 Java
Java
 javaTutorial
javaTutorial
 How to implement addition, deletion, modification and query in Java doubly linked list
How to implement addition, deletion, modification and query in Java doubly linked list
How to implement addition, deletion, modification and query in Java doubly linked list
1. Understanding the doubly linked list
The one-way linked list not only saves the current node value, but also saves the address of the next node
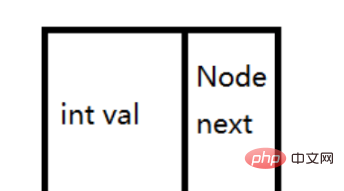
The doubly linked list not only saves the value of the current node, but also saves the address of the previous node and the address of the next node

Define the structure of a doubly linked list Point class:
The node must save not only the value of the current node, but also the address of the predecessor node of this node and the address of the successor node of this node
class DoubleNode{
public DoubleNode next;
DoubleNode prev;
int val;
DoubleNode tail;
public DoubleNode() {}
public DoubleNode(int val) {
this.val = val;
}
public DoubleNode(DoubleNode prev, int val, DoubleNode tail) {
this.prev = prev;
this.val = val;
this.tail = tail;
}
}Define a doubly linked list class:
It can be from front to back or from back to front, so in this class, the value of the head node and the tail node are saved.
public class DoubleLinkedList {
private int size;
private DoubleNode head;
private DoubleNode tail;
}2. Add, delete, modify and check the doubly linked list
1. Insert
Head plug
Insert a node at the head of the current linked list, so that the current The predecessor of the head node of the linked list points to the node node to be inserted, and then let the successor of node point to the head, and then let head = node, so that node becomes the head node of the linked list
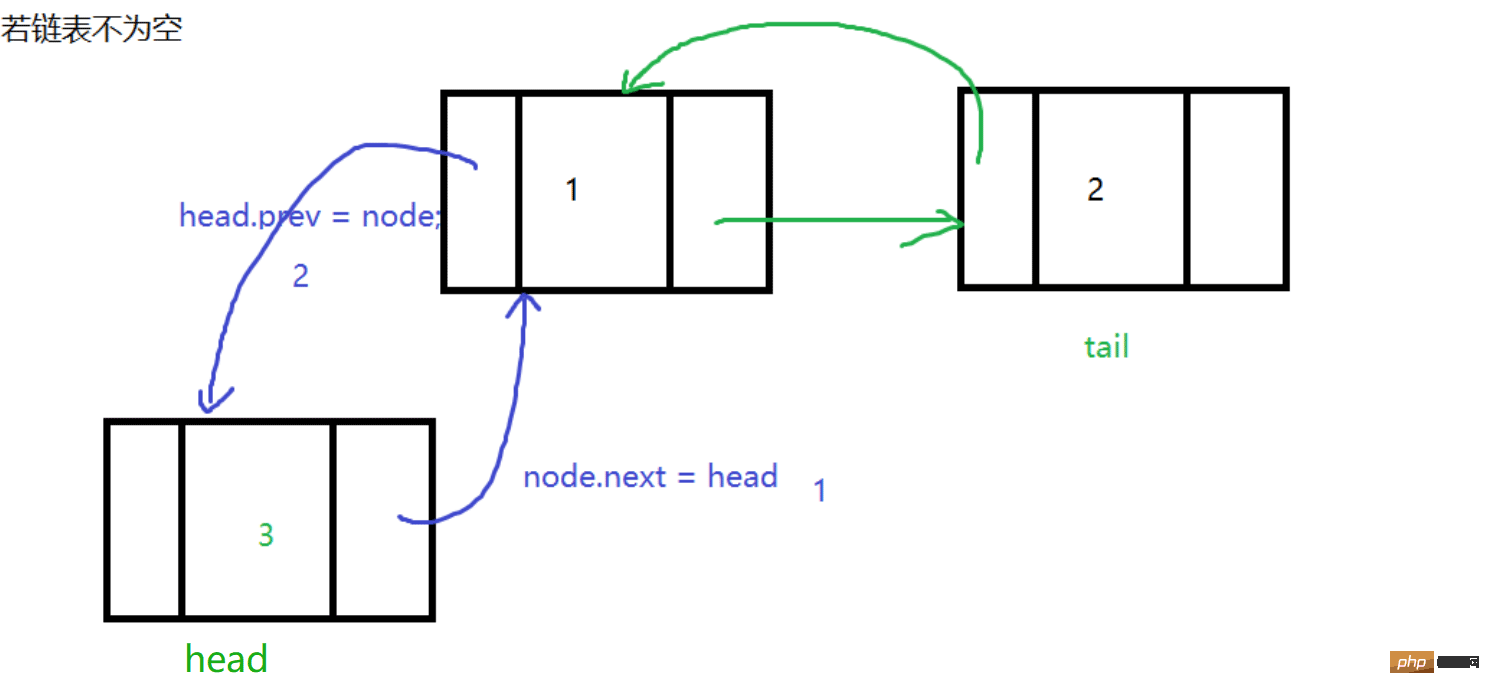
The code is as follows:
/**
* 头插
*/
public void addFirst(int val){
DoubleNode node = new DoubleNode(val);
if (head == null){
head = tail = node;
}else{
node.next = head;
head.prev = node;
head = node;
}
size++;
}Tail insertion
is the same as head insertion, except that
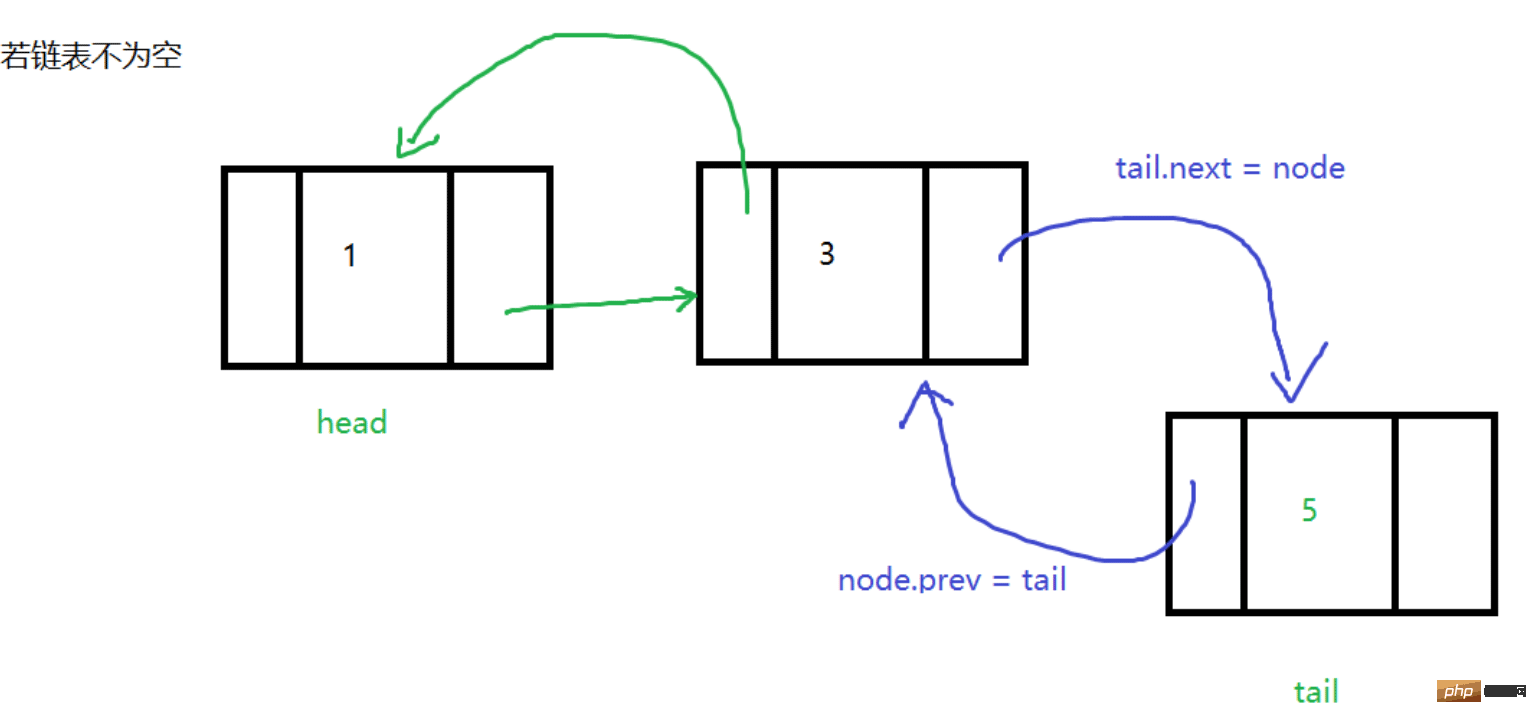
##The code is as follows:
public void addLast(int val){
DoubleNode node = new DoubleNode(val);
if (head == null){
head = tail =node;
}else{
tail.next = node;
node.prev = tail;
tail = node;
}
size++;
}Insert a node with value val at the index position:
Insertion still requires finding the predecessor node, but finding the predecessor node in a doubly linked list is much more flexible than finding the predecessor node in a one-way linked list. A one-way linked list can only go from beginning to end. If there are 100 nodes at this time, the index is 98. Insert the node at the position, then the doubly linked list can be searched from the tail node, which will be much more convenient.How to judge whether to search from front to back or from back to front?
- ##1.index < size / 2 – >Looking from front to back, the insertion position is in the front half
- 2 .index > size / 2 – >Look from back to front, the insertion position is in the second half
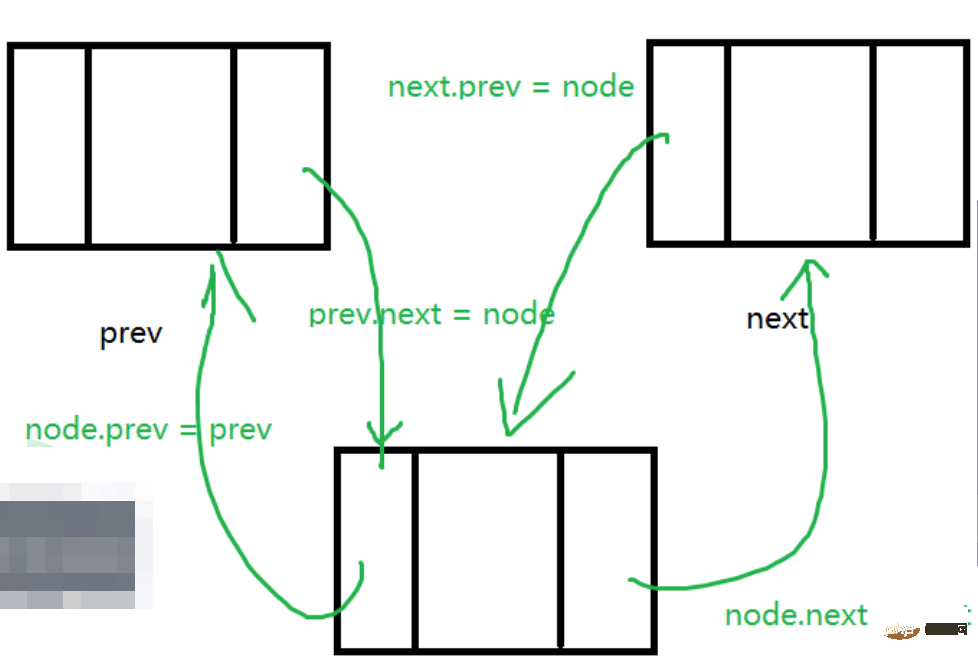 ##The code is as follows:
##The code is as follows:
/**
* 在index位置插入
* @param index
* @param val
*/
public void add(int index,int val){
DoubleNode cur = new DoubleNode(val);
if (index < 0 || index > size){
System.err.println("add index illegal");
return;
}else{
if (index == 0){addFirst(val);}
else if (index == size){addLast(val);}
else{
DoubleNode prev = node(index-1);
DoubleNode next = prev.next;
cur.next = next;
next.prev = cur;
prev.next = cur;
cur.prev = prev;
}
}
size++;
}
/**
* 根据索引值找到对应的结点
* @param index
* @return
*/
private DoubleNode node(int index){
DoubleNode x = null;
if (index < size/2){
x = head;
for (int i = 0; i < index; i++) {
x = x.next;
}
}else{
x = tail;
for (int i = size - 1; i > index ; i--) {
x = x.prev;
}
}
return x;
}code as follows:
/**
* 修改双向链表index位置的结点值为newVal
*/
public int set(int index,int newVal){
DoubleNode dummyHead = new DoubleNode();
dummyHead.next = head;
DoubleNode prev = dummyHead;
DoubleNode cur = prev.next;
if (index < 0 || index > size - 1){
System.err.println("set index illegal");
}else{
for (int i = 0; i < index; i++) {
prev = prev.next;
cur = cur.next;
}
}
int oldVal = cur.val;
cur.val = newVal;
return oldVal;
}code as follows:
/**
* 查询index位置的结点值
*/
public int get(int index){
DoubleNode dummyHead = new DoubleNode();
dummyHead.next = head;
DoubleNode prev = dummyHead;
DoubleNode cur = prev.next;
if (index < 0 || index > size - 1){
System.err.println("get index illegal");
}else{
for (int i = 0; i < index; i++) {
prev = prev.next;
cur = cur.next;
}
}
return cur.val;
}The code is as follows:
//删除链表index位置的结点
public void removeIndex(int index){
if (index < 0 || index > size - 1){
System.err.println("remove index illegal");
return;
}
DoubleNode cur = node(index);
unlink(cur);
}
/**
* 删除当前双向链表的node结点
* 分治法
* @param node
*/
private void unlink (DoubleNode node){
DoubleNode prev = node.prev;
DoubleNode successor = node.next;
//1.先处理node的前半部分
if (prev == null){
head = successor;
}else{
//前驱不为空的情况
prev.next = successor;
node.prev = null;
}
if (successor == null){
tail = prev;
}else{
successor.prev = prev;
node.next = null;
}
size--;
}The code is as follows:
//头删
public void removeFirst(){
removeIndex(0);
}The code is as follows:
//尾删
public void removeLast(){
removeIndex(size - 1);
}The code is as follows:
//删除第一个值为val的结点
public void removeValOnce(int val){
if (head == null){
return;
}
for (DoubleNode x = head;x != null;x = x.next){
if (x.val == val){
unlink(x);
break;
}
}
}
/**
* 删除当前双向链表的node结点
* 分治法
* @param node
*/
private void unlink (DoubleNode node){
DoubleNode prev = node.prev;
DoubleNode successor = node.next;
//1.先处理node的前半部分
if (prev == null){
head = successor;
}else{
//前驱不为空的情况
prev.next = successor;
node.prev = null;
}
if (successor == null){
tail = prev;
}else{
successor.prev = prev;
node.next = null;
}
size--;
}The code is as follows:
//删除链表中所有值为val的结点
public void removeAllVal(int val){
for (DoubleNode x = head;x != null;){
if (x.val == val){
//暂存一下x的下一个结点
DoubleNode next = x.next;
unlink(x);
x = next;
}else{
//val不是待删除的元素
x = x.next;
}
}
}
/**
* 删除当前双向链表的node结点
* 分治法
* @param node
*/
private void unlink (DoubleNode node){
DoubleNode prev = node.prev;
DoubleNode successor = node.next;
//1.先处理node的前半部分
if (prev == null){
head = successor;
}else{
//前驱不为空的情况
prev.next = successor;
node.prev = null;
}
if (successor == null){
tail = prev;
}else{
successor.prev = prev;
node.next = null;
}
size--;
}The above is the detailed content of How to implement addition, deletion, modification and query in Java doubly linked list. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1385
1385
 52
52
 Perfect Number in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:28 PM
Perfect Number in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:28 PM
Guide to Perfect Number in Java. Here we discuss the Definition, How to check Perfect number in Java?, examples with code implementation.
 Weka in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:28 PM
Weka in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:28 PM
Guide to Weka in Java. Here we discuss the Introduction, how to use weka java, the type of platform, and advantages with examples.
 Smith Number in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:28 PM
Smith Number in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:28 PM
Guide to Smith Number in Java. Here we discuss the Definition, How to check smith number in Java? example with code implementation.
 Java Spring Interview Questions
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:29 PM
Java Spring Interview Questions
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:29 PM
In this article, we have kept the most asked Java Spring Interview Questions with their detailed answers. So that you can crack the interview.
 Break or return from Java 8 stream forEach?
Feb 07, 2025 pm 12:09 PM
Break or return from Java 8 stream forEach?
Feb 07, 2025 pm 12:09 PM
Java 8 introduces the Stream API, providing a powerful and expressive way to process data collections. However, a common question when using Stream is: How to break or return from a forEach operation? Traditional loops allow for early interruption or return, but Stream's forEach method does not directly support this method. This article will explain the reasons and explore alternative methods for implementing premature termination in Stream processing systems. Further reading: Java Stream API improvements Understand Stream forEach The forEach method is a terminal operation that performs one operation on each element in the Stream. Its design intention is
 TimeStamp to Date in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:28 PM
TimeStamp to Date in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:28 PM
Guide to TimeStamp to Date in Java. Here we also discuss the introduction and how to convert timestamp to date in java along with examples.
 Java Program to Find the Volume of Capsule
Feb 07, 2025 am 11:37 AM
Java Program to Find the Volume of Capsule
Feb 07, 2025 am 11:37 AM
Capsules are three-dimensional geometric figures, composed of a cylinder and a hemisphere at both ends. The volume of the capsule can be calculated by adding the volume of the cylinder and the volume of the hemisphere at both ends. This tutorial will discuss how to calculate the volume of a given capsule in Java using different methods. Capsule volume formula The formula for capsule volume is as follows: Capsule volume = Cylindrical volume Volume Two hemisphere volume in, r: The radius of the hemisphere. h: The height of the cylinder (excluding the hemisphere). Example 1 enter Radius = 5 units Height = 10 units Output Volume = 1570.8 cubic units explain Calculate volume using formula: Volume = π × r2 × h (4
 How to Run Your First Spring Boot Application in Spring Tool Suite?
Feb 07, 2025 pm 12:11 PM
How to Run Your First Spring Boot Application in Spring Tool Suite?
Feb 07, 2025 pm 12:11 PM
Spring Boot simplifies the creation of robust, scalable, and production-ready Java applications, revolutionizing Java development. Its "convention over configuration" approach, inherent to the Spring ecosystem, minimizes manual setup, allo



