 Operation and Maintenance
Operation and Maintenance
 Nginx
Nginx
 How to configure nginx gzip dynamic compression and static compression
How to configure nginx gzip dynamic compression and static compression
How to configure nginx gzip dynamic compression and static compression
Dynamic compression
Dynamic compression actually means that the nginx server compresses the compiled creation. You need to enable the following configuration in the http and https modules of nginx.conf:
gzip on; # 开启gizo压缩
gzip_min_length 1k; # gizp压缩起点,文件大于1k才进行压缩
gzip_comp_level 6; # 压缩级别 数字越大压缩得越小 但是越耗性能 根据实际情况而定
gzip_proxied any; # nginx做为反向代理时启用, 详细见官方文档:http://nginx.org/en/docs/http/ngx_http_gzip_module.html#gzip_proxied
gzip_vary on; # 是否在http header中添加Vary: Accept-Encoding
gzip_buffers 16 8k; # 设置压缩所需要的缓冲区大小,以8k为单位,案例中则申请16*4k的缓冲区
gzip_http_version 1.1; # http的版本
gzip_types text/plain application/javascript text/css application/json application/x-javascript text/xml application/xml application/xml+rss text/javascript; # 文件类型Change completed Configure, restart the nginx server, check the static resource response header, if Content-Encoding: gzip **** appears, it means the startup is successful;
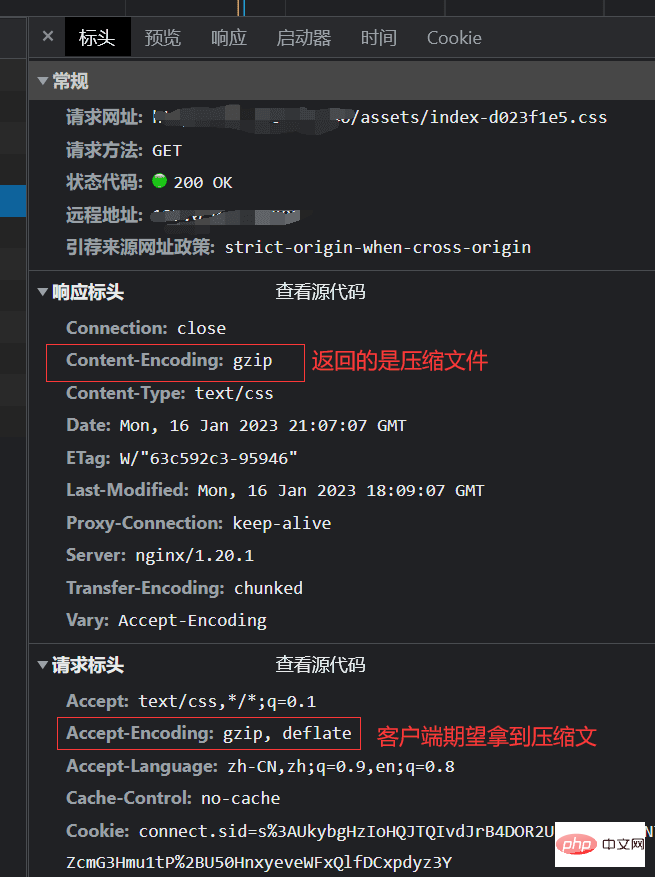
static compression
Dynamic compression is performed on the server. The higher the compression level, the more performance is consumed. Static compression is born to solve this problem. After turning on static compression, nginx will automatically look for files with the .gz suffix, and if not, return the source file; Ever since, we can perform gzip compression when building the front end;
Taking vite as an example, we need to introduce the vite-plugin-compression plug-in and configure it in vite.config.js as follows;
import viteCompression from 'vite-plugin-compression'; // gzip
plugins: [ viteCompression() ]The plug-in supports customization. The main configuration is as follows
verbose: true, // 是否在控制台输出压缩结果 这里我们打开查看压缩的效果
disable: false, // 是否禁用
threshold: 10240, // 大于这个值才进行压缩 单位为b
algorithm: 'gzip', // 算法 除了gzip还有 ['brotliCompress' ,'deflate','deflateRaw']
ext: '.gz', // 输出的后缀After introducing the plug-in and compiling, we can see that there will be some more files ending in .gz in the compiled file. These are the products of compression. , looking at the compilation output, we can see that
dist/D:/code/vue/mine/waylon-blog/packages/waylon-blog-pages/assets/index-d023f1e5.css.gz 598.32kb / gzip: 67.81kb
The size of a 598.32kb css file becomes 67.81kb after compression;
Deploy static resources to the server, in nginx.conf If you enable the following configuration in nginx, nginx will automatically look for files ending in .gz and return them directly to the client. This is the so-called static compression;
gzip_static on
pitfalls! ! !
1, nginx has higher requirements for statically compressed files, which must be generated at the same time as the original files. If they are not generated at the same time, nginx will not be able to match (for this point, the author has not included the source code after introducing the plug-in). Changes, causing the time of the gz file to be inconsistent with the original file, causing static compression to not take effect);
Official website original words:
The files can be compressed using the gzip command, or any other compatible one. It is recommended that the modification date and time of original and compressed files be the same.
2. nginx does not install the ngx_http_gzip_static_module static compression module by default. It needs to be turned on manually. How to turn it on here Without going into details, just go to the command:
After finding the configure file of the installation path, execute the following command in this folder
./configure --with-http_gzip_static_module
After the execution is completed, execute the make command
make
combination of static and dynamic
In actual applications, we usually use a combination of static compression and dynamic compression to process our static resources. The priority of static compression will be higher than dynamic compression, which does not mean that the compression is more The smaller the better. If the file has been statically compressed, there is no need to perform dynamic compression, because this wastes performance and the gain outweighs the gain. Therefore, the configuration of dynamic compression gzip_min_length is particularly important, which allows us to avoid some unnecessary operations;
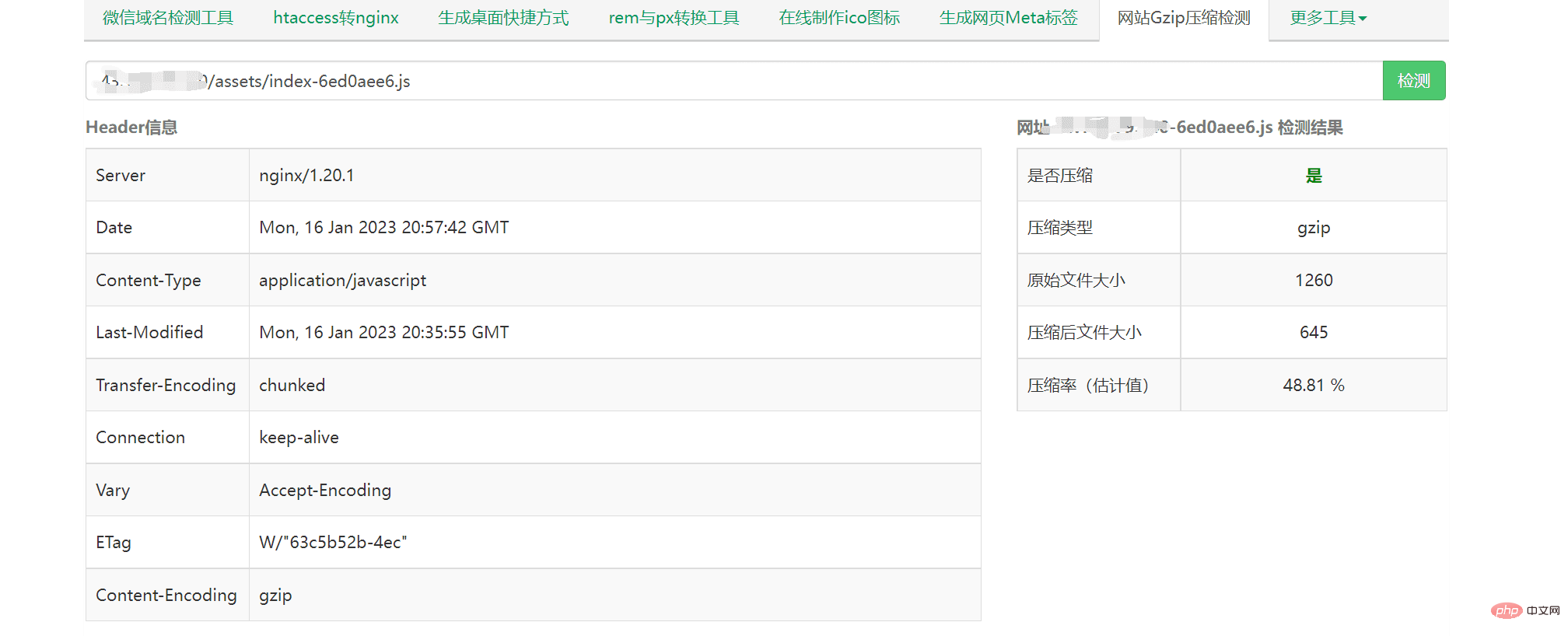
After the above series of operations, you can use the webmaster tool to test the compression effect and directly copy the connection of the static resource: https://tool.chinaz.com/Gzips/?q=c.nxw .so
As shown in the picture
The above is the detailed content of How to configure nginx gzip dynamic compression and static compression. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1378
1378
 52
52
 How to configure nginx in Windows
Apr 14, 2025 pm 12:57 PM
How to configure nginx in Windows
Apr 14, 2025 pm 12:57 PM
How to configure Nginx in Windows? Install Nginx and create a virtual host configuration. Modify the main configuration file and include the virtual host configuration. Start or reload Nginx. Test the configuration and view the website. Selectively enable SSL and configure SSL certificates. Selectively set the firewall to allow port 80 and 443 traffic.
 How to check whether nginx is started?
Apr 14, 2025 pm 12:48 PM
How to check whether nginx is started?
Apr 14, 2025 pm 12:48 PM
In Linux, use the following command to check whether Nginx is started: systemctl status nginx judges based on the command output: If "Active: active (running)" is displayed, Nginx is started. If "Active: inactive (dead)" is displayed, Nginx is stopped.
 How to start nginx in Linux
Apr 14, 2025 pm 12:51 PM
How to start nginx in Linux
Apr 14, 2025 pm 12:51 PM
Steps to start Nginx in Linux: Check whether Nginx is installed. Use systemctl start nginx to start the Nginx service. Use systemctl enable nginx to enable automatic startup of Nginx at system startup. Use systemctl status nginx to verify that the startup is successful. Visit http://localhost in a web browser to view the default welcome page.
 How to solve nginx403 error
Apr 14, 2025 pm 12:54 PM
How to solve nginx403 error
Apr 14, 2025 pm 12:54 PM
The server does not have permission to access the requested resource, resulting in a nginx 403 error. Solutions include: Check file permissions. Check the .htaccess configuration. Check nginx configuration. Configure SELinux permissions. Check the firewall rules. Troubleshoot other causes such as browser problems, server failures, or other possible errors.
 How to check whether nginx is started
Apr 14, 2025 pm 01:03 PM
How to check whether nginx is started
Apr 14, 2025 pm 01:03 PM
How to confirm whether Nginx is started: 1. Use the command line: systemctl status nginx (Linux/Unix), netstat -ano | findstr 80 (Windows); 2. Check whether port 80 is open; 3. Check the Nginx startup message in the system log; 4. Use third-party tools, such as Nagios, Zabbix, and Icinga.
 How to solve nginx403
Apr 14, 2025 am 10:33 AM
How to solve nginx403
Apr 14, 2025 am 10:33 AM
How to fix Nginx 403 Forbidden error? Check file or directory permissions; 2. Check .htaccess file; 3. Check Nginx configuration file; 4. Restart Nginx. Other possible causes include firewall rules, SELinux settings, or application issues.
 How to solve the problem of nginx cross-domain
Apr 14, 2025 am 10:15 AM
How to solve the problem of nginx cross-domain
Apr 14, 2025 am 10:15 AM
There are two ways to solve the Nginx cross-domain problem: modify the cross-domain response header: add directives to allow cross-domain requests, specify allowed methods and headers, and set cache time. Use CORS modules: Enable modules and configure CORS rules that allow cross-domain requests, methods, headers, and cache times.
 How to solve nginx304 error
Apr 14, 2025 pm 12:45 PM
How to solve nginx304 error
Apr 14, 2025 pm 12:45 PM
Answer to the question: 304 Not Modified error indicates that the browser has cached the latest resource version of the client request. Solution: 1. Clear the browser cache; 2. Disable the browser cache; 3. Configure Nginx to allow client cache; 4. Check file permissions; 5. Check file hash; 6. Disable CDN or reverse proxy cache; 7. Restart Nginx.



