How to implement bloom filter in Java?
What is Bloom filter
Bloom Filter (Bloom Filter) was proposed by Bloom in 1970. It is actually composed of a very long binary array and a series of hash algorithm mapping functions, which are used to determine whether an element exists in the set.
Bloom filters can be used to retrieve whether an element is in a collection. Its advantage is that space efficiency and query time are much better than ordinary algorithms. Its disadvantage is that it has a certain misrecognition rate and difficulty in deletion.
Scenario
Assume there are 1 billion mobile phone numbers, and then determine whether a certain mobile phone number is in the list?
Is it possible with mysql?
Under normal circumstances, if the amount of data is not large, we can consider using mysql storage. Store all data in the database, and then query the database each time to determine whether it exists. However, if the amount of data is too large, exceeding tens of millions, the MySQL query efficiency will be very low, which will particularly consume performance.
Can HashSet be used?
We can put the data into HashSet and use the natural deduplication of HashSet. The query only needs to call the contains method, but the hashset is stored in the memory. If the amount of data is too large, the memory will be directly oom.
Features of Bloom filter
The insertion and query are efficient and take up less space, but the returned results are uncertain.
If an element is judged to exist, it may not actually exist. But if it is judged that an element does not exist, then it must not exist.
Bloom filter can add elements, but must not delete elements , which will increase the false positive rate.
Bloom filter principle
A Bloom filter is actually a BIT array, which maps the corresponding hash through a series of hash algorithms, and then maps the hash corresponding to The array subscript position is changed to 1. When querying, a series of hash algorithms are performed on the data to obtain the subscript. The data is taken from the BIT array, such as . If it is 1, it means the data may exist. If it is 0, it means it definitely does not exist.
Why is there an error rate
We know that the Bloom filter actually hashes the data, so no matter what algorithm is used, it is possible that the hashes generated by two different data are indeed the same, that is, we Commonly referred to as hash conflicts.
First insert a piece of data: Learn technology well
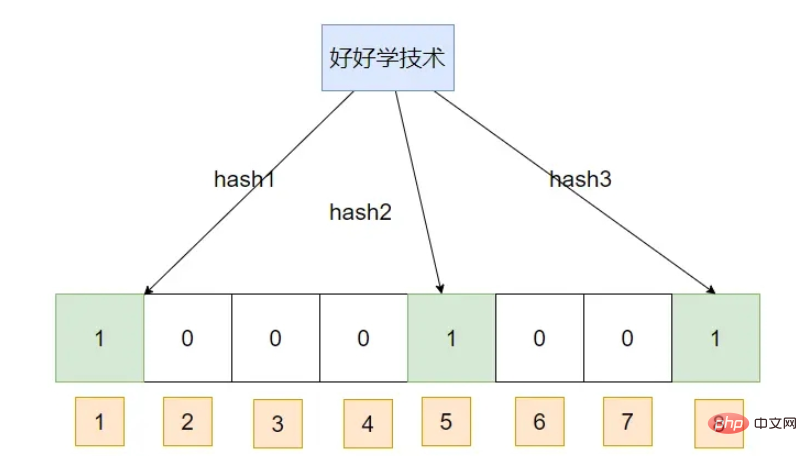
Insert a piece of data:
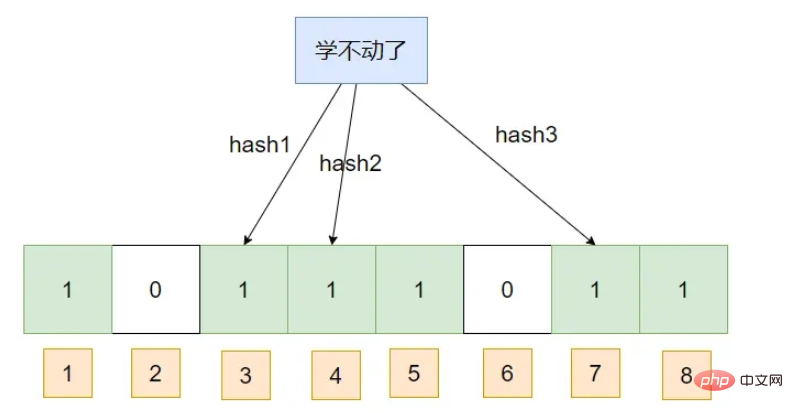
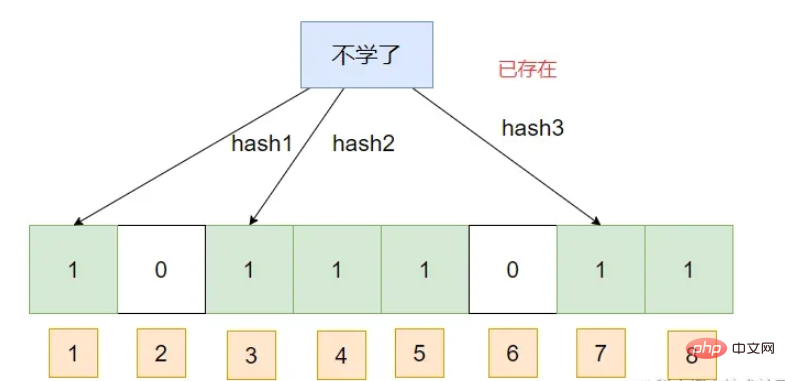
This If you query a piece of data, assuming that its hash subscript has been marked as 1, then the Bloom filter will think that it exists
Common usage scenarios
Cache penetration
Java implements Bloom filter
package com.fandf.test.redis;
import java.util.BitSet;
/**
* java布隆过滤器
*
* @author fandongfeng
*/
public class MyBloomFilter {
/**
* 位数组大小
*/
private static final int DEFAULT_SIZE = 2 << 24;
/**
* 通过这个数组创建多个Hash函数
*/
private static final int[] SEEDS = new int[]{4, 8, 16, 32, 64, 128, 256};
/**
* 初始化位数组,数组中的元素只能是 0 或者 1
*/
private final BitSet bits = new BitSet(DEFAULT_SIZE);
/**
* Hash函数数组
*/
private final MyHash[] myHashes = new MyHash[SEEDS.length];
/**
* 初始化多个包含 Hash 函数的类数组,每个类中的 Hash 函数都不一样
*/
public MyBloomFilter() {
// 初始化多个不同的 Hash 函数
for (int i = 0; i < SEEDS.length; i++) {
myHashes[i] = new MyHash(DEFAULT_SIZE, SEEDS[i]);
}
}
/**
* 添加元素到位数组
*/
public void add(Object value) {
for (MyHash myHash : myHashes) {
bits.set(myHash.hash(value), true);
}
}
/**
* 判断指定元素是否存在于位数组
*/
public boolean contains(Object value) {
boolean result = true;
for (MyHash myHash : myHashes) {
result = result && bits.get(myHash.hash(value));
}
return result;
}
/**
* 自定义 Hash 函数
*/
private class MyHash {
private int cap;
private int seed;
MyHash(int cap, int seed) {
this.cap = cap;
this.seed = seed;
}
/**
* 计算 Hash 值
*/
int hash(Object obj) {
return (obj == null) ? 0 : Math.abs(seed * (cap - 1) & (obj.hashCode() ^ (obj.hashCode() >>> 16)));
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
String str = "好好学技术";
MyBloomFilter myBloomFilter = new MyBloomFilter();
System.out.println("str是否存在:" + myBloomFilter.contains(str));
myBloomFilter.add(str);
System.out.println("str是否存在:" + myBloomFilter.contains(str));
}
}Guava implements Bloom filter
Introducing dependencies
<dependency>
<groupId>com.google.guava</groupId>
<artifactId>guava</artifactId>
<version>31.1-jre</version>
</dependency>package com.fandf.test.redis;
import com.google.common.base.Charsets;
import com.google.common.hash.BloomFilter;
import com.google.common.hash.Funnels;
/**
* @author fandongfeng
*/
public class GuavaBloomFilter {
public static void main(String[] args) {
BloomFilter<String> bloomFilter = BloomFilter.create(Funnels.stringFunnel(Charsets.UTF_8),100000,0.01);
bloomFilter.put("好好学技术");
System.out.println(bloomFilter.mightContain("不好好学技术"));
System.out.println(bloomFilter.mightContain("好好学技术"));
}
}hutool implements Bloom filter Device
Introducing dependencies
<dependency>
<groupId>cn.hutool</groupId>
<artifactId>hutool-all</artifactId>
<version>5.8.3</version>
</dependency>package com.fandf.test.redis;
import cn.hutool.bloomfilter.BitMapBloomFilter;
import cn.hutool.bloomfilter.BloomFilterUtil;
/**
* @author fandongfeng
*/
public class HutoolBloomFilter {
public static void main(String[] args) {
BitMapBloomFilter bloomFilter = BloomFilterUtil.createBitMap(1000);
bloomFilter.add("好好学技术");
System.out.println(bloomFilter.contains("不好好学技术"));
System.out.println(bloomFilter.contains("好好学技术"));
}
}Redisson implements Bloom filter
Introducing dependencies
<dependency>
<groupId>org.redisson</groupId>
<artifactId>redisson</artifactId>
<version>3.20.0</version>
</dependency>package com.fandf.test.redis;
import org.redisson.Redisson;
import org.redisson.api.RBloomFilter;
import org.redisson.api.RedissonClient;
import org.redisson.config.Config;
/**
* Redisson 实现布隆过滤器
* @author fandongfeng
*/
public class RedissonBloomFilter {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Config config = new Config();
config.useSingleServer().setAddress("redis://127.0.0.1:6379");
//构造Redisson
RedissonClient redisson = Redisson.create(config);
RBloomFilter<String> bloomFilter = redisson.getBloomFilter("name");
//初始化布隆过滤器:预计元素为100000000L,误差率为1%
bloomFilter.tryInit(100000000L,0.01);
bloomFilter.add("好好学技术");
System.out.println(bloomFilter.contains("不好好学技术"));
System.out.println(bloomFilter.contains("好好学技术"));
}
}The above is the detailed content of How to implement bloom filter in Java?. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 Square Root in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:26 PM
Square Root in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:26 PM
Guide to Square Root in Java. Here we discuss how Square Root works in Java with example and its code implementation respectively.
 Perfect Number in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:28 PM
Perfect Number in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:28 PM
Guide to Perfect Number in Java. Here we discuss the Definition, How to check Perfect number in Java?, examples with code implementation.
 Random Number Generator in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:27 PM
Random Number Generator in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:27 PM
Guide to Random Number Generator in Java. Here we discuss Functions in Java with examples and two different Generators with ther examples.
 Weka in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:28 PM
Weka in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:28 PM
Guide to Weka in Java. Here we discuss the Introduction, how to use weka java, the type of platform, and advantages with examples.
 Armstrong Number in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:26 PM
Armstrong Number in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:26 PM
Guide to the Armstrong Number in Java. Here we discuss an introduction to Armstrong's number in java along with some of the code.
 Smith Number in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:28 PM
Smith Number in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:28 PM
Guide to Smith Number in Java. Here we discuss the Definition, How to check smith number in Java? example with code implementation.
 Java Spring Interview Questions
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:29 PM
Java Spring Interview Questions
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:29 PM
In this article, we have kept the most asked Java Spring Interview Questions with their detailed answers. So that you can crack the interview.
 Break or return from Java 8 stream forEach?
Feb 07, 2025 pm 12:09 PM
Break or return from Java 8 stream forEach?
Feb 07, 2025 pm 12:09 PM
Java 8 introduces the Stream API, providing a powerful and expressive way to process data collections. However, a common question when using Stream is: How to break or return from a forEach operation? Traditional loops allow for early interruption or return, but Stream's forEach method does not directly support this method. This article will explain the reasons and explore alternative methods for implementing premature termination in Stream processing systems. Further reading: Java Stream API improvements Understand Stream forEach The forEach method is a terminal operation that performs one operation on each element in the Stream. Its design intention is






