 Technology peripherals
Technology peripherals
 AI
AI
 From mice walking in the maze to AlphaGo defeating humans, the development of reinforcement learning
From mice walking in the maze to AlphaGo defeating humans, the development of reinforcement learning
From mice walking in the maze to AlphaGo defeating humans, the development of reinforcement learning
When it comes to reinforcement learning, many researchers’ adrenaline surges uncontrollably! It plays a very important role in game AI systems, modern robots, chip design systems and other applications.
There are many different types of reinforcement learning algorithms, but they are mainly divided into two categories: "model-based" and "model-free".
In a conversation with TechTalks, neuroscientist and author of "The Birth of Intelligence" Daeyeol Lee discusses different models of reinforcement learning in humans and animals, artificial intelligence and natural intelligence, and future research directions .

Model-free reinforcement learning
In the late 19th century, the "law of effect" proposed by psychologist Edward Thorndike became the basis of model-free reinforcement learning . Thorndike proposed that behaviors that have a positive impact in a specific situation are more likely to happen again in that situation, while behaviors that have a negative impact are less likely to happen again.
Thorndike explored this "law of effect" in an experiment. He placed a cat in a maze box and measured the time it took for the cat to escape from the box. To escape, the cat must operate a series of gadgets, such as ropes and levers. Thorndike observed that as the cat interacted with the puzzle box, it learned behaviors that aided in its escape. As time goes by, the cat escapes the box faster and faster. Thorndike concluded that cats can learn from the rewards and punishments their behaviors provide. The "Law of Effect" later paved the way for behaviorism. Behaviorism is a branch of psychology that attempts to explain human and animal behavior in terms of stimuli and responses. The “Law of Effect” is also the basis of model-free reinforcement learning. In model-free reinforcement learning, an agent perceives the world and then takes actions while measuring rewards.
In model-free reinforcement learning, there is no direct knowledge or world model. RL agents must directly experience the results of each action through trial and error.
Model-based reinforcement learning
Thorndike’s “Law of Effect” remained popular until the 1930s. Another psychologist at the time, Edward Tolman, discovered an important insight while exploring how rats quickly learned to navigate mazes. During his experiments, Tolman realized that animals could learn about their environment without reinforcement.
For example, when a mouse is released in a maze, it will freely explore the tunnel and gradually understand the structure of the environment. If the rat is then reintroduced to the same environment and provided with reinforcing signals, such as searching for food or finding an exit, it can reach the goal faster than an animal that has not explored the maze. Tolman calls this "latent learning", which becomes the basis of model-based reinforcement learning. "Latent learning" allows animals and humans to form a mental representation of their world, simulate hypothetical scenarios in their minds, and predict outcomes.
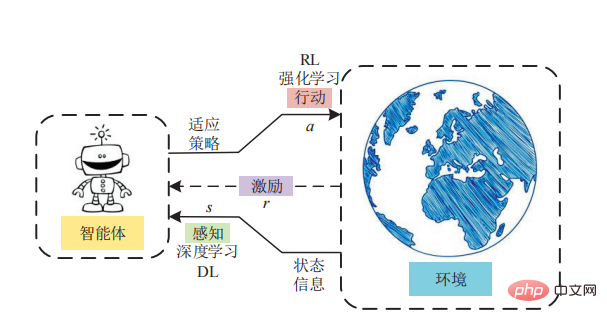
# The advantage of model-based reinforcement learning is that it eliminates the need for the agent to perform trial and error in the environment. It’s worth emphasizing that model-based reinforcement learning has been particularly successful in developing artificial intelligence systems capable of mastering board games such as chess and Go, possibly because the environments of these games are deterministic.

Model-based VS model-free
Generally speaking, model-based reinforcement learning will be very time-consuming. When it is extremely time-sensitive, it may Fatal danger occurs. "Computationally, model-based reinforcement learning is much more complex," Lee said. "First you have to obtain the model, perform a mental simulation, and then you have to find the trajectory of the neural process and then take action. However, model-based reinforcement learning is not necessarily It's more complicated than model-free RL." When the environment is very complex, if it can be modeled with a relatively simple model (which can be obtained quickly), then the simulation will be much simpler and cost-effective.
Multiple learning modes
In fact, neither model-based reinforcement learning nor model-free reinforcement learning is a perfect solution. Wherever you see a reinforcement learning system solving a complex problem, it's likely that it uses both model-based and model-free reinforcement learning, and possibly even more forms of learning. Research in neuroscience shows that both humans and animals have multiple ways of learning, and that the brain is constantly switching between these modes at any given moment. In recent years, there has been growing interest in creating artificial intelligence systems that combine multiple reinforcement learning models. Recent research by scientists at UC San Diego shows that combining model-free reinforcement learning and model-based reinforcement learning can achieve superior performance in control tasks. "If you look at a complex algorithm like AlphaGo, it has both model-free RL elements and model-based RL elements," Lee said. "It learns state values based on the board configuration. It's basically model-free RL, but it Model-based forward search is also performed."
Despite significant achievements, progress in reinforcement learning remains slow. Once an RL model faces a complex and unpredictable environment, its performance begins to degrade.
Lee said: "I think our brain is a complex world of learning algorithms that have evolved to handle many different situations."
In addition to constantly moving between these learning modes Beyond switching, the brain also manages to maintain and update them all the time, even when they are not actively involved in decision-making.
Psychologist Daniel Kahneman said: "Maintaining different learning modules and updating them simultaneously can help improve the efficiency and accuracy of artificial intelligence systems."
We also need to understand another aspect. Thing - how to apply the right inductive bias in AI systems to ensure they learn the right things in a cost-effective way. Billions of years of evolution have given humans and animals the inductive bias needed to learn effectively while using as little data as possible. Inductive bias can be understood as summarizing the rules from the phenomena observed in real life, and then placing certain constraints on the model, which can play the role of model selection, that is, selecting a model that is more consistent with the real rules from the hypothesis space. . "We get very little information from the environment. Using that information, we have to generalize," Lee said. "The reason is that the brain has an inductive bias, and there's a bias to generalizing from a small set of examples. That's a product of evolution." "More and more neuroscientists are interested in this." However, while inductive bias is easy to understand in object recognition tasks, it becomes obscure in abstract problems such as constructing social relationships. In the future, there is still a lot we need to know~~~
Reference materials:
https://thenextweb.com/news/everything-you-need-to-know-about- model-free-and-model-based-reinforcement-learning
The above is the detailed content of From mice walking in the maze to AlphaGo defeating humans, the development of reinforcement learning. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1378
1378
 52
52
 How to implement file sorting by debian readdir
Apr 13, 2025 am 09:06 AM
How to implement file sorting by debian readdir
Apr 13, 2025 am 09:06 AM
In Debian systems, the readdir function is used to read directory contents, but the order in which it returns is not predefined. To sort files in a directory, you need to read all files first, and then sort them using the qsort function. The following code demonstrates how to sort directory files using readdir and qsort in Debian system: #include#include#include#include#include//Custom comparison function, used for qsortintcompare(constvoid*a,constvoid*b){returnstrcmp(*(
 How to set the Debian Apache log level
Apr 13, 2025 am 08:33 AM
How to set the Debian Apache log level
Apr 13, 2025 am 08:33 AM
This article describes how to adjust the logging level of the ApacheWeb server in the Debian system. By modifying the configuration file, you can control the verbose level of log information recorded by Apache. Method 1: Modify the main configuration file to locate the configuration file: The configuration file of Apache2.x is usually located in the /etc/apache2/ directory. The file name may be apache2.conf or httpd.conf, depending on your installation method. Edit configuration file: Open configuration file with root permissions using a text editor (such as nano): sudonano/etc/apache2/apache2.conf
 How to optimize the performance of debian readdir
Apr 13, 2025 am 08:48 AM
How to optimize the performance of debian readdir
Apr 13, 2025 am 08:48 AM
In Debian systems, readdir system calls are used to read directory contents. If its performance is not good, try the following optimization strategy: Simplify the number of directory files: Split large directories into multiple small directories as much as possible, reducing the number of items processed per readdir call. Enable directory content caching: build a cache mechanism, update the cache regularly or when directory content changes, and reduce frequent calls to readdir. Memory caches (such as Memcached or Redis) or local caches (such as files or databases) can be considered. Adopt efficient data structure: If you implement directory traversal by yourself, select more efficient data structures (such as hash tables instead of linear search) to store and access directory information
 Debian mail server firewall configuration tips
Apr 13, 2025 am 11:42 AM
Debian mail server firewall configuration tips
Apr 13, 2025 am 11:42 AM
Configuring a Debian mail server's firewall is an important step in ensuring server security. The following are several commonly used firewall configuration methods, including the use of iptables and firewalld. Use iptables to configure firewall to install iptables (if not already installed): sudoapt-getupdatesudoapt-getinstalliptablesView current iptables rules: sudoiptables-L configuration
 Debian mail server SSL certificate installation method
Apr 13, 2025 am 11:39 AM
Debian mail server SSL certificate installation method
Apr 13, 2025 am 11:39 AM
The steps to install an SSL certificate on the Debian mail server are as follows: 1. Install the OpenSSL toolkit First, make sure that the OpenSSL toolkit is already installed on your system. If not installed, you can use the following command to install: sudoapt-getupdatesudoapt-getinstallopenssl2. Generate private key and certificate request Next, use OpenSSL to generate a 2048-bit RSA private key and a certificate request (CSR): openss
 How debian readdir integrates with other tools
Apr 13, 2025 am 09:42 AM
How debian readdir integrates with other tools
Apr 13, 2025 am 09:42 AM
The readdir function in the Debian system is a system call used to read directory contents and is often used in C programming. This article will explain how to integrate readdir with other tools to enhance its functionality. Method 1: Combining C language program and pipeline First, write a C program to call the readdir function and output the result: #include#include#include#includeintmain(intargc,char*argv[]){DIR*dir;structdirent*entry;if(argc!=2){
 How Debian OpenSSL prevents man-in-the-middle attacks
Apr 13, 2025 am 10:30 AM
How Debian OpenSSL prevents man-in-the-middle attacks
Apr 13, 2025 am 10:30 AM
In Debian systems, OpenSSL is an important library for encryption, decryption and certificate management. To prevent a man-in-the-middle attack (MITM), the following measures can be taken: Use HTTPS: Ensure that all network requests use the HTTPS protocol instead of HTTP. HTTPS uses TLS (Transport Layer Security Protocol) to encrypt communication data to ensure that the data is not stolen or tampered during transmission. Verify server certificate: Manually verify the server certificate on the client to ensure it is trustworthy. The server can be manually verified through the delegate method of URLSession
 How to learn Debian syslog
Apr 13, 2025 am 11:51 AM
How to learn Debian syslog
Apr 13, 2025 am 11:51 AM
This guide will guide you to learn how to use Syslog in Debian systems. Syslog is a key service in Linux systems for logging system and application log messages. It helps administrators monitor and analyze system activity to quickly identify and resolve problems. 1. Basic knowledge of Syslog The core functions of Syslog include: centrally collecting and managing log messages; supporting multiple log output formats and target locations (such as files or networks); providing real-time log viewing and filtering functions. 2. Install and configure Syslog (using Rsyslog) The Debian system uses Rsyslog by default. You can install it with the following command: sudoaptupdatesud



