How to use Java to implement paging query function
Paging query
Paging query displays the huge data in the database in segments. Each page displays a user-defined number of rows to improve the user experience. The most important thing is that if it is read from the server disk at one time Output all the data to the memory, there is a risk of memory overflow
True and false paging
False paging: The principle is to read all the data into the memory, turn the page to read the data from the memory, Advantages: Simple implementation, high performance Disadvantages: If the data is large, it is easy to cause memory overflow
True paging: Query data from the database (i.e. disk) every time the page is turned, Advantages: It is not easy to cause memory overflow Disadvantages: Complex implementation, relatively low performance Some
Paging effects
General paging functions include: Home page Previous page Next page Last page How many pages are there currently How many pages in total How many rows in total How many pages does the data jump to? How many pages per page We need to query this data and encapsulate it into an object, which embodies the idea of encapsulation and saves a lot of complex code
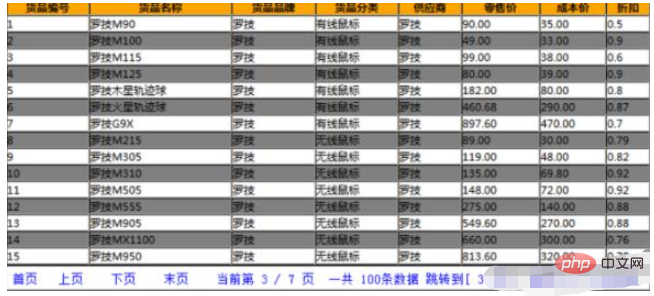
Parameters that need to be passed for paging
Parameters that need to be passed in by the user:
currentPage: current page, which page to jump to, the first time we visit, we create an object, the default value is 1
pageSize: every How many rows of data are displayed on the page? For the first time, we also give a default value, such as 10.
Data to be displayed in each page
1. Product information of the current page
2. What page is the homepage?
3. What page is the previous page?
4. What page is the next page?
5. How many pages are there in total? The value of the last page is the same.
6. How many pieces (rows) of data are there in total?
7. What page is the current page?
8. How many pieces of information are displayed on each page?
The source of the data that needs to be displayed in paging
Sourced from user upload: current page, how many pieces of data are displayed on each page
Sourced from database query: total number of data, product information to be displayed on each page
Sourced from based on Calculation of the above known information: total number of pages, previous page, next page
Write the sql statement to query from the database
The first sql query in the database How many pieces of data are there? There can be no spaces after COUNT
1 |
|
The second sql queries the page based on the parameters passed in, and the result set of how many pieces of data on one page
1 2 3 |
|
Next analyze the page Two of the two SQLs? Value source:
Assume that there are 21 pieces of data in the product table, and each page is divided into 5 pieces of data:
Query the first page of data: SELECT * FROM product LIMIT 0, 5
Query the data on the second page: SELECT * FROM product LIMIT 5, 5
Query the data on the third page: SELECT * FROM product LIMIT 10, 5
Query the data on the fourth page: SELECT * FROM product LIMIT 15, 5
By looking for the rules, we found: the first? value comes from (currentPage - 1) * pageSize; the second? value comes from
pageSize, that is, they all come from the paging parameters passed by the user.
Total number of pages, previous page and next page
1 2 3 4 5 6 |
|
Paging query implementation
Access process:
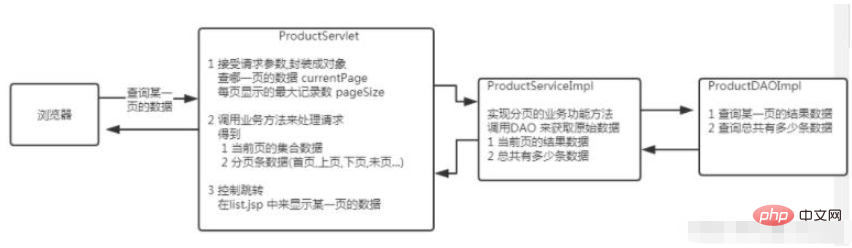
Encapsulate the data that needs to be displayed
If the data is not encapsulated, each data needs to be stored in the scope, and the data is too scattered. It is inconvenient for unified management
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 |
|
Persistence layer DAO
The operation method provided by Mybatis can only pass in one parameter to execute the SQL task, and we are now querying the data of a certain page , we need to know the two parameters of which page it is and how many pieces of data per page, so we need to encapsulate these two parameters in an object
Write a class (named query object class) to encapsulate these query data
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 |
|
Then write the persistence layer DAO interface and implementation class
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 |
|
Modify productMapper.xml
1 2 3 4 5 6 |
|
Modify QueryObject.java
Add the getStart method to this class, Returns the row size of each page that needs to be displayed from the database based on the current page
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 |
|
Business layer ProductService
Calls the persistence layer DAO to complete the data query, and Multiple data are encapsulated into one object
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 |
|
Implementation of front-end paging function
1. The business layer components must be completed first to ensure that the background test passes.
2. Follow the MVC idea.
3. The browser sends the paging request parameters (which page to go to/how many pieces of data per page), receives these parameters in the Servlet, and encapsulates them
4. To the QueryObject object, call the paging query method in the Service ( query).
5. Share the obtained paging query result object (PageResult) in the request scope, jump to JSP, and display it.
6. Modify the JSP page and write out the paging bar information (the information in the paging bar comes from the PageResult object).
Modify ProductServlet.java and display jsp
1. Get the page request parameters, determine it is a query operation, call the query method, and get the paging parameters
2. The parameters are encapsulated into QueryObject
3. Call the business layer method to query a certain page of data
4. Store the query results in the scope
5. Forward to the display page jsp
6. Take the results out of the scope in jsp and respond to the browser
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 |
|
Modify the jsp file and use JSTL EL to obtain the data in the scope
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 |
|
FAQ
If the page turning operation is successful and you can't turn after a few pages, you can only turn tomcat by restarting. Problem: The SqlSession object is not closed in DAO
The above is the detailed content of How to use Java to implement paging query function. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1359
1359
 52
52
 Square Root in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:26 PM
Square Root in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:26 PM
Guide to Square Root in Java. Here we discuss how Square Root works in Java with example and its code implementation respectively.
 Perfect Number in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:28 PM
Perfect Number in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:28 PM
Guide to Perfect Number in Java. Here we discuss the Definition, How to check Perfect number in Java?, examples with code implementation.
 Random Number Generator in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:27 PM
Random Number Generator in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:27 PM
Guide to Random Number Generator in Java. Here we discuss Functions in Java with examples and two different Generators with ther examples.
 Armstrong Number in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:26 PM
Armstrong Number in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:26 PM
Guide to the Armstrong Number in Java. Here we discuss an introduction to Armstrong's number in java along with some of the code.
 Weka in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:28 PM
Weka in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:28 PM
Guide to Weka in Java. Here we discuss the Introduction, how to use weka java, the type of platform, and advantages with examples.
 Smith Number in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:28 PM
Smith Number in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:28 PM
Guide to Smith Number in Java. Here we discuss the Definition, How to check smith number in Java? example with code implementation.
 Java Spring Interview Questions
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:29 PM
Java Spring Interview Questions
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:29 PM
In this article, we have kept the most asked Java Spring Interview Questions with their detailed answers. So that you can crack the interview.
 Break or return from Java 8 stream forEach?
Feb 07, 2025 pm 12:09 PM
Break or return from Java 8 stream forEach?
Feb 07, 2025 pm 12:09 PM
Java 8 introduces the Stream API, providing a powerful and expressive way to process data collections. However, a common question when using Stream is: How to break or return from a forEach operation? Traditional loops allow for early interruption or return, but Stream's forEach method does not directly support this method. This article will explain the reasons and explore alternative methods for implementing premature termination in Stream processing systems. Further reading: Java Stream API improvements Understand Stream forEach The forEach method is a terminal operation that performs one operation on each element in the Stream. Its design intention is




