
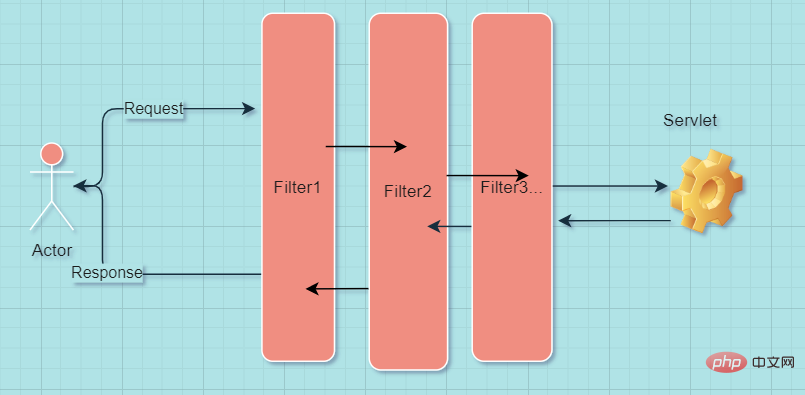
First look at the location of the filter of the web server. Filter is a chain connected before and after. After the previous processing is completed, it is passed to the next filter for processing.
public interface Filter {
//初始化方法,整个生命周期中只执行一次。
//在init方法成功(失败如抛异常等)执行完前,不能提供过滤服务。
//参数FilterConfig用于获取初始化参数
public void init(FilterConfig filterConfig) throws ServletException;
//执行过滤任务的方法,参数FilterChain表示过滤器链,doFilter方法中只有执行chain.doFilter()后才能调用下一个过滤器的doFilter方法
//才能将请求交经下一个Filter或Servlet执行
public void doFilter(ServletRequest request, ServletResponse response, FilterChain chain) throws IOException, ServletException;
//销毁方法,当移出服务时由web容器调用。整个生命周期中destroy方法只会执行一次
//destroy方法可用于释放持有的资源,如内存、文件句柄等
public void destroy();
}The input parameters of filter are request and response. Filter is generally used to do some preprocessing work, such as doing some Check, verify and other work.
public class LoginFilter implements Filter {
@Override
public void destroy() {
System.out.println("filter destroy method");
}
@Override
public void doFilter(ServletRequest arg0, ServletResponse arg1, FilterChain filterChain)
throws IOException, ServletException {
System.out.println("filter doFilter method ");
// 继续传递下去
filterChain.doFilter(arg0,arg1);
}
@Override
public void init(FilterConfig arg0) throws ServletException {
System.out.println("filter init method");
}
}@Configuration
public class FilterConfig {
@Bean
public FilterRegistrationBean indexFilterRegistration() {
FilterRegistrationBean registration = new FilterRegistrationBean(new LoginFilter());
registration.addUrlPatterns("/");
return registration;
}
}2.2.1 Add the annotation @WebFilter
@WebFilter(urlPatterns = "/",filterName = "filter1")
@Order(1)
public class LoginFilter implements Filter {
@Override
public void destroy() {
System.out.println("filter destroy method");
}
@Override
public void doFilter(ServletRequest arg0, ServletResponse arg1, FilterChain filterChain)
throws IOException, ServletException {
System.out.println("filter doFilter method 1 ");
filterChain.doFilter(arg0,arg1);
}
@Override
public void init(FilterConfig arg0) throws ServletException {
System.out.println("filter init method");
}
}2.2.2 Add the annotation @ServletComponentScan
@SpringBootApplication
@ServletComponentScan
public class FilterTestApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(FilterTestApplication.class, args);
}
}to the startup class Note:
@ServletComponentScan will scan all classes with @WebFilter and register them as servlets.
If the startup class does not add this annotation, adding the Component annotation on the filter can also be registered as a filter
The order annotation can adjust the order of the filter
@Autowired ServletContext servletContext; servletContext.addFilter()
The Web container will create a ServletContext object for each web application when it is started, and this ServletContext object represents the current web application.
A ServletContext object represents a web application. All Servlets and other resources in the web application share a ServletContext object.
If necessary, we can communicate between Servlets through the ServletContext object. .
ServletContext is a global storage space for information. It exists when the server starts and is released only when the server is shut down. A user can have multiple requests; session, one for each user; and servletContext, all users share one.
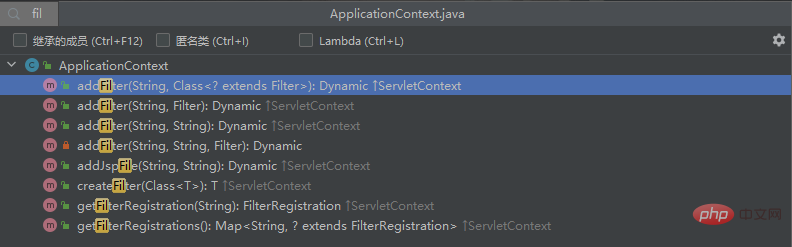
ApplicationContext is the implementation class of ServletContext. You can see that there are corresponding registration methods in it
Get ServletContext in the program
3.1.1 Use automatic injection
@Autowired private ServletContext servletContext;
3.1.2 request to obtain servletContext
ServletContext servletContext = request.getServletContext();
3.1.3 Implement ServletContextListener
@Component
public class TestListener implements ServletContextListener {
@Override
public void contextInitialized(ServletContextEvent sce) {
System.out.println(sce);
}
}Look at the definition of Filter, you can see that it is the same as the webfilter annotation content
public class ServletRegistrationBean<T extends Servlet> extends DynamicRegistrationBean<ServletRegistration.Dynamic> {
private static final String[] DEFAULT_MAPPINGS = new String[]{"/*"};
private T servlet;
private Set<String> urlMappings;
private boolean alwaysMapUrl;
private int loadOnStartup;
private MultipartConfigElement multipartConfig;
......
}In development, its subclass FilterRegistrationBean is generally used, and manual registration is done using 2.1 above .
The above is the detailed content of What is the principle and registration method of filter in Springboot. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!




