
Boolean represents one of two values: True or False.
In programming, you often need to know whether an expression is True or False.
You can evaluate any expression in Python and get one of two answers, True or False.
When comparing two values, the expression is evaluated and Python returns a Boolean answer:
Example
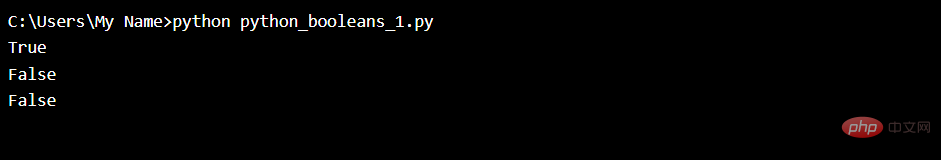
print(8 > 7) print(8 == 7) print(8 < 7)
Running Example
When a condition is run in an if statement, Python returns True or False:
Example
According to whether the condition is true Still wrong, prints a message:
a = 200
b = 33
if b > a:
print("b is greater than a")
else:
print("b is not greater than a")Run the instance

The bool() function allows you to evaluate any value and returns True or False for you.
Example
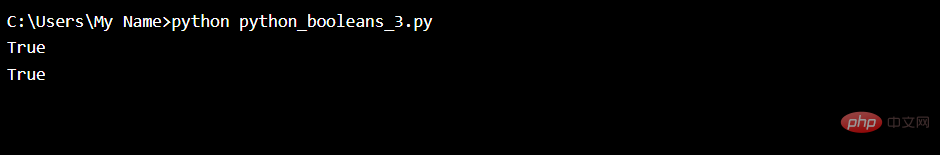
Evaluate strings and numbers:
print(bool("Hello"))
print(bool(10))Run Example
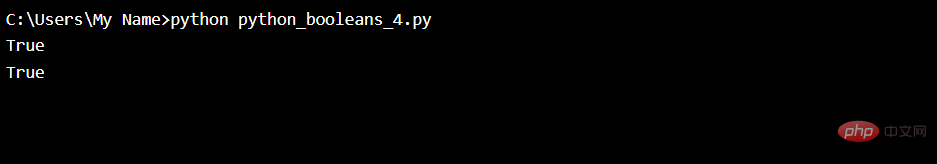
##Example
Evaluate two variables:x = "Hello" y = 10 print(bool(x)) print(bool(y))
Instance
The following example will return True:bool("abc")
bool(123)
bool(["apple", "cherry", "banana"])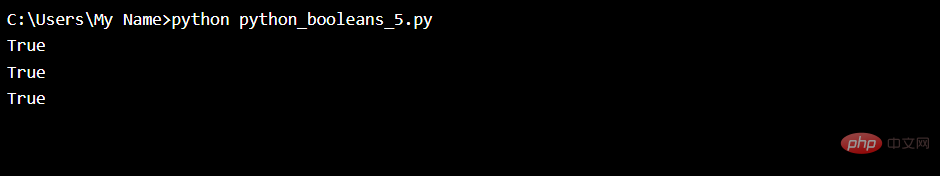
Example
The following example will return False:bool(False)
bool(None)
bool(0)
bool("")
bool(())
bool([])
bool({})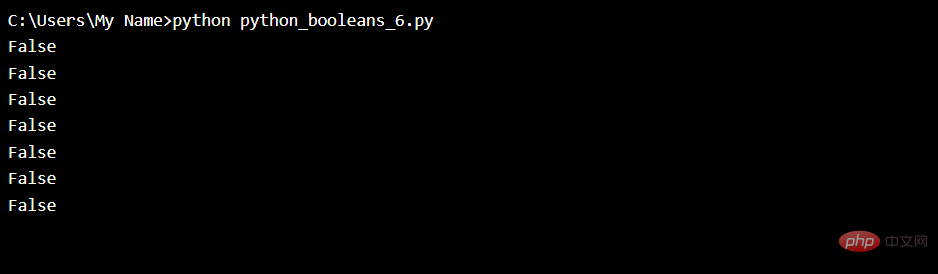
len function that returns 0 or False:
Example
class myclass():
def __len__(self):
return 0
myobj = myclass()
print(bool(myobj))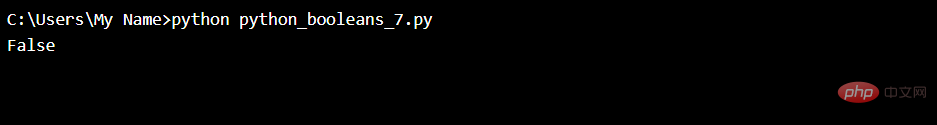
Instance
Check whether the object is an integer:x = 200 print(isinstance(x, int))

The above is the detailed content of Example code for analyzing Python Boolean values. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!




