Analyze Java ArrayQueue source code.
ArrayQueue internal implementation
Before talking about the internal implementation of ArrayQueue, let’s first look at an ArrayQueue Usage example:
public void testQueue() {
ArrayQueue<Integer> queue = new ArrayQueue<>(10);
queue.add(1);
queue.add(2);
queue.add(3);
queue.add(4);
System.out.println(queue);
queue.remove(0); // 这个参数只能为0 表示删除队列当中第一个元素,也就是队头元素
System.out.println(queue);
queue.remove(0);
System.out.println(queue);
}
// 输出结果
[1, 2, 3, 4]
[2, 3, 4]
[3, 4]First of all, ArrayQueue is internally implemented by a circular array, which may ensure that the time complexity of adding and deleting data is the same, unlike ArrayListdeleting data. The time complexity of is. There are two integer data head and tail inside ArrayQueue. The functions of these two are mainly to point to the head and tail of the queue, and its initial state. The layout in the memory is as shown below:

Because the values of head and tail are both equal to 0 in the initial state, Points to the first data in the array. Now we add 5 pieces of data to ArrayQueue, then its memory layout will be as shown below:
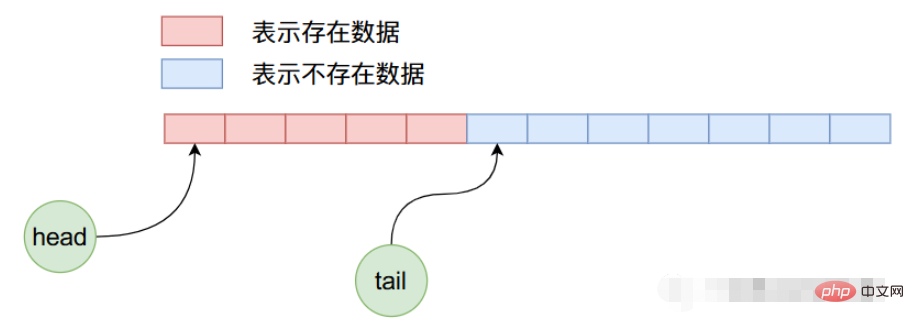
Now we delete 4 pieces of data, then After 4 deletion operations in the above picture, the internal data layout of ArrayQueue is as follows:

In the above state, we continue to add 8 data, then The layout is as follows:

We know that when adding data in the above figure, not only the space in the second half of the array is used up, but also the unused space in the first half can be continued to be used. , that is to say, a recycling process is implemented inside ArrayQueue.
ArrayQueue source code analysis
Constructor
public ArrayQueue(int capacity) {
this.capacity = capacity + 1;
this.queue = newArray(capacity + 1);
this.head = 0;
this.tail = 0;
}
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
private T[] newArray(int size) {
return (T[]) new Object[size];
}The above constructor code is relatively easy to understand. It mainly applies for an array based on the length of the array space entered by the user, but it is specific When applying for an array, one more space will be applied for.
add function
public boolean add(T o) {
queue[tail] = o;
// 循环使用数组
int newtail = (tail + 1) % capacity;
if (newtail == head)
throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException("Queue full");
tail = newtail;
return true; // we did add something
}The above code is relatively easy to understand. We have mentioned above that ArrayQueue can add data to the array in a loop. This is also reflected in the code above.
remove function
public T remove(int i) {
if (i != 0)
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Can only remove head of queue");
if (head == tail)
throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException("Queue empty");
T removed = queue[head];
queue[head] = null;
head = (head + 1) % capacity;
return removed;
}As can be seen from the above code, we must pass parameter 0 in the remove function, otherwise an exception will be thrown. In this function, we will only delete the data at the current head subscript position, and then perform a cyclic operation of adding 1 to the value of head.
get function
public T get(int i) {
int size = size();
if (i < 0 || i >= size) {
final String msg = "Index " + i + ", queue size " + size;
throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException(msg);
}
int index = (head + i) % capacity;
return queue[index];
}getThe parameters of the function indicate that the ith data is obtained, and the ith data is not It is not the ith data in the array position, but the data at the i position from head. Knowing this, the above code is easy to understand. of.
resize function
public void resize(int newcapacity) {
int size = size();
if (newcapacity < size)
throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException("Resizing would lose data");
newcapacity++;
if (newcapacity == this.capacity)
return;
T[] newqueue = newArray(newcapacity);
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++)
newqueue[i] = get(i);
this.capacity = newcapacity;
this.queue = newqueue;
this.head = 0;
this.tail = size;
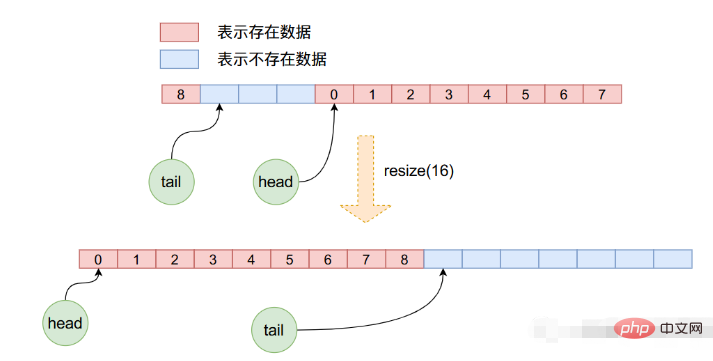
}In the resize function, first apply for an array space of new length, and then copy the data of the original array to the new array one by one. Note During this copy process, head and tail are updated again, and it is not a simple array copy, because in the previous operation, head may no longer be 0, so the new copy requires us to take it out from the old array one by one and then put it into the new array. The following figure can clearly see this process:
The above is the detailed content of Analyze Java ArrayQueue source code.. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 Square Root in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:26 PM
Square Root in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:26 PM
Guide to Square Root in Java. Here we discuss how Square Root works in Java with example and its code implementation respectively.
 Perfect Number in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:28 PM
Perfect Number in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:28 PM
Guide to Perfect Number in Java. Here we discuss the Definition, How to check Perfect number in Java?, examples with code implementation.
 Random Number Generator in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:27 PM
Random Number Generator in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:27 PM
Guide to Random Number Generator in Java. Here we discuss Functions in Java with examples and two different Generators with ther examples.
 Armstrong Number in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:26 PM
Armstrong Number in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:26 PM
Guide to the Armstrong Number in Java. Here we discuss an introduction to Armstrong's number in java along with some of the code.
 Weka in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:28 PM
Weka in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:28 PM
Guide to Weka in Java. Here we discuss the Introduction, how to use weka java, the type of platform, and advantages with examples.
 Smith Number in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:28 PM
Smith Number in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:28 PM
Guide to Smith Number in Java. Here we discuss the Definition, How to check smith number in Java? example with code implementation.
 Java Spring Interview Questions
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:29 PM
Java Spring Interview Questions
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:29 PM
In this article, we have kept the most asked Java Spring Interview Questions with their detailed answers. So that you can crack the interview.
 Break or return from Java 8 stream forEach?
Feb 07, 2025 pm 12:09 PM
Break or return from Java 8 stream forEach?
Feb 07, 2025 pm 12:09 PM
Java 8 introduces the Stream API, providing a powerful and expressive way to process data collections. However, a common question when using Stream is: How to break or return from a forEach operation? Traditional loops allow for early interruption or return, but Stream's forEach method does not directly support this method. This article will explain the reasons and explore alternative methods for implementing premature termination in Stream processing systems. Further reading: Java Stream API improvements Understand Stream forEach The forEach method is a terminal operation that performs one operation on each element in the Stream. Its design intention is






