Backend Development
Backend Development
 Python Tutorial
Python Tutorial
 How to implement gradient descent to solve logistic regression in python
How to implement gradient descent to solve logistic regression in python
How to implement gradient descent to solve logistic regression in python
Linear regression
1. Linear regression function
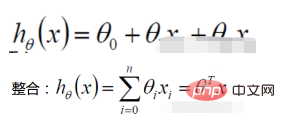
Definition of likelihood function: given joint sample valueXThe following functions about (unknown) parameters
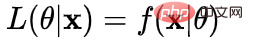

##Likelihood function: What Such parameters are exactly the true values when combined with our data.
2. Linear regression likelihood function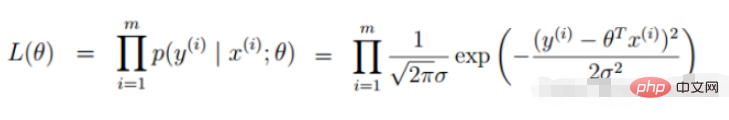
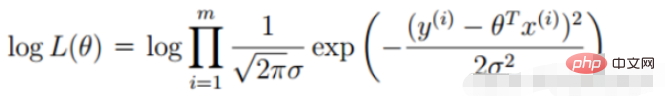
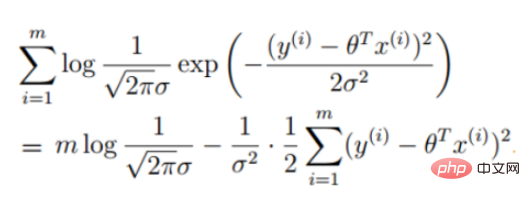
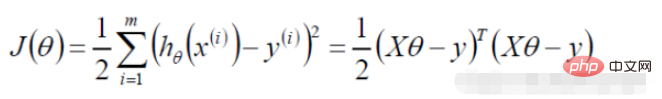
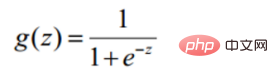
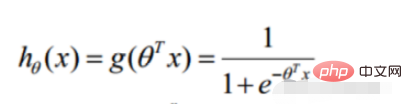
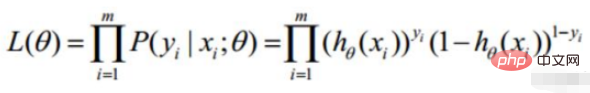
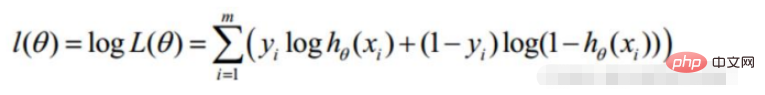
Convert to gradient descent task, logistic regression objective function
def sigmoid(z): return 1 / (1 + np.exp(-z))
def model(X, theta):
return sigmoid(np.dot(X, theta.T))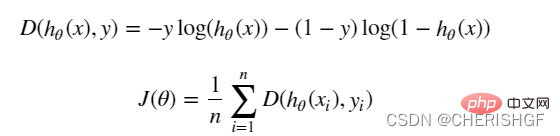
def cost(X, y, theta):
left = np.multiply(-y, np.log(model(X, theta)))
right = np.multiply(1 - y, np.log(1 - model(X, theta)))
return np.sum(left - right) / (len(X))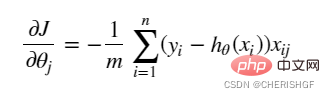
def gradient(X, y, theta):
grad = np.zeros(theta.shape)
error = (model(X, theta)- y).ravel()
for j in range(len(theta.ravel())): #for each parmeter
term = np.multiply(error, X[:,j])
grad[0, j] = np.sum(term) / len(X)
return gradSTOP_ITER = 0
STOP_COST = 1
STOP_GRAD = 2
def stopCriterion(type, value, threshold):
# 设定三种不同的停止策略
if type == STOP_ITER: # 设定迭代次数
return value > threshold
elif type == STOP_COST: # 根据损失值停止
return abs(value[-1] - value[-2]) < threshold
elif type == STOP_GRAD: # 根据梯度变化停止
return np.linalg.norm(value) < thresholdimport numpy.random
#洗牌
def shuffleData(data):
np.random.shuffle(data)
cols = data.shape[1]
X = data[:, 0:cols-1]
y = data[:, cols-1:]
return X, ydef descent(data, theta, batchSize, stopType, thresh, alpha):
# 梯度下降求解
init_time = time.time()
i = 0 # 迭代次数
k = 0 # batch
X, y = shuffleData(data)
grad = np.zeros(theta.shape) # 计算的梯度
costs = [cost(X, y, theta)] # 损失值
while True:
grad = gradient(X[k:k + batchSize], y[k:k + batchSize], theta)
k += batchSize # 取batch数量个数据
if k >= n:
k = 0
X, y = shuffleData(data) # 重新洗牌
theta = theta - alpha * grad # 参数更新
costs.append(cost(X, y, theta)) # 计算新的损失
i += 1
if stopType == STOP_ITER:
value = i
elif stopType == STOP_COST:
value = costs
elif stopType == STOP_GRAD:
value = grad
if stopCriterion(stopType, value, thresh): break
return theta, i - 1, costs, grad, time.time() - init_timeimport numpy as np
import pandas as pd
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import os
import numpy.random
import time
def sigmoid(z):
return 1 / (1 + np.exp(-z))
def model(X, theta):
return sigmoid(np.dot(X, theta.T))
def cost(X, y, theta):
left = np.multiply(-y, np.log(model(X, theta)))
right = np.multiply(1 - y, np.log(1 - model(X, theta)))
return np.sum(left - right) / (len(X))
def gradient(X, y, theta):
grad = np.zeros(theta.shape)
error = (model(X, theta) - y).ravel()
for j in range(len(theta.ravel())): # for each parmeter
term = np.multiply(error, X[:, j])
grad[0, j] = np.sum(term) / len(X)
return grad
STOP_ITER = 0
STOP_COST = 1
STOP_GRAD = 2
def stopCriterion(type, value, threshold):
# 设定三种不同的停止策略
if type == STOP_ITER: # 设定迭代次数
return value > threshold
elif type == STOP_COST: # 根据损失值停止
return abs(value[-1] - value[-2]) < threshold
elif type == STOP_GRAD: # 根据梯度变化停止
return np.linalg.norm(value) < threshold
# 洗牌
def shuffleData(data):
np.random.shuffle(data)
cols = data.shape[1]
X = data[:, 0:cols - 1]
y = data[:, cols - 1:]
return X, y
def descent(data, theta, batchSize, stopType, thresh, alpha):
# 梯度下降求解
init_time = time.time()
i = 0 # 迭代次数
k = 0 # batch
X, y = shuffleData(data)
grad = np.zeros(theta.shape) # 计算的梯度
costs = [cost(X, y, theta)] # 损失值
while True:
grad = gradient(X[k:k + batchSize], y[k:k + batchSize], theta)
k += batchSize # 取batch数量个数据
if k >= n:
k = 0
X, y = shuffleData(data) # 重新洗牌
theta = theta - alpha * grad # 参数更新
costs.append(cost(X, y, theta)) # 计算新的损失
i += 1
if stopType == STOP_ITER:
value = i
elif stopType == STOP_COST:
value = costs
elif stopType == STOP_GRAD:
value = grad
if stopCriterion(stopType, value, thresh): break
return theta, i - 1, costs, grad, time.time() - init_time
def runExpe(data, theta, batchSize, stopType, thresh, alpha):
# import pdb
# pdb.set_trace()
theta, iter, costs, grad, dur = descent(data, theta, batchSize, stopType, thresh, alpha)
name = "Original" if (data[:, 1] > 2).sum() > 1 else "Scaled"
name += " data - learning rate: {} - ".format(alpha)
if batchSize == n:
strDescType = "Gradient" # 批量梯度下降
elif batchSize == 1:
strDescType = "Stochastic" # 随机梯度下降
else:
strDescType = "Mini-batch ({})".format(batchSize) # 小批量梯度下降
name += strDescType + " descent - Stop: "
if stopType == STOP_ITER:
strStop = "{} iterations".format(thresh)
elif stopType == STOP_COST:
strStop = "costs change < {}".format(thresh)
else:
strStop = "gradient norm < {}".format(thresh)
name += strStop
print("***{}\nTheta: {} - Iter: {} - Last cost: {:03.2f} - Duration: {:03.2f}s".format(
name, theta, iter, costs[-1], dur))
fig, ax = plt.subplots(figsize=(12, 4))
ax.plot(np.arange(len(costs)), costs, 'r')
ax.set_xlabel('Iterations')
ax.set_ylabel('Cost')
ax.set_title(name.upper() + ' - Error vs. Iteration')
return theta
path = 'data' + os.sep + 'LogiReg_data.txt'
pdData = pd.read_csv(path, header=None, names=['Exam 1', 'Exam 2', 'Admitted'])
positive = pdData[pdData['Admitted'] == 1]
negative = pdData[pdData['Admitted'] == 0]
# 画图观察样本情况
fig, ax = plt.subplots(figsize=(10, 5))
ax.scatter(positive['Exam 1'], positive['Exam 2'], s=30, c='b', marker='o', label='Admitted')
ax.scatter(negative['Exam 1'], negative['Exam 2'], s=30, c='r', marker='x', label='Not Admitted')
ax.legend()
ax.set_xlabel('Exam 1 Score')
ax.set_ylabel('Exam 2 Score')
pdData.insert(0, 'Ones', 1)
# 划分训练数据与标签
orig_data = pdData.values
cols = orig_data.shape[1]
X = orig_data[:, 0:cols - 1]
y = orig_data[:, cols - 1:cols]
# 设置初始参数0
theta = np.zeros([1, 3])
# 选择的梯度下降方法是基于所有样本的
n = 100
runExpe(orig_data, theta, n, STOP_ITER, thresh=5000, alpha=0.000001)
runExpe(orig_data, theta, n, STOP_COST, thresh=0.000001, alpha=0.001)
runExpe(orig_data, theta, n, STOP_GRAD, thresh=0.05, alpha=0.001)
runExpe(orig_data, theta, 1, STOP_ITER, thresh=5000, alpha=0.001)
runExpe(orig_data, theta, 1, STOP_ITER, thresh=15000, alpha=0.000002)
runExpe(orig_data, theta, 16, STOP_ITER, thresh=15000, alpha=0.001)
from sklearn import preprocessing as pp
# 数据预处理
scaled_data = orig_data.copy()
scaled_data[:, 1:3] = pp.scale(orig_data[:, 1:3])
runExpe(scaled_data, theta, n, STOP_ITER, thresh=5000, alpha=0.001)
runExpe(scaled_data, theta, n, STOP_GRAD, thresh=0.02, alpha=0.001)
theta = runExpe(scaled_data, theta, 1, STOP_GRAD, thresh=0.002 / 5, alpha=0.001)
runExpe(scaled_data, theta, 16, STOP_GRAD, thresh=0.002 * 2, alpha=0.001)
# 设定阈值
def predict(X, theta):
return [1 if x >= 0.5 else 0 for x in model(X, theta)]
# 计算精度
scaled_X = scaled_data[:, :3]
y = scaled_data[:, 3]
predictions = predict(scaled_X, theta)
correct = [1 if ((a == 1 and b == 1) or (a == 0 and b == 0)) else 0 for (a, b) in zip(predictions, y)]
accuracy = (sum(map(int, correct)) % len(correct))
print('accuracy = {0}%'.format(accuracy))Copy after loginAdvantages and disadvantages of logistic regression
Advantages
- The form is simple and the interpretability of the model is very good. From the weight of the feature, we can see the impact of different features on the final result. If the weight value of a certain feature is relatively high, then this feature will have a greater impact on the final result.
- The model works well. It is acceptable in engineering (as a baseline). If feature engineering is done well, the effect will not be too bad, and feature engineering can be developed in parallel, greatly speeding up development.
- Training speed is faster. When classifying, the amount of calculation is only related to the number of features. Moreover, the distributed optimization sgd of logistic regression is relatively mature, and the training speed can be further improved through heap machines, so that we can iterate several versions of the model in a short period of time.
- It takes up little resources, especially memory. Because only the feature values of each dimension need to be stored.
- Conveniently adjust the output results. Logistic regression can easily obtain the final classification result, because the output is the probability score of each sample, and we can easily cutoff these probability scores, that is, divide the threshold (those greater than a certain threshold are classified into one category, and those less than a certain threshold are classified into one category). A certain threshold is a category).
Disadvantages
- The accuracy is not very high. Because the form is very simple (very similar to a linear model), it is difficult to fit the true distribution of the data.
It is difficult to deal with the problem of data imbalance. For example: If we deal with a problem where positive and negative samples are very unbalanced, such as the ratio of positive and negative samples is 10000:1. If we predict all samples as positive, we can also make the value of the loss function smaller. But as a classifier, its ability to distinguish positive and negative samples will not be very good.
Processing nonlinear data is more troublesome. Logistic regression, without introducing other methods, can only handle linearly separable data, or further, handle binary classification problems.
Logistic regression itself cannot filter features. Sometimes, we use gbdt to filter features and then use logistic regression.
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import os
import numpy.random
import time
def sigmoid(z):
return 1 / (1 + np.exp(-z))
def model(X, theta):
return sigmoid(np.dot(X, theta.T))
def cost(X, y, theta):
left = np.multiply(-y, np.log(model(X, theta)))
right = np.multiply(1 - y, np.log(1 - model(X, theta)))
return np.sum(left - right) / (len(X))
def gradient(X, y, theta):
grad = np.zeros(theta.shape)
error = (model(X, theta) - y).ravel()
for j in range(len(theta.ravel())): # for each parmeter
term = np.multiply(error, X[:, j])
grad[0, j] = np.sum(term) / len(X)
return grad
STOP_ITER = 0
STOP_COST = 1
STOP_GRAD = 2
def stopCriterion(type, value, threshold):
# 设定三种不同的停止策略
if type == STOP_ITER: # 设定迭代次数
return value > threshold
elif type == STOP_COST: # 根据损失值停止
return abs(value[-1] - value[-2]) < threshold
elif type == STOP_GRAD: # 根据梯度变化停止
return np.linalg.norm(value) < threshold
# 洗牌
def shuffleData(data):
np.random.shuffle(data)
cols = data.shape[1]
X = data[:, 0:cols - 1]
y = data[:, cols - 1:]
return X, y
def descent(data, theta, batchSize, stopType, thresh, alpha):
# 梯度下降求解
init_time = time.time()
i = 0 # 迭代次数
k = 0 # batch
X, y = shuffleData(data)
grad = np.zeros(theta.shape) # 计算的梯度
costs = [cost(X, y, theta)] # 损失值
while True:
grad = gradient(X[k:k + batchSize], y[k:k + batchSize], theta)
k += batchSize # 取batch数量个数据
if k >= n:
k = 0
X, y = shuffleData(data) # 重新洗牌
theta = theta - alpha * grad # 参数更新
costs.append(cost(X, y, theta)) # 计算新的损失
i += 1
if stopType == STOP_ITER:
value = i
elif stopType == STOP_COST:
value = costs
elif stopType == STOP_GRAD:
value = grad
if stopCriterion(stopType, value, thresh): break
return theta, i - 1, costs, grad, time.time() - init_time
def runExpe(data, theta, batchSize, stopType, thresh, alpha):
# import pdb
# pdb.set_trace()
theta, iter, costs, grad, dur = descent(data, theta, batchSize, stopType, thresh, alpha)
name = "Original" if (data[:, 1] > 2).sum() > 1 else "Scaled"
name += " data - learning rate: {} - ".format(alpha)
if batchSize == n:
strDescType = "Gradient" # 批量梯度下降
elif batchSize == 1:
strDescType = "Stochastic" # 随机梯度下降
else:
strDescType = "Mini-batch ({})".format(batchSize) # 小批量梯度下降
name += strDescType + " descent - Stop: "
if stopType == STOP_ITER:
strStop = "{} iterations".format(thresh)
elif stopType == STOP_COST:
strStop = "costs change < {}".format(thresh)
else:
strStop = "gradient norm < {}".format(thresh)
name += strStop
print("***{}\nTheta: {} - Iter: {} - Last cost: {:03.2f} - Duration: {:03.2f}s".format(
name, theta, iter, costs[-1], dur))
fig, ax = plt.subplots(figsize=(12, 4))
ax.plot(np.arange(len(costs)), costs, 'r')
ax.set_xlabel('Iterations')
ax.set_ylabel('Cost')
ax.set_title(name.upper() + ' - Error vs. Iteration')
return theta
path = 'data' + os.sep + 'LogiReg_data.txt'
pdData = pd.read_csv(path, header=None, names=['Exam 1', 'Exam 2', 'Admitted'])
positive = pdData[pdData['Admitted'] == 1]
negative = pdData[pdData['Admitted'] == 0]
# 画图观察样本情况
fig, ax = plt.subplots(figsize=(10, 5))
ax.scatter(positive['Exam 1'], positive['Exam 2'], s=30, c='b', marker='o', label='Admitted')
ax.scatter(negative['Exam 1'], negative['Exam 2'], s=30, c='r', marker='x', label='Not Admitted')
ax.legend()
ax.set_xlabel('Exam 1 Score')
ax.set_ylabel('Exam 2 Score')
pdData.insert(0, 'Ones', 1)
# 划分训练数据与标签
orig_data = pdData.values
cols = orig_data.shape[1]
X = orig_data[:, 0:cols - 1]
y = orig_data[:, cols - 1:cols]
# 设置初始参数0
theta = np.zeros([1, 3])
# 选择的梯度下降方法是基于所有样本的
n = 100
runExpe(orig_data, theta, n, STOP_ITER, thresh=5000, alpha=0.000001)
runExpe(orig_data, theta, n, STOP_COST, thresh=0.000001, alpha=0.001)
runExpe(orig_data, theta, n, STOP_GRAD, thresh=0.05, alpha=0.001)
runExpe(orig_data, theta, 1, STOP_ITER, thresh=5000, alpha=0.001)
runExpe(orig_data, theta, 1, STOP_ITER, thresh=15000, alpha=0.000002)
runExpe(orig_data, theta, 16, STOP_ITER, thresh=15000, alpha=0.001)
from sklearn import preprocessing as pp
# 数据预处理
scaled_data = orig_data.copy()
scaled_data[:, 1:3] = pp.scale(orig_data[:, 1:3])
runExpe(scaled_data, theta, n, STOP_ITER, thresh=5000, alpha=0.001)
runExpe(scaled_data, theta, n, STOP_GRAD, thresh=0.02, alpha=0.001)
theta = runExpe(scaled_data, theta, 1, STOP_GRAD, thresh=0.002 / 5, alpha=0.001)
runExpe(scaled_data, theta, 16, STOP_GRAD, thresh=0.002 * 2, alpha=0.001)
# 设定阈值
def predict(X, theta):
return [1 if x >= 0.5 else 0 for x in model(X, theta)]
# 计算精度
scaled_X = scaled_data[:, :3]
y = scaled_data[:, 3]
predictions = predict(scaled_X, theta)
correct = [1 if ((a == 1 and b == 1) or (a == 0 and b == 0)) else 0 for (a, b) in zip(predictions, y)]
accuracy = (sum(map(int, correct)) % len(correct))
print('accuracy = {0}%'.format(accuracy))It is difficult to deal with the problem of data imbalance. For example: If we deal with a problem where positive and negative samples are very unbalanced, such as the ratio of positive and negative samples is 10000:1. If we predict all samples as positive, we can also make the value of the loss function smaller. But as a classifier, its ability to distinguish positive and negative samples will not be very good.
Processing nonlinear data is more troublesome. Logistic regression, without introducing other methods, can only handle linearly separable data, or further, handle binary classification problems.
Logistic regression itself cannot filter features. Sometimes, we use gbdt to filter features and then use logistic regression.
The above is the detailed content of How to implement gradient descent to solve logistic regression in python. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1386
1386
 52
52
 Can vs code run in Windows 8
Apr 15, 2025 pm 07:24 PM
Can vs code run in Windows 8
Apr 15, 2025 pm 07:24 PM
VS Code can run on Windows 8, but the experience may not be great. First make sure the system has been updated to the latest patch, then download the VS Code installation package that matches the system architecture and install it as prompted. After installation, be aware that some extensions may be incompatible with Windows 8 and need to look for alternative extensions or use newer Windows systems in a virtual machine. Install the necessary extensions to check whether they work properly. Although VS Code is feasible on Windows 8, it is recommended to upgrade to a newer Windows system for a better development experience and security.
 How to run programs in terminal vscode
Apr 15, 2025 pm 06:42 PM
How to run programs in terminal vscode
Apr 15, 2025 pm 06:42 PM
In VS Code, you can run the program in the terminal through the following steps: Prepare the code and open the integrated terminal to ensure that the code directory is consistent with the terminal working directory. Select the run command according to the programming language (such as Python's python your_file_name.py) to check whether it runs successfully and resolve errors. Use the debugger to improve debugging efficiency.
 Can visual studio code be used in python
Apr 15, 2025 pm 08:18 PM
Can visual studio code be used in python
Apr 15, 2025 pm 08:18 PM
VS Code can be used to write Python and provides many features that make it an ideal tool for developing Python applications. It allows users to: install Python extensions to get functions such as code completion, syntax highlighting, and debugging. Use the debugger to track code step by step, find and fix errors. Integrate Git for version control. Use code formatting tools to maintain code consistency. Use the Linting tool to spot potential problems ahead of time.
 Is the vscode extension malicious?
Apr 15, 2025 pm 07:57 PM
Is the vscode extension malicious?
Apr 15, 2025 pm 07:57 PM
VS Code extensions pose malicious risks, such as hiding malicious code, exploiting vulnerabilities, and masturbating as legitimate extensions. Methods to identify malicious extensions include: checking publishers, reading comments, checking code, and installing with caution. Security measures also include: security awareness, good habits, regular updates and antivirus software.
 What is vscode What is vscode for?
Apr 15, 2025 pm 06:45 PM
What is vscode What is vscode for?
Apr 15, 2025 pm 06:45 PM
VS Code is the full name Visual Studio Code, which is a free and open source cross-platform code editor and development environment developed by Microsoft. It supports a wide range of programming languages and provides syntax highlighting, code automatic completion, code snippets and smart prompts to improve development efficiency. Through a rich extension ecosystem, users can add extensions to specific needs and languages, such as debuggers, code formatting tools, and Git integrations. VS Code also includes an intuitive debugger that helps quickly find and resolve bugs in your code.
 Python: Automation, Scripting, and Task Management
Apr 16, 2025 am 12:14 AM
Python: Automation, Scripting, and Task Management
Apr 16, 2025 am 12:14 AM
Python excels in automation, scripting, and task management. 1) Automation: File backup is realized through standard libraries such as os and shutil. 2) Script writing: Use the psutil library to monitor system resources. 3) Task management: Use the schedule library to schedule tasks. Python's ease of use and rich library support makes it the preferred tool in these areas.
 Golang vs. Python: Concurrency and Multithreading
Apr 17, 2025 am 12:20 AM
Golang vs. Python: Concurrency and Multithreading
Apr 17, 2025 am 12:20 AM
Golang is more suitable for high concurrency tasks, while Python has more advantages in flexibility. 1.Golang efficiently handles concurrency through goroutine and channel. 2. Python relies on threading and asyncio, which is affected by GIL, but provides multiple concurrency methods. The choice should be based on specific needs.
 Can vscode run ipynb
Apr 15, 2025 pm 07:30 PM
Can vscode run ipynb
Apr 15, 2025 pm 07:30 PM
The key to running Jupyter Notebook in VS Code is to ensure that the Python environment is properly configured, understand that the code execution order is consistent with the cell order, and be aware of large files or external libraries that may affect performance. The code completion and debugging functions provided by VS Code can greatly improve coding efficiency and reduce errors.