
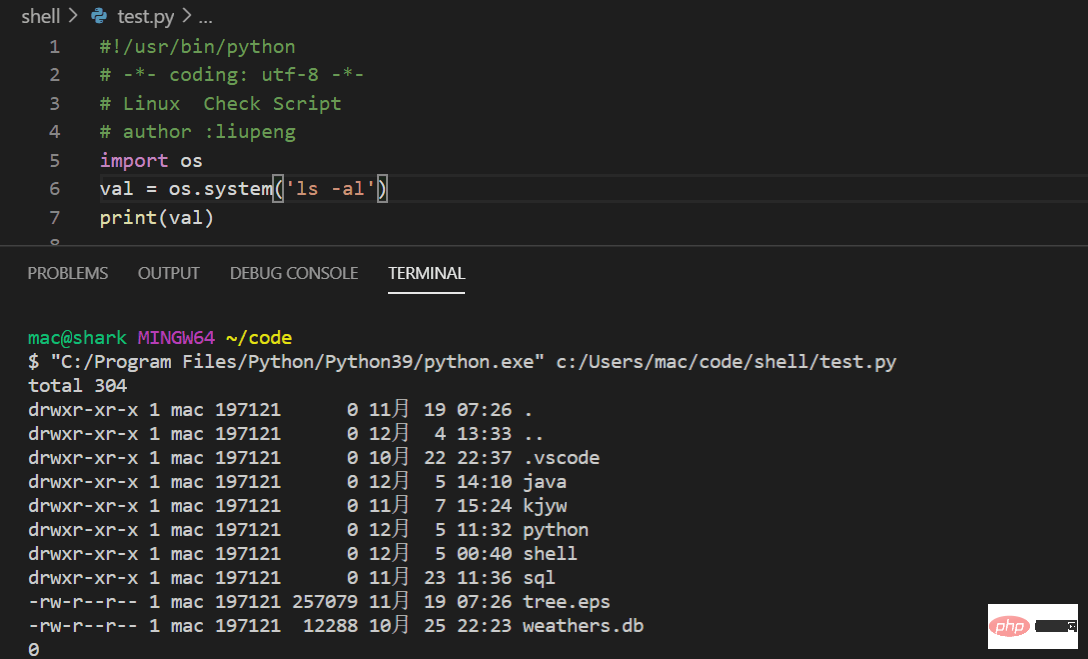
os.system (cmd), the return value is the status code returned after the shell command is run,
int type,
0-- Indicates that the shell command was executed successfully,
256-- indicates that the shell was not found,
This method is suitable for scenarios where the shell command does not need to output content.
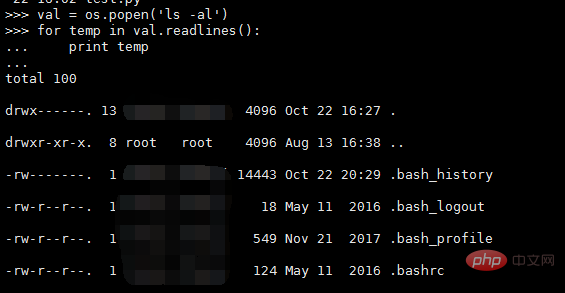
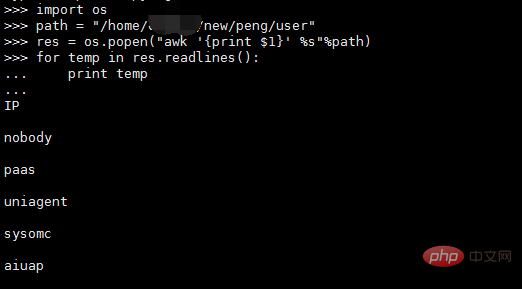
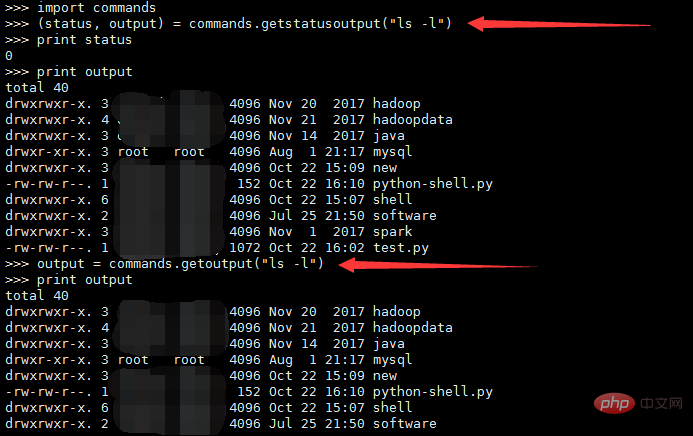
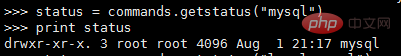
This method returns the result of running the shell command in the form of a file,
needs to obtain the content You can use the read() or readlines() method, for example:
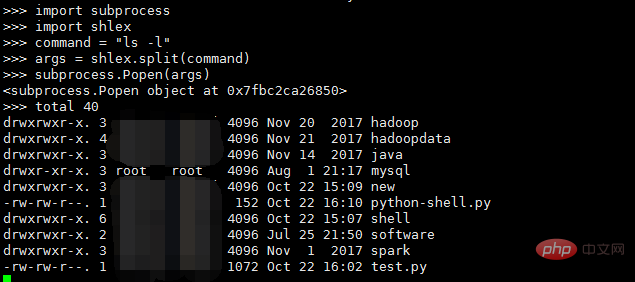
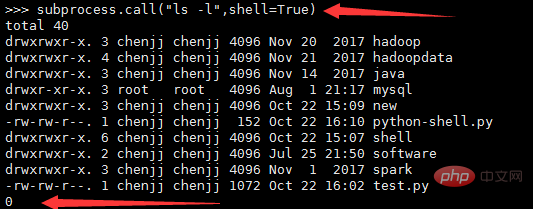
# Stubs for subprocess
# Based on http://docs.python.org/2/library/subprocess.html and Python 3 stub
from typing import Sequence, Any, Mapping, Callable, Tuple, IO, Union, Optional, List, Text
_FILE = Union[None, int, IO[Any]]
_TXT = Union[bytes, Text]
_CMD = Union[_TXT, Sequence[_TXT]]
_ENV = Union[Mapping[bytes, _TXT], Mapping[Text, _TXT]]
# Same args as Popen.__init__
def call(args: _CMD,
bufsize: int = ...,
executable: _TXT = ...,
stdin: _FILE = ...,
stdout: _FILE = ...,
stderr: _FILE = ...,
preexec_fn: Callable[[], Any] = ...,
close_fds: bool = ...,
shell: bool = ...,
cwd: _TXT = ...,
env: _ENV = ...,
universal_newlines: bool = ...,
startupinfo: Any = ...,
creationflags: int = ...) -> int: ...
def check_call(args: _CMD,
bufsize: int = ...,
executable: _TXT = ...,
stdin: _FILE = ...,
stdout: _FILE = ...,
stderr: _FILE = ...,
preexec_fn: Callable[[], Any] = ...,
close_fds: bool = ...,
shell: bool = ...,
cwd: _TXT = ...,
env: _ENV = ...,
universal_newlines: bool = ...,
startupinfo: Any = ...,
creationflags: int = ...) -> int: ...
# Same args as Popen.__init__ except for stdout
def check_output(args: _CMD,
bufsize: int = ...,
executable: _TXT = ...,
stdin: _FILE = ...,
stderr: _FILE = ...,
preexec_fn: Callable[[], Any] = ...,
close_fds: bool = ...,
shell: bool = ...,
cwd: _TXT = ...,
env: _ENV = ...,
universal_newlines: bool = ...,
startupinfo: Any = ...,
creationflags: int = ...) -> bytes: ...
PIPE = ... # type: int
STDOUT = ... # type: int
class CalledProcessError(Exception):
returncode = 0
# morally: _CMD
cmd = ... # type: Any
# morally: Optional[bytes]
output = ... # type: Any
def __init__(self,
returncode: int,
cmd: _CMD,
output: Optional[bytes] = ...) -> None: ...
class Popen:
stdin = ... # type: Optional[IO[Any]]
stdout = ... # type: Optional[IO[Any]]
stderr = ... # type: Optional[IO[Any]]
pid = 0
returncode = 0
def __init__(self,
args: _CMD,
bufsize: int = ...,
executable: Optional[_TXT] = ...,
stdin: Optional[_FILE] = ...,
stdout: Optional[_FILE] = ...,
stderr: Optional[_FILE] = ...,
preexec_fn: Optional[Callable[[], Any]] = ...,
close_fds: bool = ...,
shell: bool = ...,
cwd: Optional[_TXT] = ...,
env: Optional[_ENV] = ...,
universal_newlines: bool = ...,
startupinfo: Optional[Any] = ...,
creationflags: int = ...) -> None: ...
def poll(self) -> int: ...
def wait(self) -> int: ...
# morally: -> Tuple[Optional[bytes], Optional[bytes]]
def communicate(self, input: Optional[_TXT] = ...) -> Tuple[Any, Any]: ...
def send_signal(self, signal: int) -> None: ...
def terminate(self) -> None: ...
def kill(self) -> None: ...
def __enter__(self) -> 'Popen': ...
def __exit__(self, type, value, traceback) -> bool: ...
# Windows-only: STARTUPINFO etc.
STD_INPUT_HANDLE = ... # type: Any
STD_OUTPUT_HANDLE = ... # type: Any
STD_ERROR_HANDLE = ... # type: Any
SW_HIDE = ... # type: Any
STARTF_USESTDHANDLES = ... # type: Any
STARTF_USESHOWWINDOW = ... # type: Any
CREATE_NEW_CONSOLE = ... # type: Any
CREATE_NEW_PROCESS_GROUP = ... # type: AnyThe above is the detailed content of How to write python inspection script. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!




