print("dc1:",dc1) # 13
dc2 = get_sum(1) # a=1 b=5 c=10
print("dc2:",dc2) # 16
dc3 = get_sum()
print("dc3:",dc3) # 35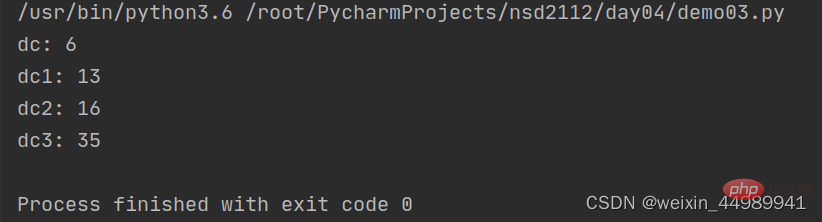
修改菲波那切数列
def new_fib(n=8):
list01 = [0,1] #定义列表,指定初始值
for dc in range(n-2):
list01.append(list01[-1]+list01[-2])
return list01
dc = new_fib() #不加参数默认是8
dc1 = new_fib(10)
print("dc:",dc)
print("dc1:",dc1)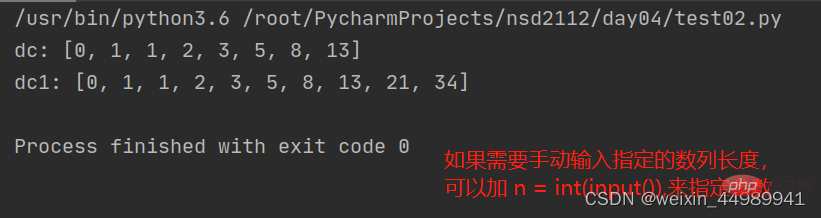
生成随机密码:
#练习:生成随机密码
#创建 randpass.py 脚本,要求如下:
#编写一个能生成8位随机密码的程序
#使用 random 的 choice 函数随机取出字符
#由用户决定密码长度
import random
def new_password():
n = int(input("密码长度:"))
password = ""
all = "0123456789zxcvbnmlkjhgfdsaqwertyuiopPOIUYTREWQASDFGHJKLMNBVCXZ" # 0-9 a-z A-Z
random.choice(all)
for i in range(n):
dc = random.choice(all)
password += dc
# print("passwd:",password)
return password
# 调用函数,才能执行函数内部逻辑
dc = new_password()
print("dc:",dc)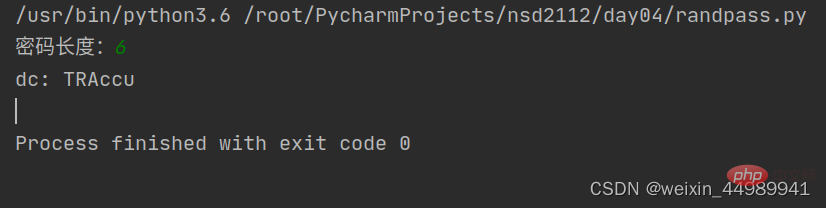
#练习:生成随机密码
#创建 randpass.py 脚本,要求如下:
#编写一个能生成8位随机密码的程序
#使用 random 的 choice 函数随机取出字符
#由用户决定密码长度
import random,string
def new_password():
n = int(input("密码长度:"))
password = ""
all = string.ascii_letters + string.digits
random.choice(all)
for i in range(n):
dc = random.choice(all)
password += dc
# print("passwd:",password)
return password
# 调用函数,才能执行函数内部逻辑
dc = new_password()
print("dc:",dc)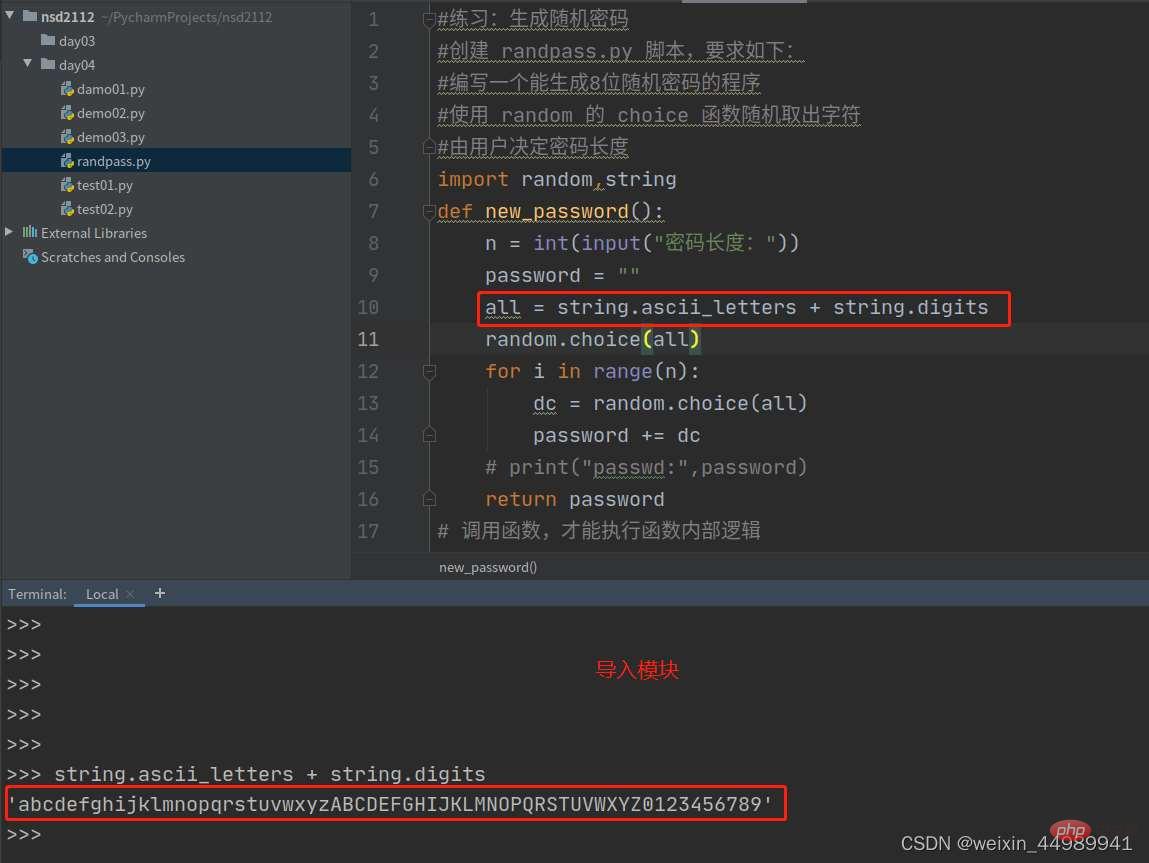
模块基础
定义模块
基本概念
模块是从逻辑上组织python代码的形式
当代码量变得相当大的时候,最好把代码分成一些有组织的代码段,前提是保证它们的 彼此交互
这些代码片段相互间有一定的联系,可能是一个包含数据成员和方法的类,也可能是一组相关但彼此独立的操作函数
导入模块 (import)
使用 import 导入模块
模块属性通过 “模块名.属性” 的方法调用
如果仅需要模块中的某些属性,也可以单独导入
为什么需要导入模块?
可以提升开发效率,简化代码
正确使用
# test.py,将 file_copy.py 放在同级目录下 # 需求:要将/etc/passwd复制到/tmp/passwd src_path = "/etc/passwd" dst_path = "/tmp/passwd" # 如何复制? # 调用已有模块中的方法 # - 很推荐,简单粗暴不动脑 # - 直接使用 file_copy.py的方法即可 # 导入方法一:直接导入模块 import file_copy # 要注意路径问题 file_copy.copy(src_path, dst_path) # 导入方法二:只导入 file_copy 模块的 copy 方法 from file_copy import copy # 如果相同时导入多个模块 from file_copy import * copy(src_path, dst_path) # 导入方法四:导入模块起别名 as import file_copy as fc fc.copy(src_path, dst_path)
常用的导入模块的方法
一行指导入一个模块,可以导入多行, 例如:
import random只导入模块中的某些方法,例如:
from random import choice,randint
模块加载 (load)
一个模块只被 加载一次,无论它被导入多少次
只加载一次可以 阻止多重导入时,代码被多次执行
如果两个文件相互导入,防止了无限的相互加载
模块加载时,顶层代码会自动执行,所以只将函数放入模块的顶层是最好的编程习惯
模块特性及案例
模块特性
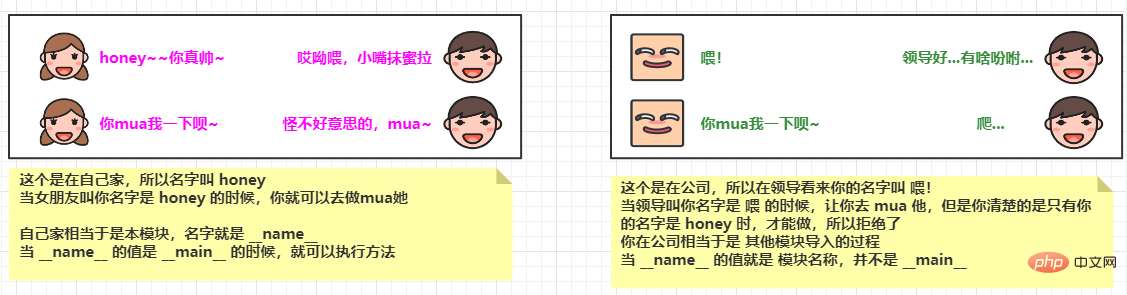
模块在被导入时,会先完整的执行一次模块中的 所有程序
案例
# foo.py print(__name__) # bar.py import foo # 导入foo.py,会将 foo.py 中的代码完成的执行一次,所以会执行 foo 中的 print(__name__)
结果:
# foo.py -> __main__ 当模块文件直接执行时,__name__的值为‘__main__’
# bar.py -> foo 当模块被另一个文件导入时,__name__的值就是该模块的名字
所以我们以后在 Python 模块中执行代码的标准格式:
def test():
......
if __name__ == "__main__":
test()The above is the detailed content of How to create and call functions in Python?. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1386
1386
 52
52
 Can visual studio code be used in python
Apr 15, 2025 pm 08:18 PM
Can visual studio code be used in python
Apr 15, 2025 pm 08:18 PM
VS Code can be used to write Python and provides many features that make it an ideal tool for developing Python applications. It allows users to: install Python extensions to get functions such as code completion, syntax highlighting, and debugging. Use the debugger to track code step by step, find and fix errors. Integrate Git for version control. Use code formatting tools to maintain code consistency. Use the Linting tool to spot potential problems ahead of time.
 How to run programs in terminal vscode
Apr 15, 2025 pm 06:42 PM
How to run programs in terminal vscode
Apr 15, 2025 pm 06:42 PM
In VS Code, you can run the program in the terminal through the following steps: Prepare the code and open the integrated terminal to ensure that the code directory is consistent with the terminal working directory. Select the run command according to the programming language (such as Python's python your_file_name.py) to check whether it runs successfully and resolve errors. Use the debugger to improve debugging efficiency.
 Can vs code run in Windows 8
Apr 15, 2025 pm 07:24 PM
Can vs code run in Windows 8
Apr 15, 2025 pm 07:24 PM
VS Code can run on Windows 8, but the experience may not be great. First make sure the system has been updated to the latest patch, then download the VS Code installation package that matches the system architecture and install it as prompted. After installation, be aware that some extensions may be incompatible with Windows 8 and need to look for alternative extensions or use newer Windows systems in a virtual machine. Install the necessary extensions to check whether they work properly. Although VS Code is feasible on Windows 8, it is recommended to upgrade to a newer Windows system for a better development experience and security.
 Is the vscode extension malicious?
Apr 15, 2025 pm 07:57 PM
Is the vscode extension malicious?
Apr 15, 2025 pm 07:57 PM
VS Code extensions pose malicious risks, such as hiding malicious code, exploiting vulnerabilities, and masturbating as legitimate extensions. Methods to identify malicious extensions include: checking publishers, reading comments, checking code, and installing with caution. Security measures also include: security awareness, good habits, regular updates and antivirus software.
 Python: Automation, Scripting, and Task Management
Apr 16, 2025 am 12:14 AM
Python: Automation, Scripting, and Task Management
Apr 16, 2025 am 12:14 AM
Python excels in automation, scripting, and task management. 1) Automation: File backup is realized through standard libraries such as os and shutil. 2) Script writing: Use the psutil library to monitor system resources. 3) Task management: Use the schedule library to schedule tasks. Python's ease of use and rich library support makes it the preferred tool in these areas.
 What is vscode What is vscode for?
Apr 15, 2025 pm 06:45 PM
What is vscode What is vscode for?
Apr 15, 2025 pm 06:45 PM
VS Code is the full name Visual Studio Code, which is a free and open source cross-platform code editor and development environment developed by Microsoft. It supports a wide range of programming languages and provides syntax highlighting, code automatic completion, code snippets and smart prompts to improve development efficiency. Through a rich extension ecosystem, users can add extensions to specific needs and languages, such as debuggers, code formatting tools, and Git integrations. VS Code also includes an intuitive debugger that helps quickly find and resolve bugs in your code.
 Can vs code run python
Apr 15, 2025 pm 08:21 PM
Can vs code run python
Apr 15, 2025 pm 08:21 PM
Yes, VS Code can run Python code. To run Python efficiently in VS Code, complete the following steps: Install the Python interpreter and configure environment variables. Install the Python extension in VS Code. Run Python code in VS Code's terminal via the command line. Use VS Code's debugging capabilities and code formatting to improve development efficiency. Adopt good programming habits and use performance analysis tools to optimize code performance.
 Can visual studio code run python
Apr 15, 2025 pm 08:00 PM
Can visual studio code run python
Apr 15, 2025 pm 08:00 PM
VS Code not only can run Python, but also provides powerful functions, including: automatically identifying Python files after installing Python extensions, providing functions such as code completion, syntax highlighting, and debugging. Relying on the installed Python environment, extensions act as bridge connection editing and Python environment. The debugging functions include setting breakpoints, step-by-step debugging, viewing variable values, and improving debugging efficiency. The integrated terminal supports running complex commands such as unit testing and package management. Supports extended configuration and enhances features such as code formatting, analysis and version control.




