 Java
Java
 javaTutorial
javaTutorial
 How does springboot read lists, arrays, map collections and objects in yml files?
How does springboot read lists, arrays, map collections and objects in yml files?
How does springboot read lists, arrays, map collections and objects in yml files?
application.yml defines the list collection
The first way is to use the @ConfigurationProperties annotation to get all the values of the list collection
type:
code:
status:
- 200
- 300
- 400
- 500Write the entity class corresponding to the configuration file, What needs to be noted here is that to define the list collection, first define a configuration class Bean, and then use the annotation @ConfigurationProperties annotation to obtain the list collection value. Here we will explain the role of the relevant annotations.
@Component Hands over the entity class to Spring management
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = “type.code”) Read the yml file list
@Data automatically generates getter and setter methods
As shown in the figure below
package com.o2o.data;
import lombok.Data;
import org.springframework.boot.context.properties.ConfigurationProperties;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import java.util.List;
@Component
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "type.code") // 配置文件的前缀
@Data
public class TypeCodeConfig {
private List<String> status;
public void setStatus(List<String> status){
this.status = status;
}
public List<String> getStatus(){
return status;
}
}Then where to use For automatic injection, I read this list directly in the startup class. It should be noted that using the list configured in yml requires injecting the object first, and then reading the value in the configuration file through the get method.
@Autowired private TypeCodeConfig typeCodeConfig; Use annotations to inject objects
System.out.println(typeCodeConfig.getStatus()); Call getter Method to read the value
package com.o2o;
import com.o2o.data.TypeCodeConfig;
import org.mybatis.spring.annotation.MapperScan;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.boot.CommandLineRunner;
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.jdbc.DataSourceAutoConfiguration;
@SpringBootApplication(exclude = {DataSourceAutoConfiguration.class})
@MapperScan("com.o2o.mapper")
public class AutoTestApplication implements CommandLineRunner {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(AutoTestApplication.class, args);
}
@Autowired
private TypeCodeConfig typeCodeConfig;
@Override
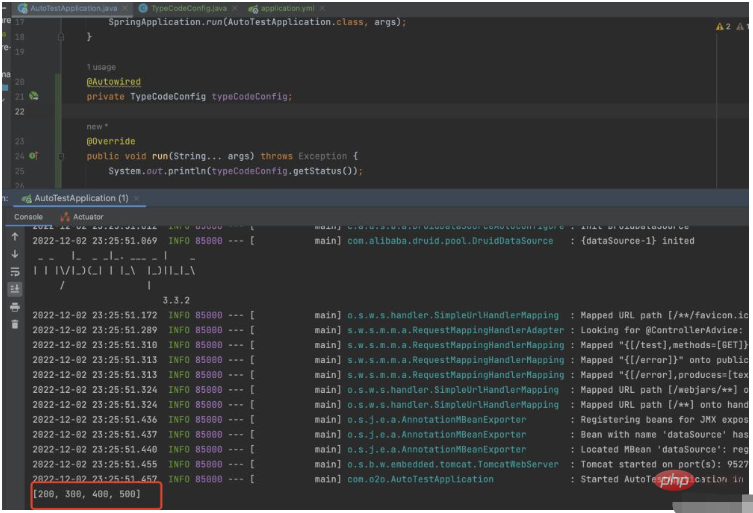
public void run(String... args) throws Exception {
System.out.println(typeCodeConfig.getStatus());Start springboot We have successfully read all the values of the list collection in the yml file from the console
The second method uses the @value annotation to obtain all the values of the list collection
The yml file is configured as follows
student:
ids:
- 7
- 8
- 9Then create an entity class
@Data
public class Student {
@Value("${student.ids}")
private List<Integer> ids;
}Create a new configuration class for the list attribute
@Component
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "student")
@Data
public class TypeCodeConfig {
private List<Integer> ids;
public void setIds(List<Integer> ids) {
this.ids = ids;
}
public List<Integer> getIds(){
return ids;
}Inject in the startup class
@SpringBootApplication(exclude = {DataSourceAutoConfiguration.class})
@MapperScan("com.o2o.mapper")
public class AutoTestApplication implements CommandLineRunner {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(AutoTestApplication.class, args);
}
@Autowired
private TypeCodeConfig typeCodeConfig;
@Override
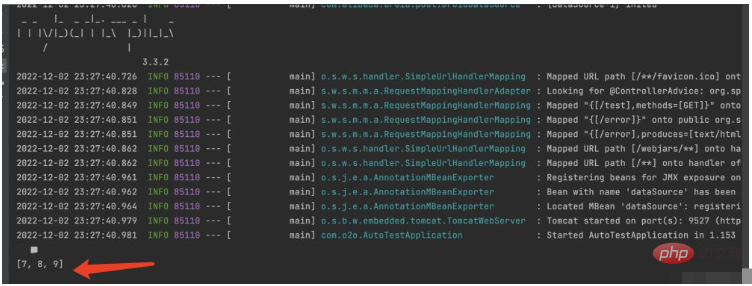
public void run(String... args) throws Exception {
System.out.println(typeCodeConfig.getIds());
}Start springboot and we have successfully read all the values of the list collection in the yml file from the console
application.yml defines the array type
yml configuration file is as shown below
dataSync: enable: true type: - "1" - "2" - "3"
Get the array value through @value annotation
@Value("${dataSync.enable.type}")
private String[] type; can also be obtained by creating a configuration class bean and using the @ConfigurationProperties annotation , as shown in the following figure:
@Data
@Component
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "dataSync.enable") // 配置 文件的前缀
public class InterceptorPathBean
{
private String[] type;
}yml files can also store objects and collections of objects. The usage method is the same as The basic types are similar.
Simple example:
Define map collection configuration
interceptorconfig:
path:
maps:
name: 小明
age: 24By creating a configuration class bean, use the @ConfigurationProperties annotation to obtain the map value, as shown in the figure below
@Data
@Component
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "interceptorconfig.path") // 配置 文件的前缀
public class InterceptorPathBean
{
private Map<String , String> maps;
}Use objects Configuration
student: id: 1 name: Bruce gender: male
Use object collection configuration
students:
- id: 1
name: Bruce
gender: male
- id: 2
name: ...
...Here I will summarize some important points for you:
1. In the list type yml configuration file, you need to use "- " to form a collection of lists.
2. There is no level limit for the prefix in yml. If it is multi-level, such as demo/code here, the prefix for configuring the ConfigurationProperties annotation in the java class is written as "demo.code"
3. The attribute name supports the hyphen "-" in the yml file, such as four-span. When configuring the attribute in the java class, it needs to be converted to camel case, fourSpan.
4. Java class attributes need to be configured with set and get methods.
The above is the detailed content of How does springboot read lists, arrays, map collections and objects in yml files?. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1378
1378
 52
52
 How to use Redis to implement distributed locks in SpringBoot
Jun 03, 2023 am 08:16 AM
How to use Redis to implement distributed locks in SpringBoot
Jun 03, 2023 am 08:16 AM
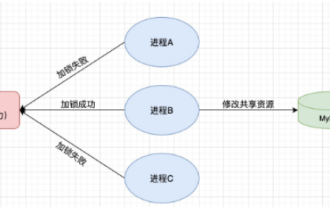
1. Redis implements distributed lock principle and why distributed locks are needed. Before talking about distributed locks, it is necessary to explain why distributed locks are needed. The opposite of distributed locks is stand-alone locks. When we write multi-threaded programs, we avoid data problems caused by operating a shared variable at the same time. We usually use a lock to mutually exclude the shared variables to ensure the correctness of the shared variables. Its scope of use is in the same process. If there are multiple processes that need to operate a shared resource at the same time, how can they be mutually exclusive? Today's business applications are usually microservice architecture, which also means that one application will deploy multiple processes. If multiple processes need to modify the same row of records in MySQL, in order to avoid dirty data caused by out-of-order operations, distribution needs to be introduced at this time. The style is locked. Want to achieve points
 How to solve the problem that springboot cannot access the file after reading it into a jar package
Jun 03, 2023 pm 04:38 PM
How to solve the problem that springboot cannot access the file after reading it into a jar package
Jun 03, 2023 pm 04:38 PM
Springboot reads the file, but cannot access the latest development after packaging it into a jar package. There is a situation where springboot cannot read the file after packaging it into a jar package. The reason is that after packaging, the virtual path of the file is invalid and can only be accessed through the stream. Read. The file is under resources publicvoidtest(){Listnames=newArrayList();InputStreamReaderread=null;try{ClassPathResourceresource=newClassPathResource("name.txt");Input
 How to implement Springboot+Mybatis-plus without using SQL statements to add multiple tables
Jun 02, 2023 am 11:07 AM
How to implement Springboot+Mybatis-plus without using SQL statements to add multiple tables
Jun 02, 2023 am 11:07 AM
When Springboot+Mybatis-plus does not use SQL statements to perform multi-table adding operations, the problems I encountered are decomposed by simulating thinking in the test environment: Create a BrandDTO object with parameters to simulate passing parameters to the background. We all know that it is extremely difficult to perform multi-table operations in Mybatis-plus. If you do not use tools such as Mybatis-plus-join, you can only configure the corresponding Mapper.xml file and configure The smelly and long ResultMap, and then write the corresponding sql statement. Although this method seems cumbersome, it is highly flexible and allows us to
 Comparison and difference analysis between SpringBoot and SpringMVC
Dec 29, 2023 am 11:02 AM
Comparison and difference analysis between SpringBoot and SpringMVC
Dec 29, 2023 am 11:02 AM
SpringBoot and SpringMVC are both commonly used frameworks in Java development, but there are some obvious differences between them. This article will explore the features and uses of these two frameworks and compare their differences. First, let's learn about SpringBoot. SpringBoot was developed by the Pivotal team to simplify the creation and deployment of applications based on the Spring framework. It provides a fast, lightweight way to build stand-alone, executable
 How SpringBoot customizes Redis to implement cache serialization
Jun 03, 2023 am 11:32 AM
How SpringBoot customizes Redis to implement cache serialization
Jun 03, 2023 am 11:32 AM
1. Customize RedisTemplate1.1, RedisAPI default serialization mechanism. The API-based Redis cache implementation uses the RedisTemplate template for data caching operations. Here, open the RedisTemplate class and view the source code information of the class. publicclassRedisTemplateextendsRedisAccessorimplementsRedisOperations, BeanClassLoaderAware{//Declare key, Various serialization methods of value, the initial value is empty @NullableprivateRedisSe
 How to get the value in application.yml in springboot
Jun 03, 2023 pm 06:43 PM
How to get the value in application.yml in springboot
Jun 03, 2023 pm 06:43 PM
In projects, some configuration information is often needed. This information may have different configurations in the test environment and the production environment, and may need to be modified later based on actual business conditions. We cannot hard-code these configurations in the code. It is best to write them in the configuration file. For example, you can write this information in the application.yml file. So, how to get or use this address in the code? There are 2 methods. Method 1: We can get the value corresponding to the key in the configuration file (application.yml) through the ${key} annotated with @Value. This method is suitable for situations where there are relatively few microservices. Method 2: In actual projects, When business is complicated, logic
 SpringBoot+Dubbo+Nacos development practical tutorial
Aug 15, 2023 pm 04:49 PM
SpringBoot+Dubbo+Nacos development practical tutorial
Aug 15, 2023 pm 04:49 PM
This article will write a detailed example to talk about the actual development of dubbo+nacos+Spring Boot. This article will not cover too much theoretical knowledge, but will write the simplest example to illustrate how dubbo can be integrated with nacos to quickly build a development environment.
 3 ways for SpringBoot to read yml files
Jun 29, 2023 pm 11:25 PM
3 ways for SpringBoot to read yml files
Jun 29, 2023 pm 11:25 PM
The main ways SpringBoot reads yml files are as follows: 1. @Value annotation We can use the @Value annotation on the properties of the bean to directly read the value in yml, such as: application.yml:name:ZhangsanBean:publicclassMyBean{ @Value("${name}")privateStringname;}2.Environment object We can read the yml value by injecting the Environment object, such as: @AutowiredprivateEnvironmentenv



