How to implement springboot rabbitmq reply message direct reply mode
1. Usage Scenarios
The functions of MQ include decoupling, asynchronous, etc.
Usually producers are only responsible for producing messages, and do not care who gets the messages, or what the consumption results are; consumers are only responsible for receiving specified messages for business processing and do not care where the messages come from, first-level reply business processing Condition. But there is a special business in our project. As a message producer, we need to receive the response result of the consumer after producing the message (to put it bluntly, it is similar to the MQ use of synchronous call request response). After research, MQ’s Reply mode (direct reply model) was created for this business model.
2. Reply actual combat
(1) Dependency and YML configuration
Dependency:
I only list the core here Required dependencies for rabbitMq
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-amqp</artifactId>
</dependency>Configuration:
No other special configuration, because reply is just an interaction method of rabbitmq
spring:
rabbitmq:
host: 10.50.40.116
port: 5673
username: admin
password: admin(2 ) RabbitMq bean configuration
package com.leilei.demo;
import org.springframework.amqp.core.FanoutExchange;
import org.springframework.amqp.core.Queue;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
/**
* @author lei
* @create 2022-09-19 21:44
* @desc mq配置
**/
@Configuration
public class RabbitMqConfig {
@Bean
public Queue bizQueue() {
return new Queue("bizQueue");
}
@Bean
public Queue replyQueue() {
return new Queue("replyQueue");
}
@Bean
FanoutExchange bizExchange() {
return new FanoutExchange("bizExchange");
}
}Business class:
@Data
@NoArgsConstructor
@AllArgsConstructor
public class Vehicle implements Serializable {
private Integer id;
private String name;
}(3) Message production end
What the message production end needs to do: Have a message produced , Accept message consumption response
(1) Produce message
1. Produce message, depending on the business scenario, choose whether to generate a globally unique custom message Message ID
2. Specify the queue for response after message consumption (Reply)
/**
* 生产消息
*
* @param
* @return void
* @author lei
* @date 2022-09-19 21:59:18
*/
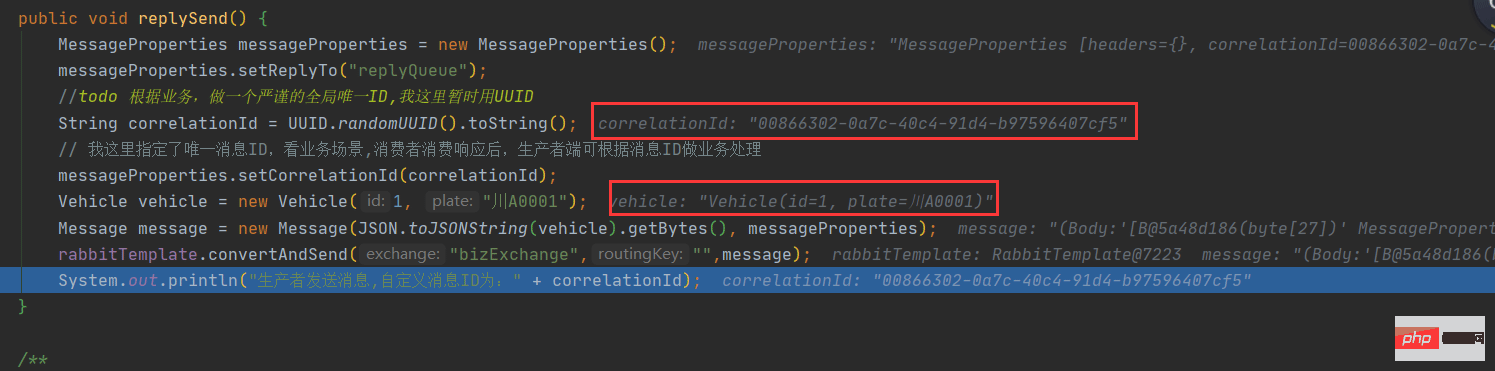
public void replySend() {
MessageProperties messageProperties = new MessageProperties();
messageProperties.setReplyTo("replyQueue");
//todo 根据业务,做一个严谨的全局唯一ID,我这里暂时用UUID
String correlationId = UUID.randomUUID().toString();
// 我这里指定了唯一消息ID,看业务场景,消费者消费响应后,生产者端可根据消息ID做业务处理
messageProperties.setCorrelationId(correlationId);
Vehicle vehicle = new Vehicle(1, "川A0001");
Message message = new Message(JSON.toJSONString(vehicle).getBytes(), messageProperties);
rabbitTemplate.convertAndSend("bizExchange","",message);
System.out.println("生产者发送消息,自定义消息ID为:" + correlationId);
}(2) Accept Reply response
After the consumer consumes the message, the processing result will be sent to a queue. By reading the queue here, we can get the response result of the corresponding message for business processing
/**
* 接收消息响应
*
* @param message
* @return void
* @author lei
* @date 2022-09-19 21:59:27
*/
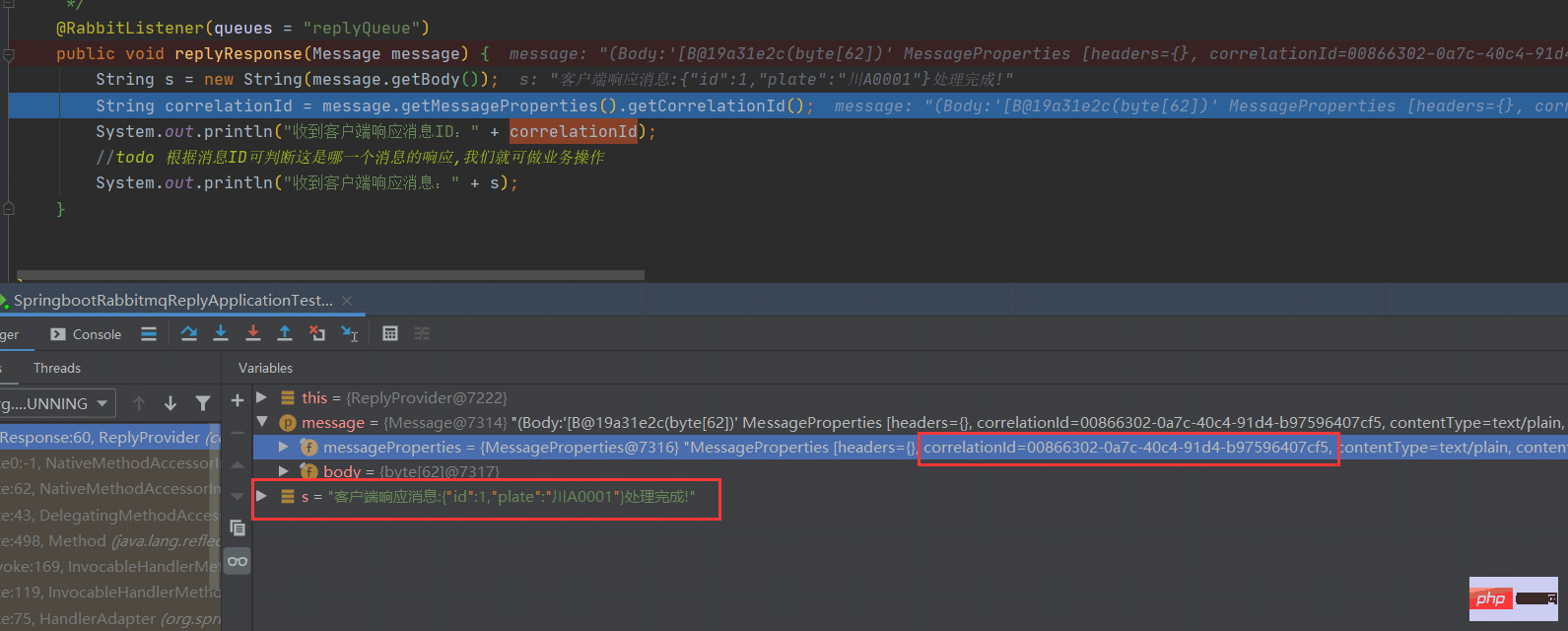
@RabbitListener(queues = "replyQueue")
public void replyResponse(Message message) {
String s = new String(message.getBody());
String correlationId = message.getMessageProperties().getCorrelationId();
System.out.println("收到客户端响应消息ID:" + correlationId);
//todo 根据消息ID可判断这是哪一个消息的响应,我们就可做业务操作
System.out.println("收到客户端响应消息:" + s);
}(4) Message consumer end
What the message consumer end needs to do is: accept the message and then perform business processing and respond to the message
(1) Method 1: sendTo annotation method return value
Generally speaking, our mq consumer listening method does not need to return a value. If we use the sendTo annotation here, we need to define the message to be responded to as the return value. The sendTo annotation specifies which queue to respond to
Key points:
1. The sendTo annotation specifies the corresponding queue (note that it is consistent with the production end)
2. Method definition The return value content is the message to be responded to, which will eventually be sent to the corresponding queue specified by the sendTo annotation
3. The disadvantage of this method is that the consumer side is very focused, because The target queue specified by sendTo can be written blindly, causing the producer to fail to receive the message response correctly, but I believe that this is not done in general projects
/**
* 方式1 SendTo指定响应队列
*
* @param message
* @return String
* @author lei
* @date 2022-09-19 16:17:52
*/
@RabbitListener(queues ="bizQueue")
@SendTo("replyQueue")
public String handleEmailMessage(Message message) {
try {
String msg=new String(message.getBody(), StandardCharsets.UTF_8);
log.info("---consumer接收到消息----{}",msg);
return "客户端响应消息:"+msg+"处理完成!";
} catch (Exception e) {
log.error("处理业务消息失败",e);
}
return null;
}(2) Method 2 : Read the message from the production end and send it using the template
Just like the ordinary consumer method, you only need the RabbitListener annotation to listen to the business queue; but you also need to obtain the ReplyTo address based on the message, and then manually send the message within your own consumer method
1. Advantages, you can feel the interactivity of message request and response more strongly, and the process looks clearer
2. Disadvantages, code Indecent
/**
* 方式2 message消息获取内部reply rabbitmq手动发送
*
* @param message
* @return String
* @author lei
* @date 2022-09-19 16:17:52
*/
@RabbitListener(queues = "bizQueue")
public void handleEmailMessage2(Message message) {
try {
String msg = new String(message.getBody(), StandardCharsets.UTF_8);
log.info("---consumer接收到消息----{}", msg);
String replyTo = message.getMessageProperties().getReplyTo();
System.out.println("接收到的reply:" + replyTo);
rabbitTemplate.convertAndSend(replyTo, "客户端响应消息:" + msg + "处理完成!", x -> {
x.getMessageProperties().setCorrelationId(message.getMessageProperties().getCorrelationId());
return x;
});
} catch (Exception e) {
log.error("处理业务消息失败",e);
}
}(3) Method 3: Method return value
This method is actually consistent with 1, but I have tested it because the producer message specifies Without the address of ReplyTo, the consumer does not need to manually specify it again, that is, where to produce the message, whether to respond and where to send the response message are all left to the producer itself. The consumer only needs to process its own business and return results
/**
* 方式三 方法有返回值,返回要响应的数据 (reply 由生产者发送消息时指定,消费者不做任何处理)
*
* @param message
* @return String
* @author lei
* @date 2022-09-19 23:17:47
*/
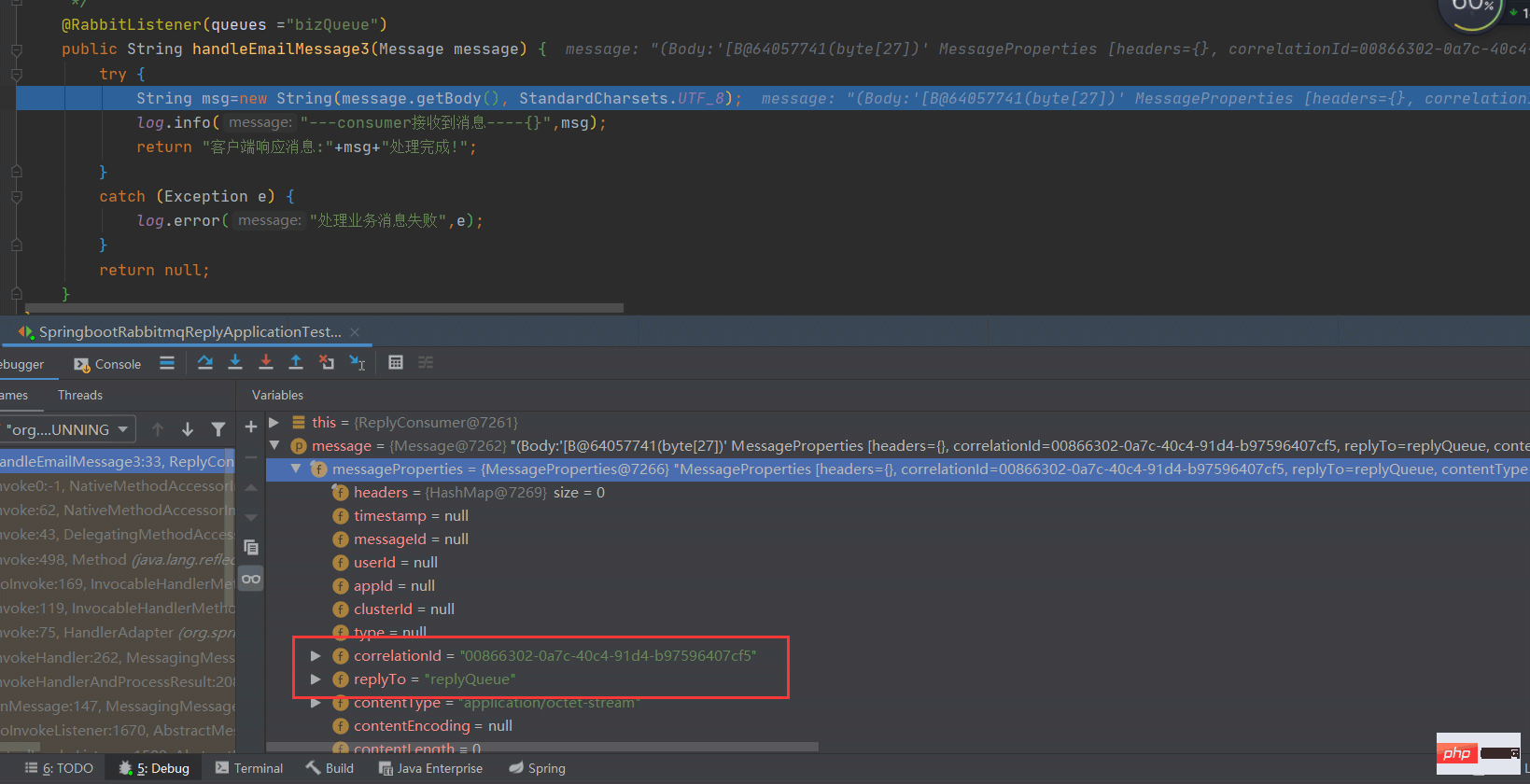
@RabbitListener(queues ="bizQueue")
public String handleEmailMessage3(Message message) {
try {
String msg=new String(message.getBody(), StandardCharsets.UTF_8);
log.info("---consumer接收到消息----{}",msg);
return "客户端响应消息:"+msg+"处理完成!";
}
catch (Exception e) {
log.error("处理业务消息失败",e);
}
return null;
}(4) Test
Production message:
##Consumption message and response:
Response received:
The above is the detailed content of How to implement springboot rabbitmq reply message direct reply mode. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1387
1387
 52
52
 How to build a reliable messaging app with React and RabbitMQ
Sep 28, 2023 pm 08:24 PM
How to build a reliable messaging app with React and RabbitMQ
Sep 28, 2023 pm 08:24 PM
How to build a reliable messaging application with React and RabbitMQ Introduction: Modern applications need to support reliable messaging to achieve features such as real-time updates and data synchronization. React is a popular JavaScript library for building user interfaces, while RabbitMQ is a reliable messaging middleware. This article will introduce how to combine React and RabbitMQ to build a reliable messaging application, and provide specific code examples. RabbitMQ overview:
 How to use RabbitMQ to implement distributed message processing in PHP
Jul 18, 2023 am 11:00 AM
How to use RabbitMQ to implement distributed message processing in PHP
Jul 18, 2023 am 11:00 AM
How to use RabbitMQ to implement distributed message processing in PHP Introduction: In large-scale application development, distributed systems have become a common requirement. Distributed message processing is a pattern that improves the efficiency and reliability of the system by distributing tasks to multiple processing nodes. RabbitMQ is an open source, reliable message queuing system that uses the AMQP protocol to implement message delivery and processing. In this article we will cover how to use RabbitMQ in PHP for distribution
 Comparison and difference analysis between SpringBoot and SpringMVC
Dec 29, 2023 am 11:02 AM
Comparison and difference analysis between SpringBoot and SpringMVC
Dec 29, 2023 am 11:02 AM
SpringBoot and SpringMVC are both commonly used frameworks in Java development, but there are some obvious differences between them. This article will explore the features and uses of these two frameworks and compare their differences. First, let's learn about SpringBoot. SpringBoot was developed by the Pivotal team to simplify the creation and deployment of applications based on the Spring framework. It provides a fast, lightweight way to build stand-alone, executable
 Using RabbitMQ in Go: A Complete Guide
Jun 19, 2023 am 08:10 AM
Using RabbitMQ in Go: A Complete Guide
Jun 19, 2023 am 08:10 AM
As modern applications increase in complexity, messaging has become a powerful tool. In this area, RabbitMQ has become a very popular message broker that can be used to deliver messages between different applications. In this article, we will explore how to use RabbitMQ in Go language. This guide will cover the following: Introduction to RabbitMQ RabbitMQ Installation RabbitMQ Basic Concepts Getting Started with RabbitMQ in Go RabbitMQ and Go
 SpringBoot+Dubbo+Nacos development practical tutorial
Aug 15, 2023 pm 04:49 PM
SpringBoot+Dubbo+Nacos development practical tutorial
Aug 15, 2023 pm 04:49 PM
This article will write a detailed example to talk about the actual development of dubbo+nacos+Spring Boot. This article will not cover too much theoretical knowledge, but will write the simplest example to illustrate how dubbo can be integrated with nacos to quickly build a development environment.
 Solution for real-time data synchronization between Golang and RabbitMQ
Sep 27, 2023 pm 10:41 PM
Solution for real-time data synchronization between Golang and RabbitMQ
Sep 27, 2023 pm 10:41 PM
Introduction to the solution for real-time data synchronization between Golang and RabbitMQ: In today's era, with the popularity of the Internet and the explosive growth of data volume, real-time data synchronization has become more and more important. In order to solve the problems of asynchronous data transmission and data synchronization, many companies have begun to use message queues to achieve real-time synchronization of data. This article will introduce a real-time data synchronization solution based on Golang and RabbitMQ, and provide specific code examples. 1. What is RabbitMQ? Rabbi
 Application practice of go-zero and RabbitMQ
Jun 23, 2023 pm 12:54 PM
Application practice of go-zero and RabbitMQ
Jun 23, 2023 pm 12:54 PM
Now more and more companies are beginning to adopt the microservice architecture model, and in this architecture, message queues have become an important communication method, among which RabbitMQ is widely used. In the Go language, go-zero is a framework that has emerged in recent years. It provides many practical tools and methods to allow developers to use message queues more easily. Below we will introduce go-zero based on practical applications. And the usage and application practice of RabbitMQ. 1.RabbitMQ OverviewRabbit
 Golang RabbitMQ: Architectural design and implementation of a highly available message queue system
Sep 28, 2023 am 08:18 AM
Golang RabbitMQ: Architectural design and implementation of a highly available message queue system
Sep 28, 2023 am 08:18 AM
GolangRabbitMQ: The architectural design and implementation of a highly available message queue system requires specific code examples. Introduction: With the continuous development of Internet technology and its wide application, message queues have become an indispensable part of modern software systems. As a tool to implement decoupling, asynchronous communication, fault-tolerant processing and other functions, message queue provides high availability and scalability support for distributed systems. As an efficient and concise programming language, Golang is widely used to build high-concurrency and high-performance systems.




