How to connect to MySQL using Python
1. Table and key concepts
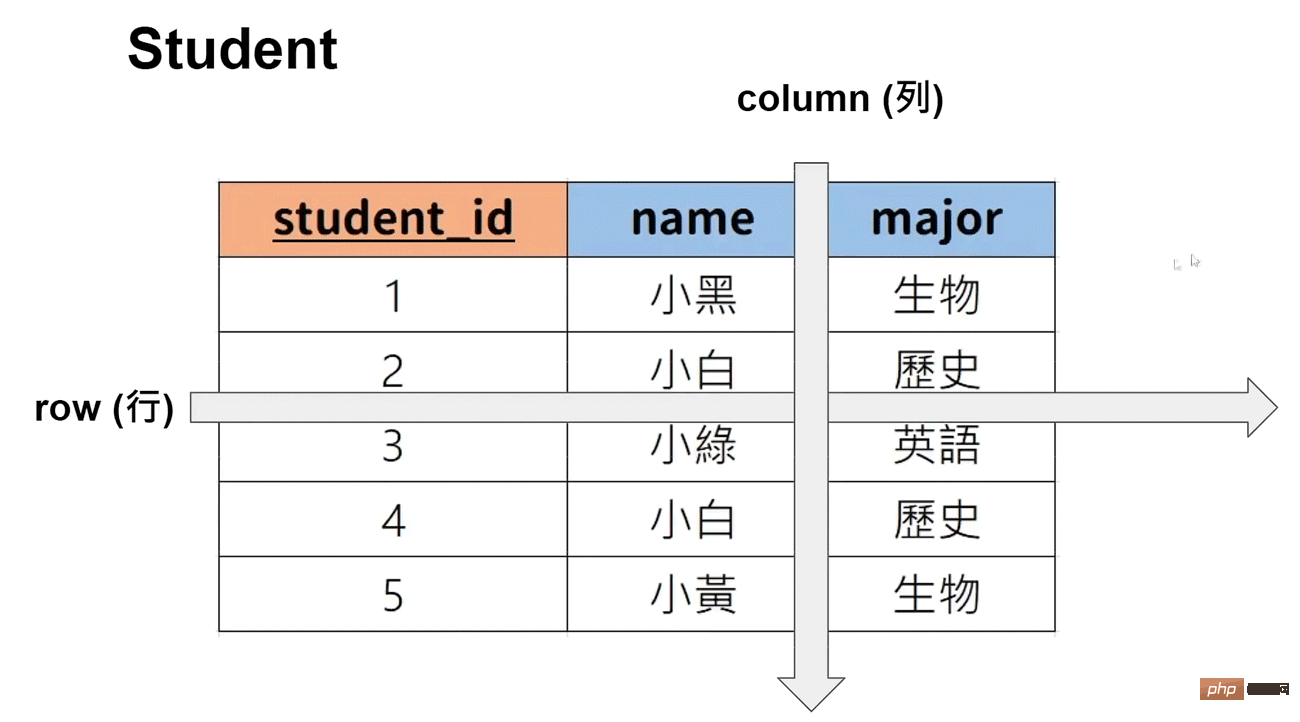
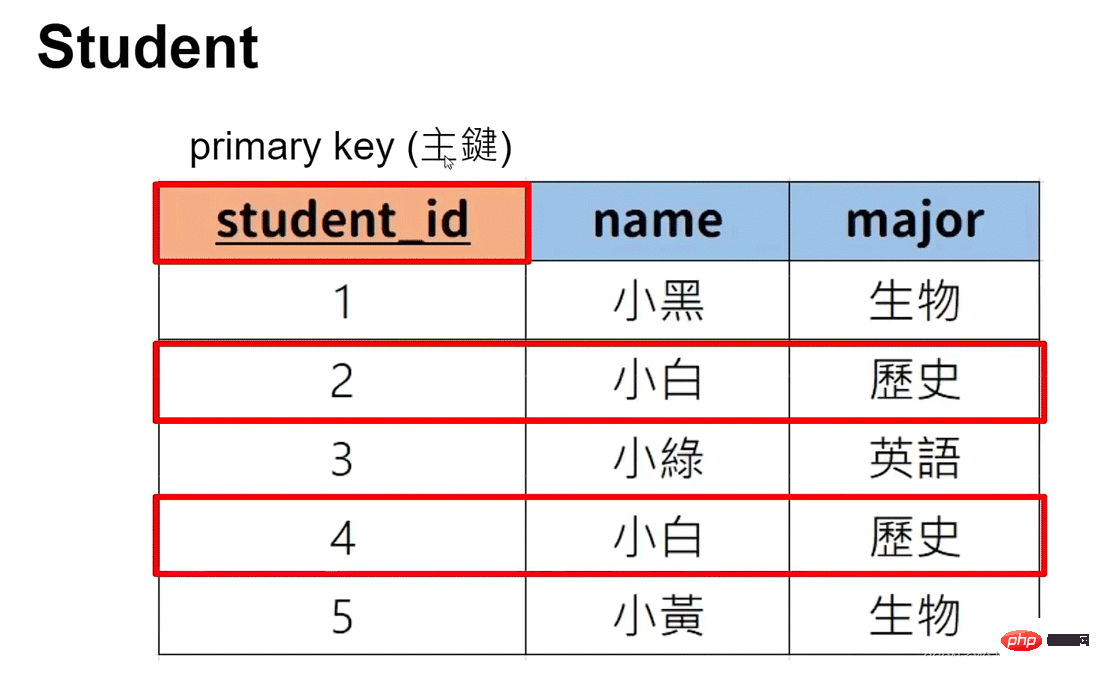
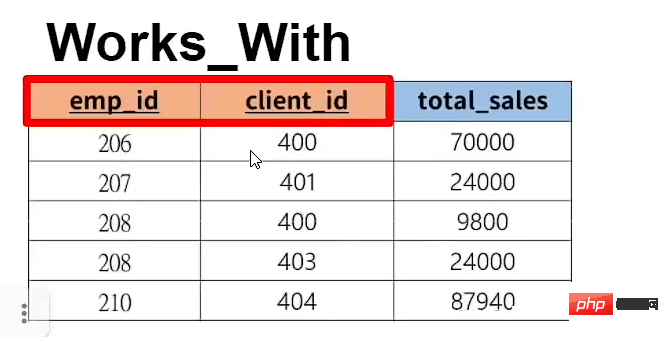
#Primary key: Can uniquely represent the data (multiple lists can be set as primary keys)
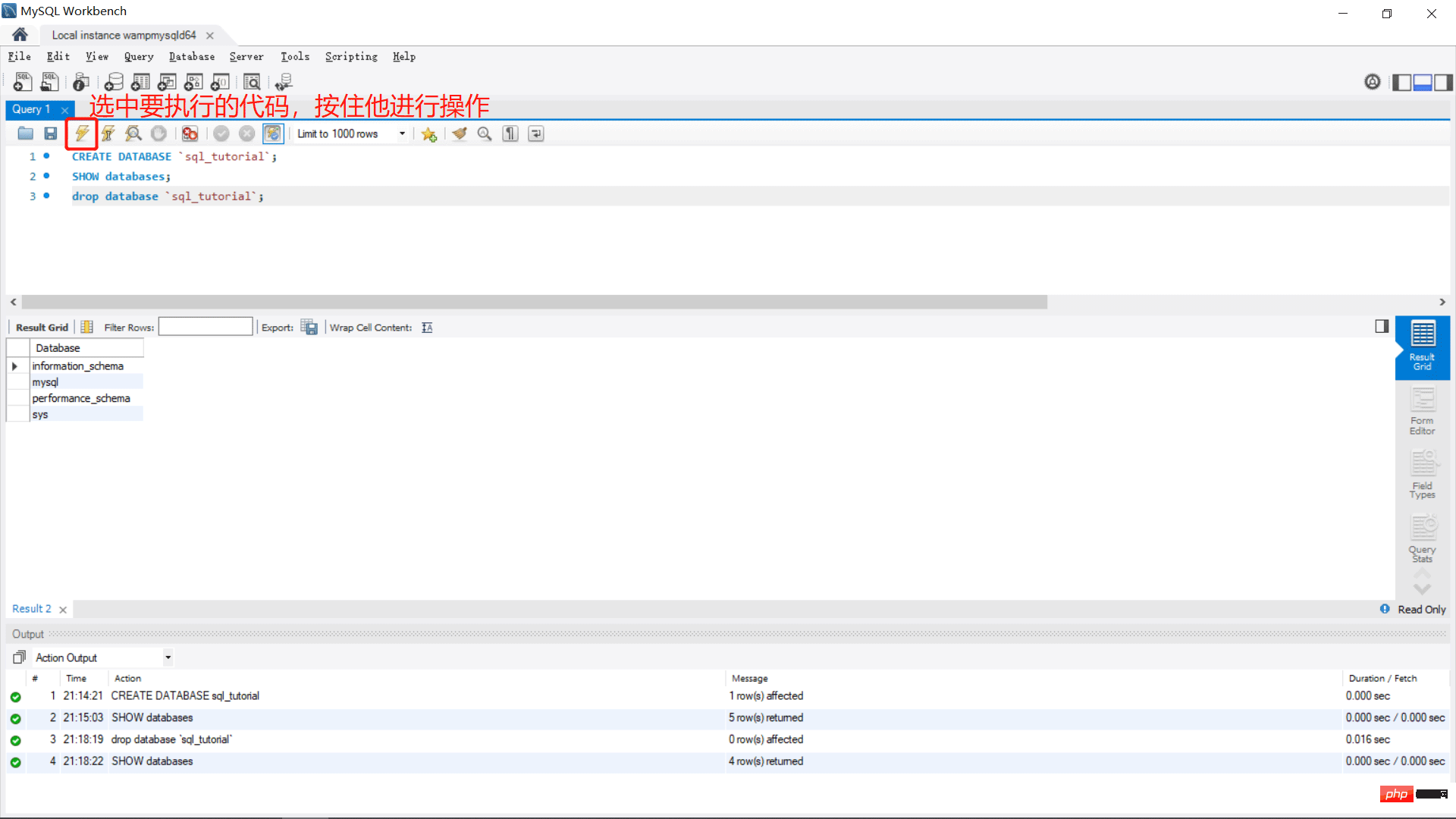
CREATE DATABASE `sql_tutorial`; --创建资料库
SHOW databases; --展示资料库
drop database `sql_tutorial`; --删除资料库
Copy after login
– as a commentCREATE DATABASE `sql_tutorial`; --创建资料库 SHOW databases; --展示资料库 drop database `sql_tutorial`; --删除资料库
; as the format of the end command
MySQL data form:
- ##INT --Integer
- DECIMAL(m,n) --The number (3,2) with a decimal point is 2.33. There are m digits in total and the decimal point has n digits
- VARCHAR(n ) --String
- BLOB --Picture video file...(binary data)
- DATE --Date (yyyy-mm -dd)
- TIMESTAMP --record time (yyyy-mm-dd hh:mm:ss)
CREATE DATABASE `sql_tutorial`; -- 创建资料库 SHOW databases; -- 展示资料库 use `sql_tutorial`; -- 选择使用的资料库 create table student( `student_id` int primary key, -- 第一列 `name` varchar(20), -- 第二列 `major` varchar(20) -- 第三列,20指的是最大字符长度 ); -- 创建表格并设计属性 describe `student`; -- 展示表格 drop table `student`; -- 删除表格 alter table `student` add gpa decimal(3,2); -- 增加资料属性 alter table `student` drop column gpa ; -- 删除资料属性Copy after login
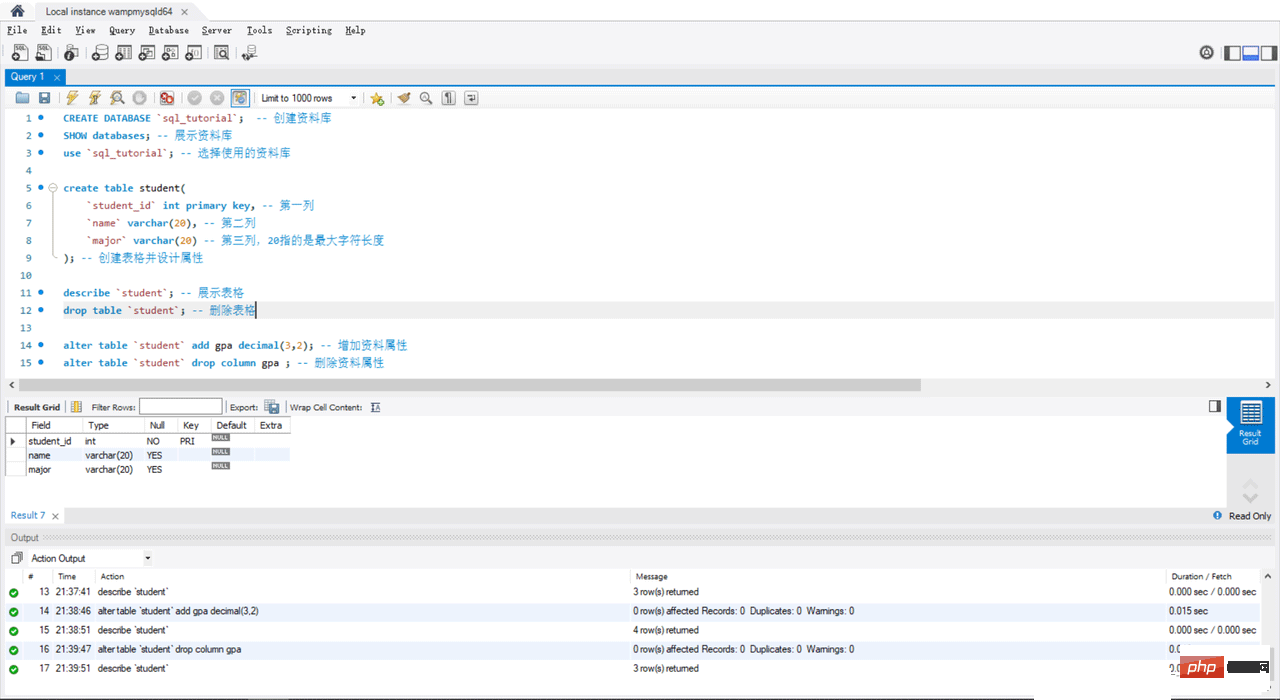 4. Storing data
4. Storing data
create table student(
`student_id` int primary key, -- 第一列
`name` varchar(20), -- 第二列
`major` varchar(20) -- 第三列,20指的是最大字符长度
); -- 创建表格并设计属性
select * from `student`; -- 搜索表格的全部资料
insert into `student` values(1,'小白','历史'); -- 写入表格数据
insert into `student` values(2,'小黑','生物'); -- 写入表格数据
insert into `student` values(3,'小绿',null); -- 写入表格数据,null为空
insert into `student`(`name`,`major`,`student_id`) values('小蓝','英语','4'); -- 按照设置写入表格数据
insert into `student`(`major`,`student_id`) values('英语','5'); -- 按照设置写入表格数据,没有的数据则为空白null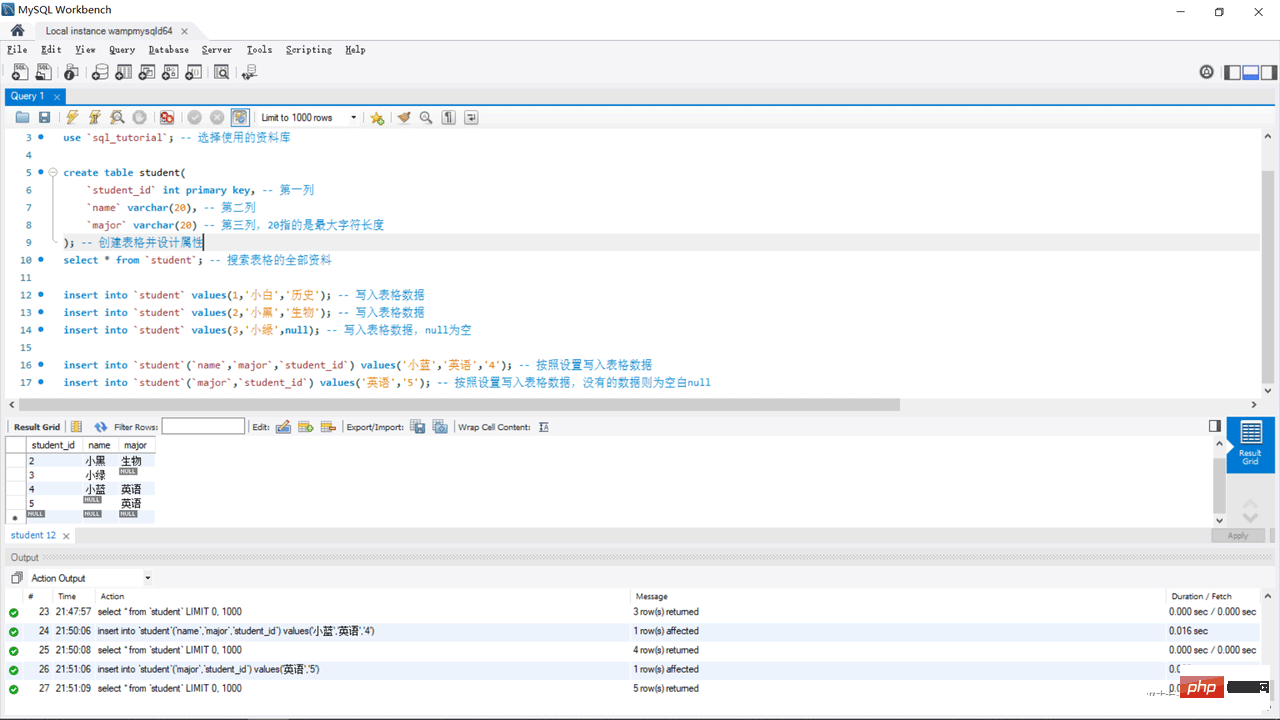 5. Restrictions
5. Restrictions
create table student(
`student_id` int primary key, -- 第一列
`name` varchar(20) not null, -- 第二列,not null指这个属性不可以为空
`major` varchar(20) unique -- 第三列,20指的是最大字符长度,unique指每个值不可以重复
); -- 创建表格并设计属性
create table student(
`student_id` int primary key auto_increment, -- 第一列,auto_increment自动会加一
`name` varchar(20), -- 第二列,not null指这个属性不可以为空
`major` varchar(20) default '历史' -- 第三列,20指的是最大字符长度,default指预设值,如果没有写该属性,则为预设值
); -- 创建表格并设计属性
drop table `student`;
select * from `student`; -- 搜索表格的全部资料
insert into `student`(`name`,`major`) values('小蓝','英语'); -- 按照设置写入表格数据
insert into `student`(`name`) values('小黑'); -- 按照设置写入表格数据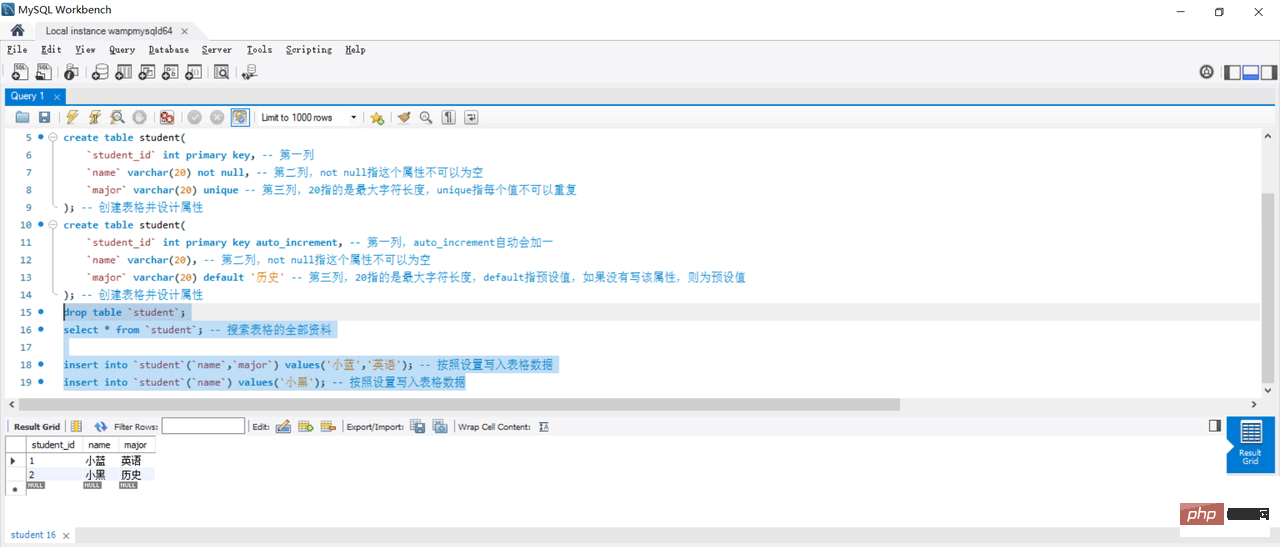 6. Modifying and deleting data
6. Modifying and deleting data
>,<,>=,<=,=,<>set sql_safe_updates = 0; -- 把预设更新模式关闭,这样更新操作才可以成功
create table student(
`student_id` int primary key auto_increment, -- 第一列
`name` varchar(20), -- 第二列
`major` varchar(20), -- 第三列,20指的是最大字符长度
`score` int
); -- 创建表格并设计属性
drop table `student`;
select * from `student`; -- 搜索表格的全部资料
insert into `student`(`name`,`major`) values('小蓝','英语'); -- 按照设置写入表格数据
insert into `student`(`name`,`major`) values('小白','化学'); -- 按照设置写入表格数据
insert into `student`(`name`,`major`) values('小黑','生物'); -- 按照设置写入表格数据
update `student` -- 更新哪个表格
set `major` = '英语文学' -- 将什么更新成什么
where `major` = '英语'; -- 将其中谁的什么进行更新
-- 还可以进行多个更新
update `student` -- 更新哪个表格
set `major` = '生化' -- 将什么更新成什么
where `major` = '生物' or `major` = '化学' ; -- 将其中谁的什么进行更新
update `student` -- 更新哪个表格
set `name` = '小辉',`major` = '生化' -- 将什么更新成什么
where `student_id`=1 ; -- 将其中谁的什么进行更新
-- 不加条件则都改
update `student` -- 更新哪个表格
set `major` = '物理'; -- 将其中谁的什么进行更新,都改成了生化
delete from `student`
where `student_id` = 3; -- 删除表格中的数据
-- 条件也可以设置多个
delete from `student`
where `name` = '小白' and `major`='物理'; -- 删除表格中的数据
delete from `student`; -- 删除所有的资料
-- 取得资料 select * from `student`; -- 取得表格的全部资料 select `name` from `student`; -- 只取得表格的对应数据 select `name`, `major` from `student`; -- 取得表格的对应多个数据 select * from `student` ORDER BY `score`; -- 取得表格的全部资料,并排序(默认正序) select * from `student` ORDER BY `score` DESC; -- 取得表格的全部资料,并排序(由高到低,asc是由低到高) select * from `student` ORDER BY `score` ,`student_id`; -- 取得表格的全部资料,并排序(先有score做排序,score中相同的再由student_id做排序) select * from `student` LIMIT 3 ; -- 限制资料范围 select * from `student` ORDER BY `score` LIMIT 3 ; -- 排序并限制资料范围 select * from `student` where `major`= '英语'; -- 查找对应资料 select * from `student` where `major`= '英语' and `student_id` = 1; -- 查找对应资料(多条件) select * from `student` where `major` in('历史','英语','生物'); -- 查找对应资料(多条件)1
8. Create company database
CREATE DATABASE `sql_tutorial`; -- 创建资料库
SHOW databases; -- 展示资料库
use `sql_tutorial`; -- 选择使用的资料库
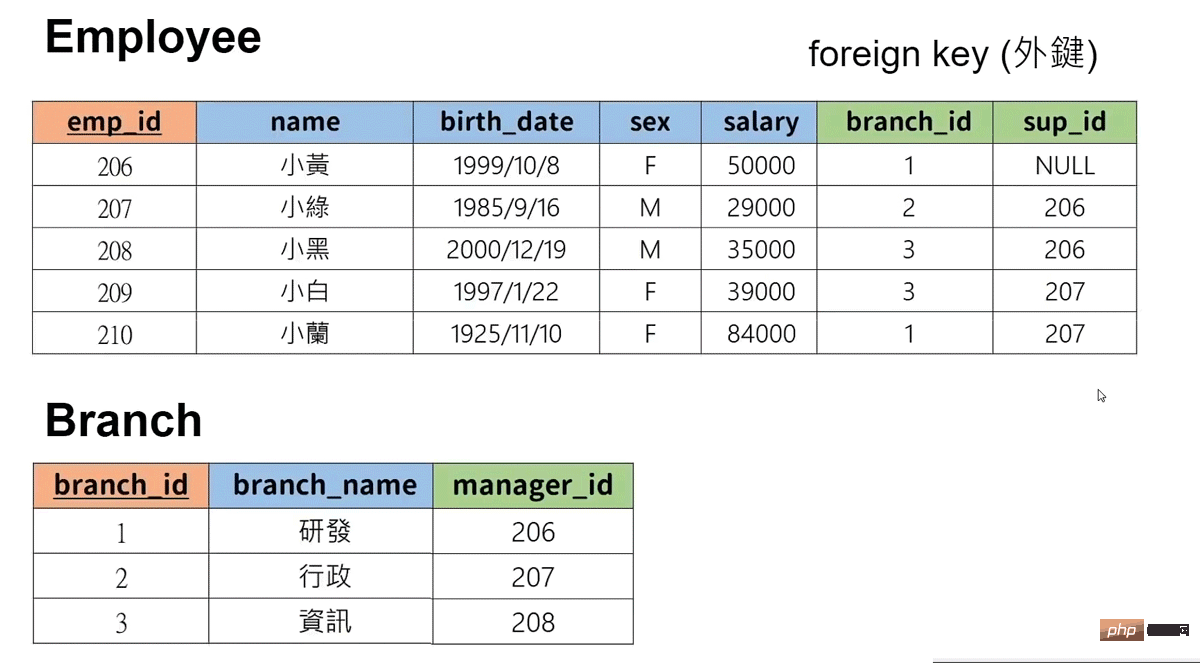
create table `employee`(
`emp_id` int primary key, -- 第一列
`name` varchar(20), -- 第二列,20指的是最大字符长度
`bath_date` date, -- 第三列
`sex` varchar(1),
`salary` int,
`branch_id` int,
`sup_id` int
); -- 创建表格并设计属性
create table `branch`(
`branch_id` int primary key , -- 第一列
`branch_name` varchar(20), -- 第二列
`manager_id` int, -- 第三列,20指的是最大字符长度
foreign key (`manager_id`) references `employee`(`emp_id`) on delete set null -- 设置好外键(选择什么是并对应什么表格的什么属性)
); -- 创建表格并设计属性
-- 补充外键(外表格对应)
alter table `employee` -- 在什么表格上进行更新
add foreign key(`branch_id`) -- 在他的什么属性上
references `branch`(`branch_id`) -- 从哪的什么属性对应
on delete set null;
-- 补充外键(内表格对应)
alter table `employee` -- 在什么表格上进行更新
add foreign key(`sup_id`) -- 在他的什么属性上
references `employee`(`emp_id`) -- 从哪的什么属性对应
on delete set null;
create table `client`(
`client_id` int primary key , -- 第一列
`client_name` varchar(20), -- 第二列
`phone` varchar(20) -- 第三列,20指的是最大字符长度
); -- 创建表格并设计属性
create table `works_with`(
`emp_id` int, -- 第一列
`client_id` int, -- 第二列
`total_sales` int, -- 第三列,20指的是最大字符长度
primary key(`emp_id`,`client_id`),
foreign key (`emp_id`) references `employee`(`emp_id`) on delete cascade, -- 设置好外键(选择什么是并对应什么表格的什么属性)
foreign key (`client_id`) references `client`(`client_id`) on delete cascade -- 设置好外键(选择什么是并对应什么表格的什么属性)
); -- 创建表格并设计属性
-- 当增加资料冲突的时候可以先将其设置为null然后再更新
insert into `branch` values(1,'研发',null);
insert into `employee` values(206,'xiaohuang','1998-10-08','F',50000,1,null);
update `branch`
set `manager_id` = 206
where `branch_id` = 1;9. Obtain company information
-- 取得对应表格所有资料 select * from `employee`; -- 取得对应表格所有资料并排序(默认低到高) select * from `employee` order by `salary`; -- 低为加desc -- 增加限制取出条件 select * from `employee` order by `salary` desc limit 3 ; -- 取出前三高 -- 取出对应属性 select `name` from `employee` ; -- 取出对应属性的内容(且不重复) select distinct `name` from `employee` ;
10. Aggregation function
-- 取得人数 select count(*) from `employee`; -- 统计几笔资料 select count(`sup_id`) from `employee`; -- 统计对应属性资料个数(null不计入) -- 增加条件取数 select count(*) from `employee` where `bath_date` > '1970-01-01' and `sex` = 'F'; -- 统计几笔资料 -- 计算对应的属性的平均 select avg(`salary`) from `employee`; -- 计算对应的属性的总和 select sum(`salary`) from `employee`; -- 取得最高的 select max(`salary`) from `employee`; -- 取得最低的 select min(`salary`) from `employee`;
11. Universal sub-element
-- %表示多个子元,_表示一个子元 -- 取得尾数335的数据 select * from `client` where `phone` like '%335'; -- 取得姓艾的 select * from `client` where `client_name` like '艾%'; -- 取得生日是10月的 select * from `employee` where `bath_date` like '_____10%';
Twelve, Union
-- 员工与客户合并为一列(类型必须相同) select `name` from `employee` union select `client_name` from `client`; -- 多个数据合并为多列(类型必须相同) select `emp_id`, `name` from `employee` union select `client_id`, `client_name` from `client`; -- 多个数据合并为多列(类型必须相同)顺便改个名 select `emp_id` as `total_id`, `name` as `total_name` from `employee` union select `client_id`, `client_name` from `client`;
Thirteen, Connection
-- 连接 -- 取得所有部门经理名字,这就需要先确定部门再确定经理(二表相连) select * from `employee` join `branch` on `emp_id` = `manager_id`; -- 还可以写成 select * from `employee` join `branch` on `employee`.`emp_id` = `branch`.`manager_id`; -- 附加条件 select * from `employee` left join `branch` on `employee`.`emp_id` = `branch`.`manager_id`; -- 左边的表格(join的左边)返回全部数据,右边的必须满足才可
Fourteen, Subquery
-- 查询套查询
select `name` from `employee`
where `emp_id` = (
select `manager_id`
from `branch`
where `branch_name` = '研发'
); -- 查找研发部门的经理名字
select `emp_id` from `employee`
where `emp_id` in (
select `emp_id`
from `works_with`
where `total_sales` > 50000
); -- 销售资金超50000的人有哪些Fifteen, On delete
- On delete set null The function is that if the data is deleted (or no longer corresponds to it), it will be set to null
- On delete decade If the corresponding data is deleted (or If it cannot be matched), then the data in the table will be deleted
Note:cannot be set to on delete set nullcreate when it is the primary key table `branch`(
16. Python connection to MySQL`branch_id` int primary key , -- 第一列 `branch_name` varchar(20), -- 第二列 `manager_id` int, -- 第三列,20指的是最大字符长度 foreign key (`manager_id`) references `employee`(`emp_id`) on delete set null -- 设置好外键(选择什么是并对应什么表格的什么属性) ); -- 创建表格并设计属性 create table `works_with`( `emp_id` int, -- 第一列 `client_id` int, -- 第二列 `total_sales` int, -- 第三列,20指的是最大字符长度 primary key(`emp_id`,`client_id`), foreign key (`emp_id`) references `employee`(`emp_id`) on delete cascade, -- 设置好外键(选择什么是并对应什么表格的什么属性) foreign key (`client_id`) references `client`(`client_id`) on delete cascade -- 设置好外键(选择什么是并对应什么表格的什么属性) ); -- 创建表格并设计属性Copy after login
# 导入功能包(mysql-connector-python)
import mysql.connector
# 创入连线
connection = mysql.connector.connect(host='localhost', # mysql的位置
port='3306', # 连接通道
user='root', # 使用者名称
password='123456') # 使用者密码
'''connection = mysql.connector.connect(host='localhost', # mysql的位置
port='3306', # 连接通道
user='root', # 使用者名称
password='123456', # 使用者密码
database='sql_tutorial') # 直接打开目标资料库'''
# 告知开始使用操作
cursor = connection.cursor()
# 在对mysql操作时即用该格式:cursor.execute("你要执行的mysql语句命令")
# 创建资料库
# cursor.execute("CREATE DATABASE `qq`;")
# 取得所有资料库名称
cursor.execute("show databases;")
records = cursor.fetchall() # 取出回传资料库
for r in records:
print(r) # 因为回传列表,为便于观察,进行循环打印
# 选择资料库
cursor.execute("use `sql_tutorial`;")
# 创建表格
# 告知关闭操作
cursor.close()
# 若要懂资料进行修改需要结尾加一个指令,这样才能提交指令生效
connection.commit()
# 关闭连线
connection.close()The above is the detailed content of How to connect to MySQL using Python. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 Is the conversion speed fast when converting XML to PDF on mobile phone?
Apr 02, 2025 pm 10:09 PM
Is the conversion speed fast when converting XML to PDF on mobile phone?
Apr 02, 2025 pm 10:09 PM
The speed of mobile XML to PDF depends on the following factors: the complexity of XML structure. Mobile hardware configuration conversion method (library, algorithm) code quality optimization methods (select efficient libraries, optimize algorithms, cache data, and utilize multi-threading). Overall, there is no absolute answer and it needs to be optimized according to the specific situation.
 Is there any mobile app that can convert XML into PDF?
Apr 02, 2025 pm 08:54 PM
Is there any mobile app that can convert XML into PDF?
Apr 02, 2025 pm 08:54 PM
An application that converts XML directly to PDF cannot be found because they are two fundamentally different formats. XML is used to store data, while PDF is used to display documents. To complete the transformation, you can use programming languages and libraries such as Python and ReportLab to parse XML data and generate PDF documents.
 How to convert XML files to PDF on your phone?
Apr 02, 2025 pm 10:12 PM
How to convert XML files to PDF on your phone?
Apr 02, 2025 pm 10:12 PM
It is impossible to complete XML to PDF conversion directly on your phone with a single application. It is necessary to use cloud services, which can be achieved through two steps: 1. Convert XML to PDF in the cloud, 2. Access or download the converted PDF file on the mobile phone.
 What is the function of C language sum?
Apr 03, 2025 pm 02:21 PM
What is the function of C language sum?
Apr 03, 2025 pm 02:21 PM
There is no built-in sum function in C language, so it needs to be written by yourself. Sum can be achieved by traversing the array and accumulating elements: Loop version: Sum is calculated using for loop and array length. Pointer version: Use pointers to point to array elements, and efficient summing is achieved through self-increment pointers. Dynamically allocate array version: Dynamically allocate arrays and manage memory yourself, ensuring that allocated memory is freed to prevent memory leaks.
 How to control the size of XML converted to images?
Apr 02, 2025 pm 07:24 PM
How to control the size of XML converted to images?
Apr 02, 2025 pm 07:24 PM
To generate images through XML, you need to use graph libraries (such as Pillow and JFreeChart) as bridges to generate images based on metadata (size, color) in XML. The key to controlling the size of the image is to adjust the values of the <width> and <height> tags in XML. However, in practical applications, the complexity of XML structure, the fineness of graph drawing, the speed of image generation and memory consumption, and the selection of image formats all have an impact on the generated image size. Therefore, it is necessary to have a deep understanding of XML structure, proficient in the graphics library, and consider factors such as optimization algorithms and image format selection.
 How to open xml format
Apr 02, 2025 pm 09:00 PM
How to open xml format
Apr 02, 2025 pm 09:00 PM
Use most text editors to open XML files; if you need a more intuitive tree display, you can use an XML editor, such as Oxygen XML Editor or XMLSpy; if you process XML data in a program, you need to use a programming language (such as Python) and XML libraries (such as xml.etree.ElementTree) to parse.
 How to convert xml into pictures
Apr 03, 2025 am 07:39 AM
How to convert xml into pictures
Apr 03, 2025 am 07:39 AM
XML can be converted to images by using an XSLT converter or image library. XSLT Converter: Use an XSLT processor and stylesheet to convert XML to images. Image Library: Use libraries such as PIL or ImageMagick to create images from XML data, such as drawing shapes and text.
 Recommended XML formatting tool
Apr 02, 2025 pm 09:03 PM
Recommended XML formatting tool
Apr 02, 2025 pm 09:03 PM
XML formatting tools can type code according to rules to improve readability and understanding. When selecting a tool, pay attention to customization capabilities, handling of special circumstances, performance and ease of use. Commonly used tool types include online tools, IDE plug-ins, and command-line tools.






