How to use Python GUI layout tool Tkinter
Graphical User Interface (GUI)
Graphical User Interface (GUI) is nothing but a desktop application that helps us interact with the computer
GUI applications like text editors can create, read, update and delete different types of files
Sudoku, Chess and Applications such as Solitaire are game versions of GUI programs
There are also GUI applications such as Google Chrome, Firefox and Microsoft Edge that are used to browse the Internet
These are some different types of GUI applications that we use daily on computers. In fact, we can also build simple similar applications through Tkinter.
Today we are an introduction to GUI, A very simple and beautiful GUI application will be created
Python library for creating GUI
Python has a large number of third-party libraries. For GUI libraries, there are mainly the following:
Kivy
Python QT
wxPython
Tkinter
Among them, Tkinter is the first choice for many learners and developers because it is easy to use and comes with Python installation
Tkinter Basics
The picture below shows how the application is actually executed in Tkinter
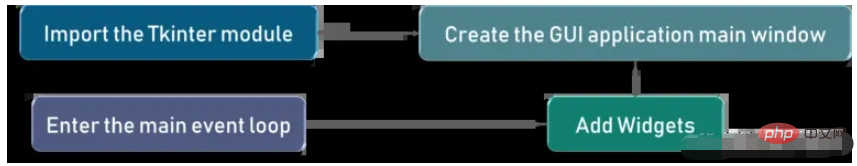
We first import the Tkinter model, then, we create the main window, in this window, we We are going to perform operations and display all visual effects, next we add Widgets, and finally we enter the Main Event Loop
There are 2 important keywords here
Widgets
Main Event Loop
The event loop basically tells the code to continue displaying the window until we manually close it, running in an infinite loop in the background
For Widgets, we will study it separately later
The following code example will give you a deeper understanding
import tkinter
window = tkinter.Tk()
# to rename the title of the window window.title("GUI")
# pack is used to show the object in the window
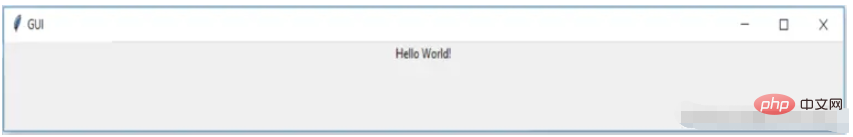
label = tkinter.Label(window, text = "Hello World!").pack()
window.mainloop()We import the Tkinter package and define a window, and then we can modify a window title, Whenever the application is opened, this title will be displayed on the title tab
Finally, we have also defined a label, the label is nothing but the output that needs to be displayed on the window, in the example hello world
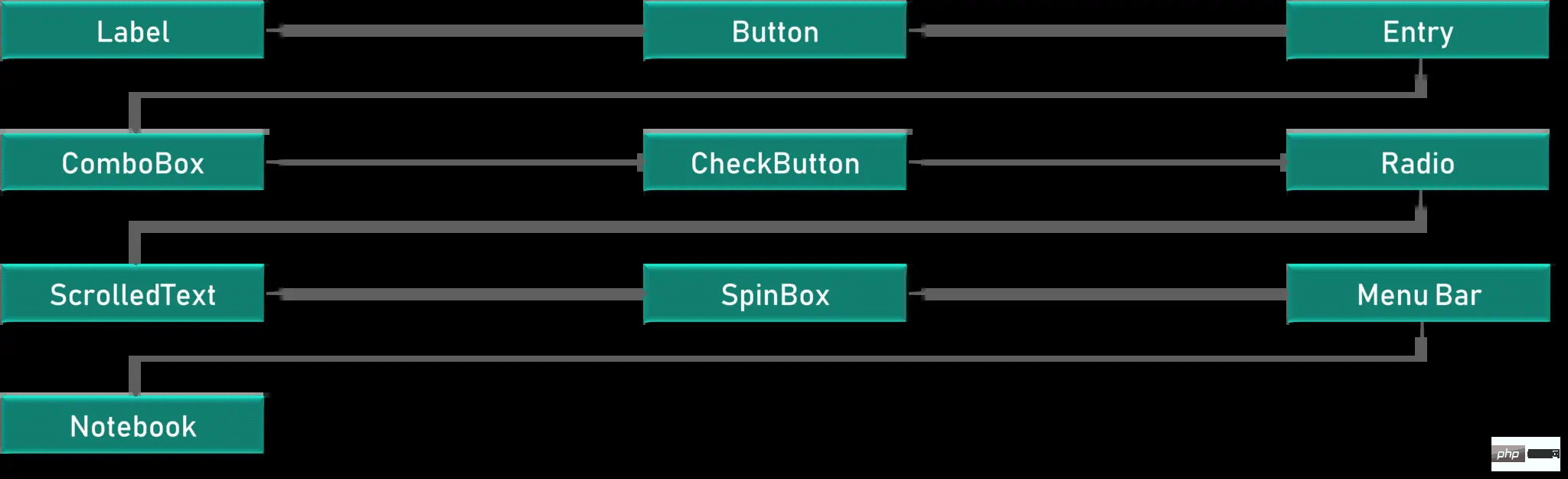
Tkinter Widgets
So what are Widgets?
Widgets are similar to elements in HTML. We can find different types of Widgets in Tkinter. Different Types of Widgets for Type Elements
Let’s see a brief introduction of all these Widgets in Tkinter
Canvas - Used with Canvas Used for drawing shapes in GUI
Button – Button used for placing buttons in Tkinter
Checkbutton – Checkbutton used for placing buttons in applications Create check buttons in
Entry - Entry is used to create input fields in GUI
Frame – Frame is used as a container in Tkinter
Label - Label is used to create single-line Widgets, such as text, images, etc.
Menu - Menu is used to create menus in GUI
Let’s take a look at the usage of each Widgets one by one
Label
Label is used to create text and images and all related, and pay attention to Yes, it can only be a single line definition
l1 = Label(window, text="萝卜大杂烩!", font=("ArialBold", 50))
l1.grid(column=0, row=0)
There is also a function geometry which is basically used to change the window size and set it as per our requirement
l1 = Label(window, text="萝卜大杂烩!", font=("ArialBold", 50))
window.geometry('350x200')In this case we set it to 350 pixels wide and 200 pixels tall
Next is the button
Button
Buttons are very similar to labels, we Create a variable and use Widgets syntax to define what the button wants to express
window.geometry('350x200') bt = Button(window, text="Enter")

We can also change the foreground color of the button or any other Widget using the parameters shown in the code FG. Similarly, you can also use the BG attribute to change the background color
bt = Button(window, text="Enter", bg="orange", fg="red") bt.grid(column=1, row=0)

Our foreground is text defined as red, and the background is orange
Let’s take a look at the click The operation of the button
def clicked():
l1.configure(text="按钮被点击了!!")
bt = Button(window, text="Enter", bg="orange", fg="red", command=clicked)We call this a click event, we need to write the function about what should happen when the button is clicked or the click event is triggered
We define a called clicked Function can display a text message. We add a parameter named command in the button definition to call the click event

Entry
它用于在 GUI 中创建输入字段以接收文本输入
txt = Entry(window, width=10)
txt.grid(column=1, row=0)
def clicked():
res = "Welcome to " + txt.get()
l1.configure(text=res)
bt = Button(window, text="Enter", bg="orange", fg="red", command=clicked)在这里,我们使用 Tkinter Entry 类创建一个文本框,grid 定义我们希望窗口小部件位于何处
同时 clicked 函数接收 Entry 的文本信息

Combobox
这是一个带有某些选项的下拉菜单
from tkinter.ttk import * combo = Combobox(window) combo['values']= (1, 2, 3, 4, 5, "Text") combo.current(3) combo.grid(column=0, row=0)
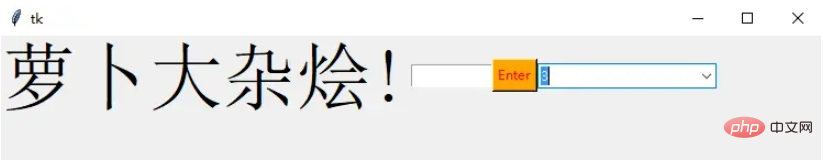
这样一个下拉菜单就完成了
Checkbutton
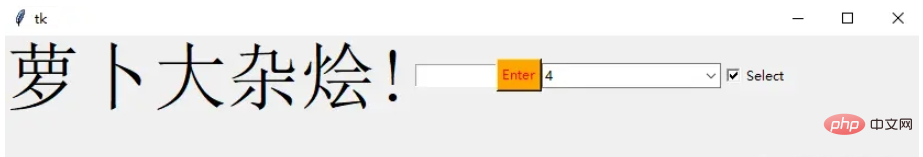
复选按钮是非常常用的组件
chk_state = BooleanVar() chk_state.set (True) chk = Checkbutton(window, text="Select", var=chk_state) chk.grid(column=4, row=0)
我们首先创建一个 booleanvar 类型的变量,这是一个 Tkinter 变量
默认情况下,我们将设置状态保持为 true,这代表按钮已经被选中 接下来,我们将 chk_state 传递给 checkbutton 类来为我们设置检查状态
Radio Button
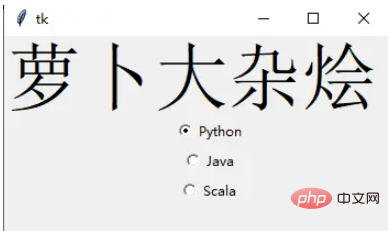
单选按钮也是非常常用的
rad1 = Radiobutton(window, text=Python', value=1) rad2 = Radiobutton(window, text=Java', value=2) rad3 = Radiobutton(window, text=Scala', value=3) rad1.grid(column=0, row=0) rad2.grid(column=1, row=0) rad3.grid(column=2, row=0)
在这里,我们使用了不同的参数值,1,2和3,如果它们相同,则会导致冲突并出现错误
它们的文本数据是可以相同,在这里,我们使用了 Python、Java 和 Scala
Scrolled Text
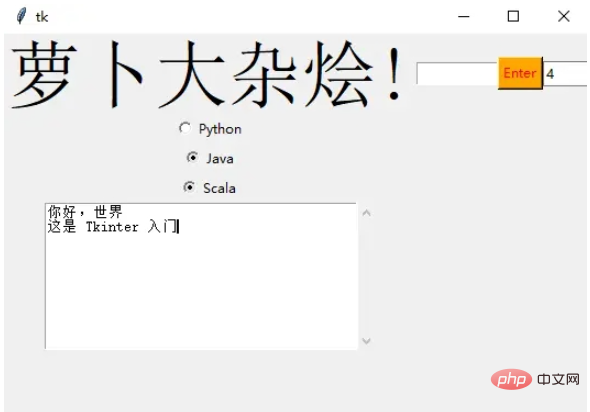
滚动文本组件
scro_txt = scrolledtext.ScrolledText(window, width=40,height=10) scro_txt.grid(column=0, row=4)
我们指定了窗口的高和宽,否则默认会填充整个 Windiws 窗口
Message Box
消息组件可以方便的弹出提醒消息
def clicked():
messagebox.showinfo('Message title', 'Message content')
btn = Button(window,text=‘ENTER', command=clicked)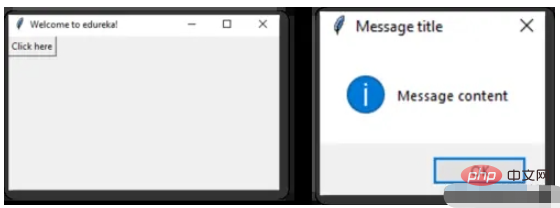
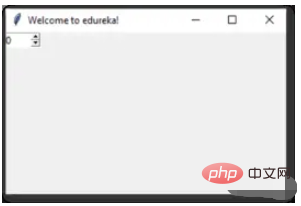
SpinBox
Spinbox 也是一个常见的组件,有两个选项卡,存在向上和向下滚动选项卡
pin = Spinbox(window, from_=0, to=100, width=5)
有 3 个参数——from、to 和 width
From – 告诉我们范围的开始和默认值
to – 给我们范围的上限阈值
width 基本上是将 widget 的大小设置为5个字符的空格
Geometry
Tkinter 中的所有 Widgets 都会有一些位置信息,这些度量使得我们可以组织 Widgets 及其父框架、窗口等
Tkinter 具有以下三个布局方式
pack():- 它在块中组织 Widgets,这意味着它占据了整个可用宽度,这是在窗口中显示 Widgets 的标准方法
grid():- 它以类似表格的结构组织 Widgets
place():- 它将 Widgets 放置在我们想要的特定位置
组织布局
为了在窗口中安排布局,我们将使用 Frame 类
Frame -- 在窗口中创建分区,我们可以根据需要使用 pack() 方法的侧面参数对齐框架
Button -- 在窗口中创建一个按钮,需要传递几个参数,如文本(按钮的值)、fg(文本的颜色)、bg(背景颜色)
在下面的代码中,我们使用 window、top_frame、bottom_frame 来布局
import tkinter
window = tkinter.Tk()
window.title("GUI")
# creating 2 frames TOP and BOTTOM
top_frame = tkinter.Frame(window).pack()
bottom_frame = tkinter.Frame(window).pack(side = "bottom")
# now, create some widgets in the top_frame and bottom_frame
btn1 = tkinter.Button(top_frame, text = "Button1", fg = "red").pack()# 'fg - foreground' is used to color the contents
btn2 = tkinter.Button(top_frame, text = "Button2", fg = "green").pack()# 'text' is used to write the text on the Button
btn3 = tkinter.Button(bottom_frame, text = "Button2", fg = "purple").pack(side = "left")# 'side' is used to align the widgets
btn4 = tkinter.Button(bottom_frame, text = "Button2", fg = "orange").pack(side = "left")
window.mainloop()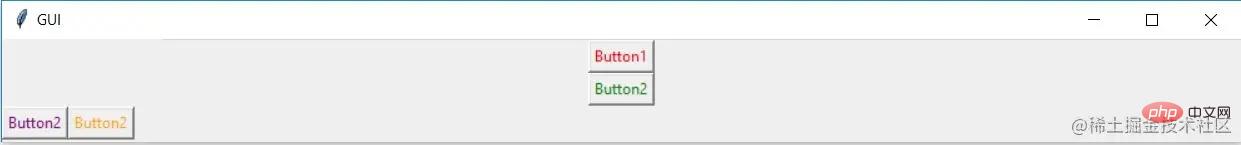
再来看一个登录的小栗子
import tkinter
window = tkinter.Tk()
window.title("GUI")
# creating 2 text labels and input labels
tkinter.Label(window, text = "Username").grid(row = 0) # this is placed in 0 0
# 'Entry' is used to display the input-field
tkinter.Entry(window).grid(row = 0, column = 1) # this is placed in 0 1
tkinter.Label(window, text = "Password").grid(row = 1) # this is placed in 1 0
tkinter.Entry(window).grid(row = 1, column = 1) # this is placed in 1 1
# 'Checkbutton' is used to create the check buttons
tkinter.Checkbutton(window, text = "Keep Me Logged In").grid(columnspan = 2) # 'columnspan' tells to take the width of 2 columns
# you can also use 'rowspan' in the similar manner
window.mainloop()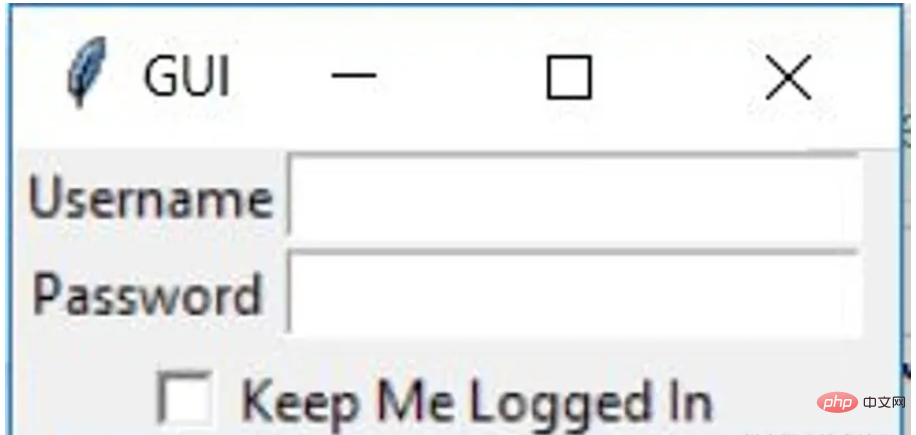
下面我们来了解 binding 函数
binding 函数
每当事件发生时调用函数就是绑定函数
在下面的示例中,当单击按钮时,它会调用一个名为 say_hi 的函数。 函数 say_hi 会创建一个带有文本 Hi 的新标签
import tkinter
window = tkinter.Tk()
window.title("GUI")
# creating a function called say_hi()
def say_hi():
tkinter.Label(window, text = "Hi").pack()
tkinter.Button(window, text = "Click Me!", command = say_hi).pack() # 'command' is executed when you click the button
# in this above case we're calling the function 'say_hi'.
window.mainloop()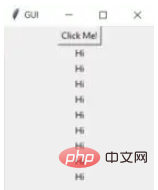
另一种绑定函数的方法是使用事件,事件类似于鼠标移动、鼠标悬停、单击和滚动等等
import tkinter
window = tkinter.Tk()
window.title("GUI")
# creating a function with an arguments 'event'
def say_hi(event): # you can rename 'event' to anything you want
tkinter.Label(window, text = "Hi").pack()
btn = tkinter.Button(window, text = "Click Me!")
btn.bind("Button-1", say_hi) # 'bind' takes 2 parameters 1st is 'event' 2nd is 'function'
btn.pack()
window.mainloop()单击事件有 3 种不同的类型,分别是 leftClick、middleClick 和 rightClick
下面的代码将使用对于的文本创建一个新标签
import tkinter
window = tkinter.Tk()
window.title("GUI")
#creating 3 different functions for 3 events
def left_click(event):
tkinter.Label(window, text = "Left Click!").pack()
def middle_click(event):
tkinter.Label(window, text = "Middle Click!").pack()
def right_click(event):
tkinter.Label(window, text = "Right Click!").pack()
window.bind("Button-1", left_click)
window.bind("Button-2", middle_click)
window.bind("Button-3", right_click)
window.mainloop()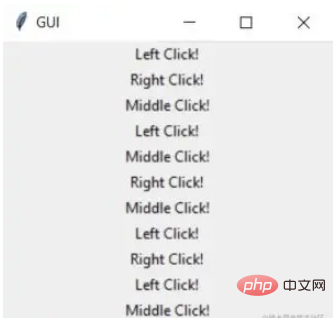
Images 和 Icons
我们可以使用 PhotoImage 方法添加图像和图标
import tkinter
window = tkinter.Tk()
window.title("GUI")
# taking image from the directory and storing the source in a variable
icon = tkinter.PhotoImage(file = "4.PNG")
# displaying the picture using a 'Label' by passing the 'picture' variriable to 'image' parameter
label = tkinter.Label(window, image = icon)
label.pack()
window.mainloop()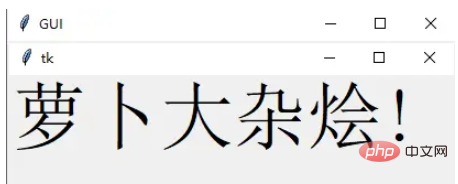
好了,进步的 Tkinter 知识我们都梳理完毕了,下面就完成一个简单的实战项目吧
计算器 APP
首先初始化页面
window = Tk()
window.geometry("350x380")
window.resizable(0, 0) # this prevents from resizing the window
window.title("小小计算器")接下来定义输入数字框
input_text = StringVar()
input_frame = Frame(window, width=312, height=50, bd=0, highlightbackground="black", highlightcolor="black",
highlightthickness=1)
input_frame.pack(side=TOP)
input_field = Entry(input_frame, font=('arial', 18, 'bold'), textvariable=input_text, width=50, bg="#eee", bd=0,
justify=RIGHT)
input_field.grid(row=0, column=0)
input_field.pack(ipady=10)然后定义按钮方法,我们以清除按钮和除法按钮为例
clear = Button(btns_frame, text="C", fg="black", width=32, height=3, bd=0, bg="#eee", cursor="hand2",
command=lambda: btn_clear()).grid(row=0, column=0, columnspan=3, padx=1, pady=1)
divide = Button(btns_frame, text="/", fg="black", width=10, height=3, bd=0, bg="#eee", cursor="hand2",
command=lambda: btn_click("/")).grid(row=0, column=3, padx=1, pady=1)最后就是计算equal逻辑
equals = Button(btns_frame, text="=", fg="black", width=10, height=3, bd=0, bg="#eee", cursor="hand2",
command=lambda: btn_equal()).grid(row=4, column=3, padx=1, pady=1)
def btn_equal():
global expression
result = str(eval(expression))
input_text.set(result)
expression = ""The above is the detailed content of How to use Python GUI layout tool Tkinter. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1387
1387
 52
52
 Is the vscode extension malicious?
Apr 15, 2025 pm 07:57 PM
Is the vscode extension malicious?
Apr 15, 2025 pm 07:57 PM
VS Code extensions pose malicious risks, such as hiding malicious code, exploiting vulnerabilities, and masturbating as legitimate extensions. Methods to identify malicious extensions include: checking publishers, reading comments, checking code, and installing with caution. Security measures also include: security awareness, good habits, regular updates and antivirus software.
 How to run programs in terminal vscode
Apr 15, 2025 pm 06:42 PM
How to run programs in terminal vscode
Apr 15, 2025 pm 06:42 PM
In VS Code, you can run the program in the terminal through the following steps: Prepare the code and open the integrated terminal to ensure that the code directory is consistent with the terminal working directory. Select the run command according to the programming language (such as Python's python your_file_name.py) to check whether it runs successfully and resolve errors. Use the debugger to improve debugging efficiency.
 Can vs code run in Windows 8
Apr 15, 2025 pm 07:24 PM
Can vs code run in Windows 8
Apr 15, 2025 pm 07:24 PM
VS Code can run on Windows 8, but the experience may not be great. First make sure the system has been updated to the latest patch, then download the VS Code installation package that matches the system architecture and install it as prompted. After installation, be aware that some extensions may be incompatible with Windows 8 and need to look for alternative extensions or use newer Windows systems in a virtual machine. Install the necessary extensions to check whether they work properly. Although VS Code is feasible on Windows 8, it is recommended to upgrade to a newer Windows system for a better development experience and security.
 Can visual studio code be used in python
Apr 15, 2025 pm 08:18 PM
Can visual studio code be used in python
Apr 15, 2025 pm 08:18 PM
VS Code can be used to write Python and provides many features that make it an ideal tool for developing Python applications. It allows users to: install Python extensions to get functions such as code completion, syntax highlighting, and debugging. Use the debugger to track code step by step, find and fix errors. Integrate Git for version control. Use code formatting tools to maintain code consistency. Use the Linting tool to spot potential problems ahead of time.
 Choosing Between PHP and Python: A Guide
Apr 18, 2025 am 12:24 AM
Choosing Between PHP and Python: A Guide
Apr 18, 2025 am 12:24 AM
PHP is suitable for web development and rapid prototyping, and Python is suitable for data science and machine learning. 1.PHP is used for dynamic web development, with simple syntax and suitable for rapid development. 2. Python has concise syntax, is suitable for multiple fields, and has a strong library ecosystem.
 Can vscode be used for mac
Apr 15, 2025 pm 07:36 PM
Can vscode be used for mac
Apr 15, 2025 pm 07:36 PM
VS Code is available on Mac. It has powerful extensions, Git integration, terminal and debugger, and also offers a wealth of setup options. However, for particularly large projects or highly professional development, VS Code may have performance or functional limitations.
 PHP and Python: Different Paradigms Explained
Apr 18, 2025 am 12:26 AM
PHP and Python: Different Paradigms Explained
Apr 18, 2025 am 12:26 AM
PHP is mainly procedural programming, but also supports object-oriented programming (OOP); Python supports a variety of paradigms, including OOP, functional and procedural programming. PHP is suitable for web development, and Python is suitable for a variety of applications such as data analysis and machine learning.
 Can vscode run ipynb
Apr 15, 2025 pm 07:30 PM
Can vscode run ipynb
Apr 15, 2025 pm 07:30 PM
The key to running Jupyter Notebook in VS Code is to ensure that the Python environment is properly configured, understand that the code execution order is consistent with the cell order, and be aware of large files or external libraries that may affect performance. The code completion and debugging functions provided by VS Code can greatly improve coding efficiency and reduce errors.




