
Nmap is the abbreviation of Network Mapper. Nmap is a free, open source network discovery and reconnaissance tool. Nmap can scan the network for active hosts, open ports, operating system version and service detection, and perform stealth information scanning. The installation method is as follows:
#yum安装 yum -y install nmap #rpm包安装 rpm -ivh nmap-4.11-1.1.x86_64.rpm
Check the open ports:
#查看本机开放端口信息(也可以查看其他ip) nmap 127.0.0.1
nmap 127.0.0.1 Check the open ports of this machine and all ports will be scanned.
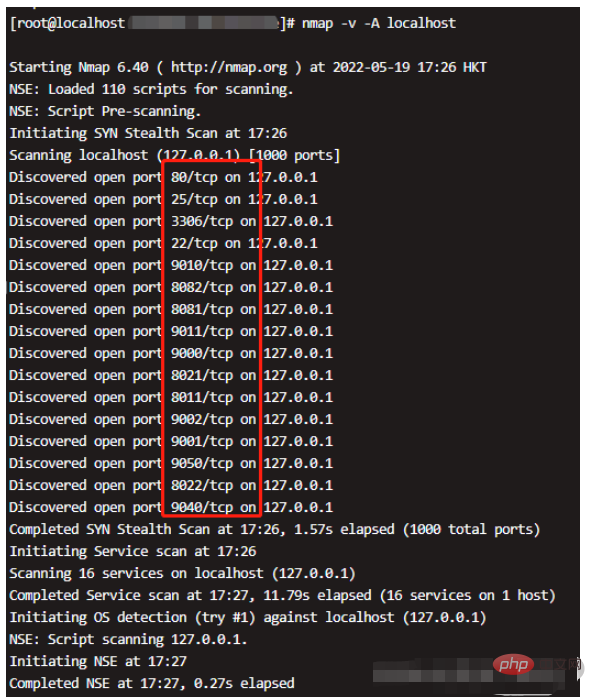
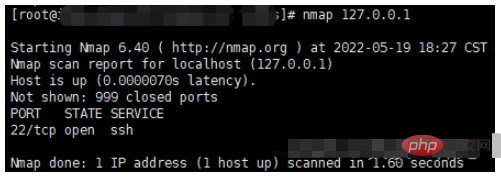
⚠️This tool queries open ports, but it does not work for Alibaba Cloud servers. Only one port 22 can be viewed.
-p: Scan the specified port
-A: Use offensive scanning
-sV: Specify Nmap to perform version detection
-F: Scan the 100 most likely open ports
-v: Display redundant information, display details during scanning
-iL: Import the target host or target network segment from the file
-sn: Only host discovery is performed, no port scanning is performed
– exclude: The connected host or website is not scanned
-sL: Only list the IP of the specified target, and do not perform host discovery
–system-dns: Specify the DNS server to use the system
–excludefile: The host or network segment in the imported file will not be scanned
-n/-R: -n means not to perform DNS resolution; -R means to perform DNS Parsing
-sU: Use UDP scanning to determine the UDP port status of the target host
-Pn: Treat all specified hosts as Enabled, skipping the process of host discovery
-T4: Specify the time used in the scanning process
#There are 6 levels, the higher the level The faster the speed, the easier it is to be detected and blocked. It is recommended to use T4
General scanning command format: nmap scan parameter target address or network segment
Command rules : telnet ip port
If the following content appears, it means that the connection can be made
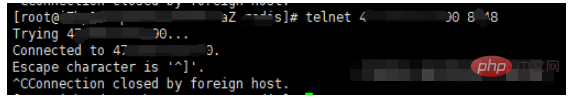
If the server does not have a telnet tool, you can execute the following command to install it:
yum -y install telnet.x86_64
Command rules: curl http:ip:port
A response indicates normal access.
nc is netcat. netcat is a simple Unix tool that uses TCP or UDP protocols to read and write data between network connections.
It is designed to be a reliable backend tool that can be used directly or simply called by other programs or scripts.
At the same time, it is also a feature-rich network debugging and exploration tool, as it can create almost any type of connection you need, and it also has several interesting features built in.
Netcat has three types of functional modes, which are connection mode, listening mode and tunnel mode.
General syntax of the nc (netcat) command:
nc [-options] [HostName or IP] [PortNumber]
In the following example, we Will check whether port 22 in the remote Linux system is open.
[root@zjq zjq666]# nc -zvw3 121.xxx.234.456 8848 Ncat: Version 7.50 ( https://nmap.org/ncat ) Ncat: Connected to 121.xxx.234.456:8848. Ncat: 0 bytes sent, 0 bytes received in 0.01 seconds.
Detailed explanation of command parameters:
nc: the body of the executed command;
z: zero I/O mode (used for scanning);
v: Explicit output;
w3: Set the timeout to 3 seconds;
121.xxx.234.456: The IP address of the target system;
8848: The port that needs to be verified.
The command is as follows:
netstat -ntlp
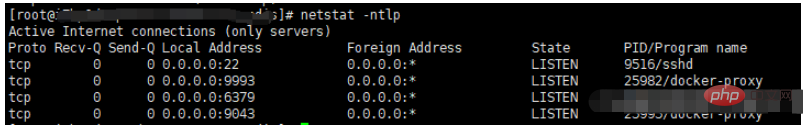
You can query the port usage to avoid Port conflict.
The above is the detailed content of How to check the open ports and enabled ports of the server in Linux. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!




