What are byte streams and character streams in Java
Byte stream and character stream
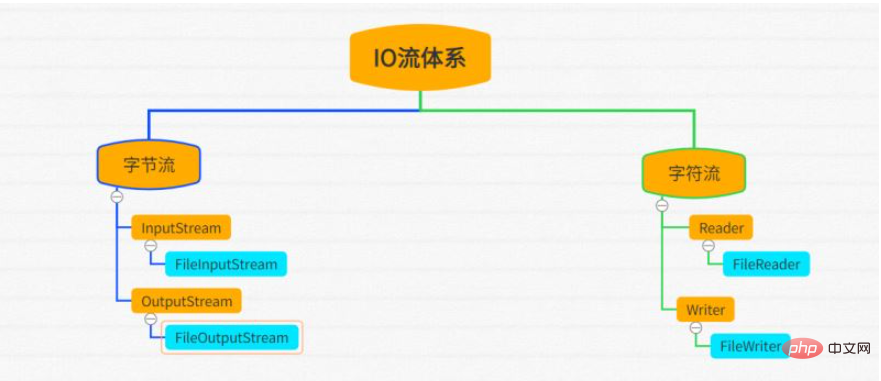
In the above figure, the orange part is the abstract class, and the blue part is the implementation class
Byte stream
Byte stream, as the name suggests, is the operation of subdividing data into bytes to read and write files. It is mainly divided into byte input stream and byte output stream.
Byte input stream
The following are the constructors and methods often used in byte input streams:
| Constructor | Description |
| public FileInputStream (File file) | Create a byte input stream pipe to connect to the source file object |
| public FileInputStream(String pathname) | Create a byte input stream pipeline and connect it to the source file path |
| Method name | Description |
| public int read() | Returns one byte each time it is read. If the byte is no longer available Read returns -1 |
| public int read(byte[] buffer) | Returns each time a byte array is read, if there are no readable bytes Return -1 |
# Next, let’s better deepen our understanding of this part of the knowledge through the code!
File file = new File("File//data.txt");
//第一种构造器,参数是File类
InputStream inputStream = new FileInputStream(file);
//第二种构造器,参数是文件的路径,可以是相对也可以是绝对的路径
InputStream inputStream1 = new FileInputStream("File//data.txt");
//通过字节读取文件中的数据
int len;
while ((len=inputStream.read()) != -1){
System.out.print((char) len);
}
System.out.println();
//通过字节数组读取文件中的数据
byte [] buffer = new byte[3];
while ((len=inputStream1.read(buffer))!=-1){
String s = new String(buffer,0,len);
System.out.print(s);
}
//输出结果:
//ab1abab
//ab1ababNow that the output result we see corresponds one-to-one with the content in the file, then there must be no problem with it? Actually not, it’s just that we haven’t encountered any problems yet. First of all, what we should understand is that in utf-8, letters and numbers are one byte, and Chinese is composed of three bytes, so when our When Chinese characters appear in the file, the first method cannot achieve normal reading, because reading one byte each time will disassemble the Chinese characters, resulting in garbled characters when output; while the second method Then the method can realize the output of Chinese characters under special circumstances. The condition that must be met is that all three bytes of Chinese characters are in the same byte array.
The byte input stream is not suitable for all file data, which leads to the character input stream.
Byte output stream
The following are commonly used methods for byte output stream:
| Method | Description |
| public void write (int a) | Write a byte out |
| public void write (byte [ ]buffer ) | Write a byte array out |
| public void write (byte [ ]buffer,int off, int len) | Put a byte Part of the array is written out |
| file.close() | The stream is closed and no more data can be written |
| file .flush() | Updating the stream, you can continue to write data |
Next, let’s better deepen our understanding of this part of the knowledge through the code. !
OutputStream outputStream = new FileOutputStream("File//data.txt",true);
//true表示可以对文件进行追加内容,若没有true则会在关闭文件之后,进行写文件的时候会对之前的内容进行覆盖。
outputStream.write('a');
outputStream.write(13);
outputStream.write('美');
outputStream.flush();
byte[] buffer = {'s','y','l','m',99};
outputStream.write(buffer);
outputStream.write(buffer,1,3);
outputStream.close();After the above series of operations, the data will be written into the data.txt file, but problems will still occur. Sometimes Chinese cannot be written normally, so it is not a file suitable for all , which leads to the character output stream.
Character stream
Character stream, as the name suggests, is the operation of subdividing data into characters to read and write files. It is mainly divided into character input stream and character output stream.
Character input stream
The following are the constructors and methods often used in character input streams:
| Constructor | Description |
| public FileReader (File file) | Create a character input stream pipeline to connect to the source file object |
| public FileReader(String pathname) | Create a character input stream pipeline and connect it to the source file path |
| Method | Description |
| public int read() | Returns one character each time it is read. If the character is no longer readable, it returns -1 |
| public int read (char [ ]buffer) | Each time a character array is read, a character array is returned and the number of characters read is returned. If there are no readable characters, - 1 |
字符输入流的构造器和方法大致上和字节输入流的相同,不同的地方在于字符输入流是以字符为单位的读取,无论你是字母还是数字,都作为一个字符进行读取,这样便可以避免在读取中文的时候出现乱码的问题。
接下来通过一部分代码来加深对它的理解吧!
File file = new File("File//data.txt");
//第一种构造器,参数是File类
FileReader fileReader = new FileReader(file);
//第二种构造器,参数是文件的绝对路径或者相对路径
FileReader fileReader1 = new FileReader("File//data.txt");
//第一种方法,一个一个字符读取
int len;
while ((len = fileReader.read())!=-1){
System.out.print((char) len);
}
//第二种方法,以字符数组进行读取
char []buffer = new char[3];
while ((len = fileReader1.read(buffer))!=-1){
String s = new String(buffer,0,len);
System.out.println(s);
}
//输出结果:
//110,119,120
//110
//,11
//9,1
//20通过以字符为单位的读写,便可以避免在读取中文的时候出现乱码的问题了。
字符输出流
下面是字符输出流中经常会用到的构造器和方法:
| 构造器 | 说明 |
| public FileWriter(File file) | 创建字符输出流管道与源文件对象接通 |
| public FileWriter(File file,boolean append) | 创建字符输出流管道与源文件对象接通,可追加数据 |
| public FileWriter(String filepath) | 创建字符输出流管道与源文件路径接通 |
| public FileWriter(String filepath,boolean append) | 创建字符输出流管道与源文件路径接通,可追加 |
| 方法 | 说明 |
| void writer(int c) | 写入一个字符 |
| void writer (char [ ] buffer) | 写入一个字符数组 |
| void writer (char[ ]buffer,int off,int len) | 写入字符数组的一部分 |
| void writer(String str) | 写入一个字符串 |
| void writer(String str,int off,int len) | 写入字符串的一部分 |
| close和flush | 输出流的关闭和刷新 |
接下来就通过代码来加深对它的理解吧!
FileWriter fileWriter = new FileWriter("File//data.txt");
fileWriter.write('k');
fileWriter.write('d');
char []buffer = {'i','r','v','i','n','g'};
fileWriter.write(buffer);
fileWriter.flush();
String s = "James";
fileWriter.write(s);
fileWriter.write(s,0,4);
fileWriter.close();字符输出流的使用便可以很好地解决了中文不能正常写入文件的问题了。
附:字节流和字符流的区别
字节流操作的基本单元为字节;字符流操作的基本单元为Unicode码元。
字节流默认不使用缓冲区;字符流使用缓冲区。
字节流在操作的时候本身是不会用到缓冲区的,是与文件本身直接操作的,所以字节流在操作文件时,即使不关闭资源,文件也能输出;字符流在操作的时候是使用到缓冲区的。如果字符流不调用close或flush方法,则不会输出任何内容。
字节流通常用于处理二进制数据,实际上它可以处理任意类型的数据,但它不支持直接写入或读取Unicode码元;字符流通常处理文本数据,它支持写入及读取Unicode码元。
字节流可用于任何类型的对象,包括二进制对象,而字符流只能处理字符或者字符串; 字节流提供了处理任何类型的IO操作的功能,但它不能直接处理Unicode字符,而字符流就可以。
字节流和字符流的转换
字节流是最基本的,所有的InputStream和OutputStream的子类都是,主要用在处理二进制数据,它是按字节来处理的,但实际中很多的数据是文本,又提出了字符流的概念,它是按虚拟机的encode来处理,也就是要进行字符集的转化,这两个之间通过 InputStreamReader,OutputStreamWriter来关联,实际上是通过byte[]和String来关联。在从字节流转化为字符流时,实际上就是byte[]转化为String时,而在字符流转化为字节流时,实际上是String转化为byte[]时。
字符流处理的单元为2个字节的Unicode字符,分别操作字符、字符数组或字符串,而字节流处理单元为1个字节,操作字节和字节数组。所以字符流是由Java虚拟机将字节转化为2个字节的Unicode字符为单位的字符而成的,所以它对多国语言支持性比较好!如果是音频文件、图片、歌曲,就用字节流好点,如果是关系到中文(文本)的,用字符流好点。所有文件的储存是都是字节(byte)的储存,在磁盘上保留的并不是文件的字符而是先把字符编码成字节,再储存这些字节到磁盘。在读取文件(特别是文本文件)时,也是一个字节一个字节地读取以形成字节序列。
字节流可用于任何类型的对象,包括二进制对象,而字符流只能处理字符或者字符串; 字节流提供了处理任何类型的IO操作的功能,但它不能直接处理Unicode字符,而字符流就可以。
字节流与字符流主要的区别是他们的的处理方式。
The above is the detailed content of What are byte streams and character streams in Java. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1386
1386
 52
52
 Perfect Number in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:28 PM
Perfect Number in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:28 PM
Guide to Perfect Number in Java. Here we discuss the Definition, How to check Perfect number in Java?, examples with code implementation.
 Weka in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:28 PM
Weka in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:28 PM
Guide to Weka in Java. Here we discuss the Introduction, how to use weka java, the type of platform, and advantages with examples.
 Smith Number in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:28 PM
Smith Number in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:28 PM
Guide to Smith Number in Java. Here we discuss the Definition, How to check smith number in Java? example with code implementation.
 Java Spring Interview Questions
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:29 PM
Java Spring Interview Questions
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:29 PM
In this article, we have kept the most asked Java Spring Interview Questions with their detailed answers. So that you can crack the interview.
 Break or return from Java 8 stream forEach?
Feb 07, 2025 pm 12:09 PM
Break or return from Java 8 stream forEach?
Feb 07, 2025 pm 12:09 PM
Java 8 introduces the Stream API, providing a powerful and expressive way to process data collections. However, a common question when using Stream is: How to break or return from a forEach operation? Traditional loops allow for early interruption or return, but Stream's forEach method does not directly support this method. This article will explain the reasons and explore alternative methods for implementing premature termination in Stream processing systems. Further reading: Java Stream API improvements Understand Stream forEach The forEach method is a terminal operation that performs one operation on each element in the Stream. Its design intention is
 TimeStamp to Date in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:28 PM
TimeStamp to Date in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:28 PM
Guide to TimeStamp to Date in Java. Here we also discuss the introduction and how to convert timestamp to date in java along with examples.
 Java Program to Find the Volume of Capsule
Feb 07, 2025 am 11:37 AM
Java Program to Find the Volume of Capsule
Feb 07, 2025 am 11:37 AM
Capsules are three-dimensional geometric figures, composed of a cylinder and a hemisphere at both ends. The volume of the capsule can be calculated by adding the volume of the cylinder and the volume of the hemisphere at both ends. This tutorial will discuss how to calculate the volume of a given capsule in Java using different methods. Capsule volume formula The formula for capsule volume is as follows: Capsule volume = Cylindrical volume Volume Two hemisphere volume in, r: The radius of the hemisphere. h: The height of the cylinder (excluding the hemisphere). Example 1 enter Radius = 5 units Height = 10 units Output Volume = 1570.8 cubic units explain Calculate volume using formula: Volume = π × r2 × h (4
 Create the Future: Java Programming for Absolute Beginners
Oct 13, 2024 pm 01:32 PM
Create the Future: Java Programming for Absolute Beginners
Oct 13, 2024 pm 01:32 PM
Java is a popular programming language that can be learned by both beginners and experienced developers. This tutorial starts with basic concepts and progresses through advanced topics. After installing the Java Development Kit, you can practice programming by creating a simple "Hello, World!" program. After you understand the code, use the command prompt to compile and run the program, and "Hello, World!" will be output on the console. Learning Java starts your programming journey, and as your mastery deepens, you can create more complex applications.




