 Technology peripherals
Technology peripherals
 AI
AI
 An easy and objective way to introduce large models to avoid over-interpretation
An easy and objective way to introduce large models to avoid over-interpretation
An easy and objective way to introduce large models to avoid over-interpretation
1. Preface
This article aims to provide readers without computer science background with some information about ChatGPT and its similar artificial intelligence systems (such as GPT-3, GPT-4, Bing Chat, Bard, etc. ) principle of how it works. ChatGPT is a chatbot built on a large language model for conversational interaction. These terms can be obscure, so I'll explain them. At the same time, we will discuss the core concepts behind them, and this article does not require the reader to have any technical or mathematical background knowledge. We will make heavy use of metaphors to explain related concepts in order to understand them better. We will also discuss the implications of these techniques and what we should or should not expect to be able to do with large language models like ChatGPT.
Next, we will start with the basic "What is artificial intelligence" in a way that does not use professional terms as much as possible, and gradually discuss in depth the terms and concepts related to large language models and ChatGPT, and will use metaphors to explain them. At the same time, we'll also talk about what these technologies mean and what we should or shouldn't expect them to be able to do.
2. What is Artificial Intelligence
First, let’s start with some basic terms that you may hear often. So what is artificial intelligence?
Artificial intelligence: refers to an entity that can exhibit behaviors similar to what humans would consider intelligent. There are some problems with using "intelligence" to define artificial intelligence, because "intelligence" itself does not have a clear definition. However, this definition is still appropriate. It basically means that if we see something man-made that performs interesting, useful, and seemingly difficult behaviors, then we might say that they are intelligent. For example, in computer games, we often refer to computer-controlled characters as “AI”. Most of these roles are simple programs based on if-then-else code (e.g., "If the player is in range, fire, otherwise move to the nearest stone and hide"). But if the characters can keep us engaged and entertained while not doing anything patently stupid, then we might think they're more complex than they actually are.
Once we understand how something works, we may not think it is magical, but expect something more complex behind the scenes. It all depends on how well we know what's going on behind the scenes.
The important point is that artificial intelligence is not magic. Because it's not magic, it can be explained.
3. What is machine learning
Another term often associated with artificial intelligence is machine learning.
Machine learning: A method of creating behavior by collecting data, forming a model, and then executing the model. Sometimes it's difficult to manually create a bunch of if-then-else statements to capture some complex phenomenon (like language). In this case, we try to find large amounts of data and model it using algorithms that can find patterns in the data.
So what is a model? A model is a simplified version of a complex phenomenon. For example, a car model is a smaller, simpler version of a real car that shares many of the properties of the real car, but is of course not meant to completely replace the original version. Model cars may look realistic and are useful when experimenting.

Just like we can build a smaller, simpler car, we can also build a smaller, simpler model of human language. We use the term "large language model" because these models are very large from the perspective of the amount of memory (video memory) they need to use. The largest models currently in production, such as ChatGPT, GPT-3, and GPT-4, are so large that they require supercomputers running on data center servers to create and run.
4. What is a neural network
There are many ways to learn a model through data, and neural networks are one of them. This technology is loosely based on the structure of the human brain, which consists of a series of interconnected neurons that pass electrical signals between them, allowing us to complete a variety of tasks. The basic concept of neural networks was invented in the 1940s, and the basic concept of how to train neural networks was invented in the 1980s. At that time, neural networks were very inefficient. It was not until computer hardware upgrades around 2017 that we could They can be used on a large scale.
However, I personally prefer to use the metaphor of a circuit to simulate a neural network. Through resistance, the flow of current through wires, we can simulate the working of neural networks.
Imagine we want to make a self-driving car that can drive on the highway. We installed distance sensors on the front, back and sides of the car. The distance sensor reports a value of 1 when an object is approaching, and a value of 0 when there is no detectable object nearby.
We also installed robots to operate the steering wheel, brake and accelerate. When the throttle receives a value of 1, it uses maximum acceleration, while a value of 0 means no acceleration. Likewise, a value of 1 sent to the braking mechanism means emergency braking, while 0 means no braking. The steering mechanism accepts a value between -1 and 1, with negative numbers turning left, positive numbers turning right, and 0 meaning staying straight.
Of course we must record driving data. When the path ahead is clear, you speed up. When there's a car in front of you, you slow down. When a car comes too close from the left, you swerve to the right and change lanes, assuming of course there is no car on the right. This process is very complex and requires different operations (turn left or right, accelerate or decelerate, brake) based on different combinations of sensor information, so each sensor needs to be connected to each robot mechanism.
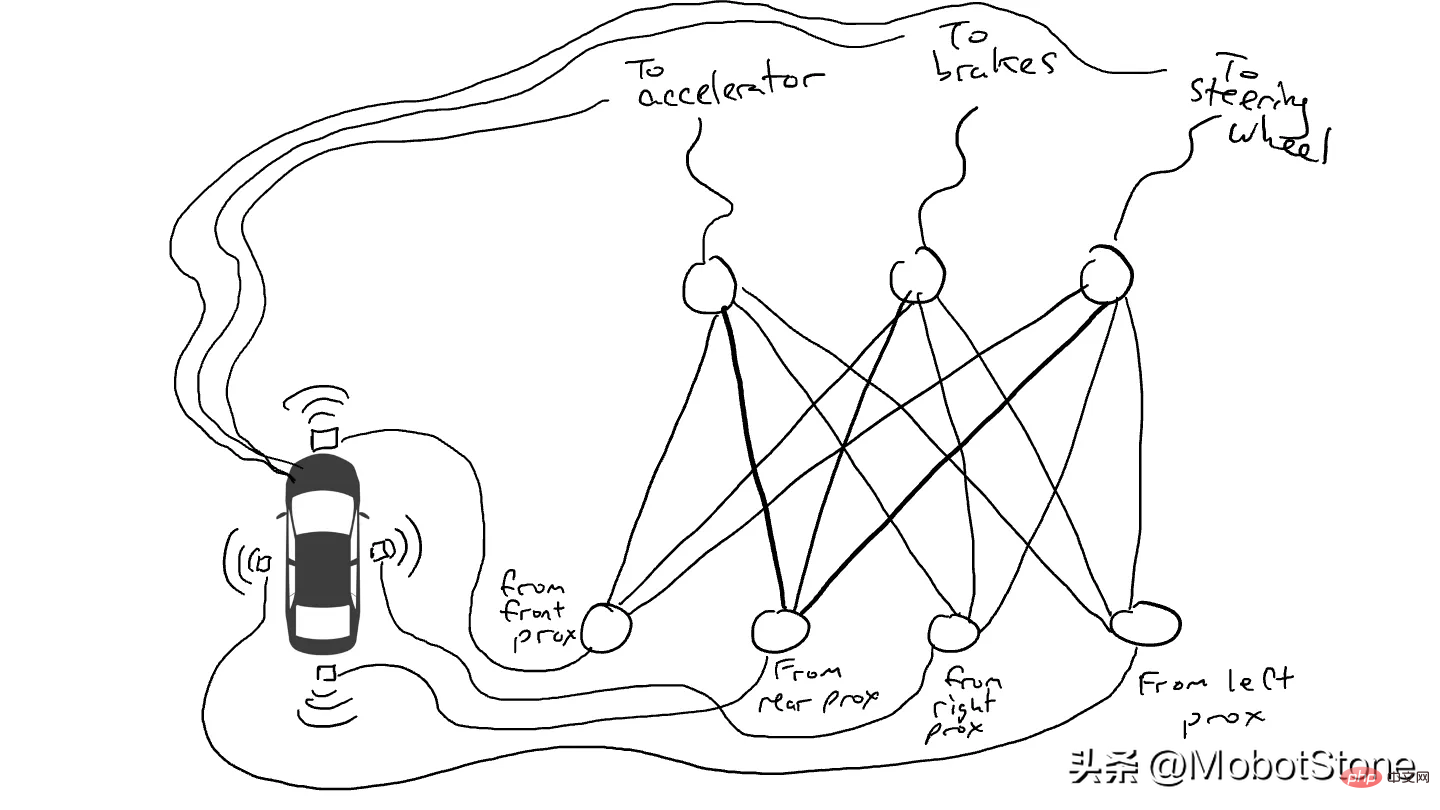
What happens when you drive on the road? Electrical current flows from all sensors to all robot actuators, and the vehicle turns left, right, accelerates and brakes simultaneously. It will create a mess.
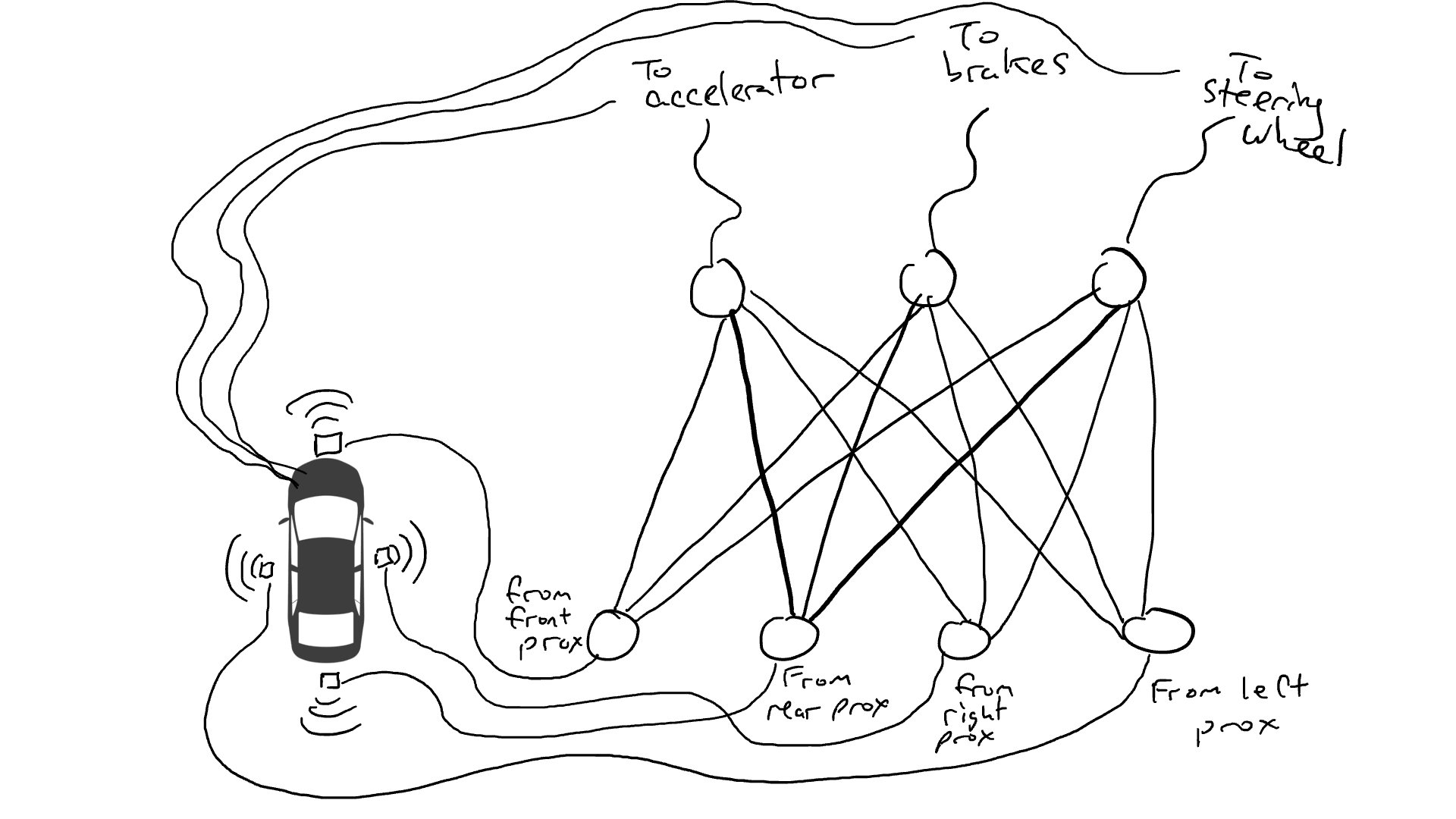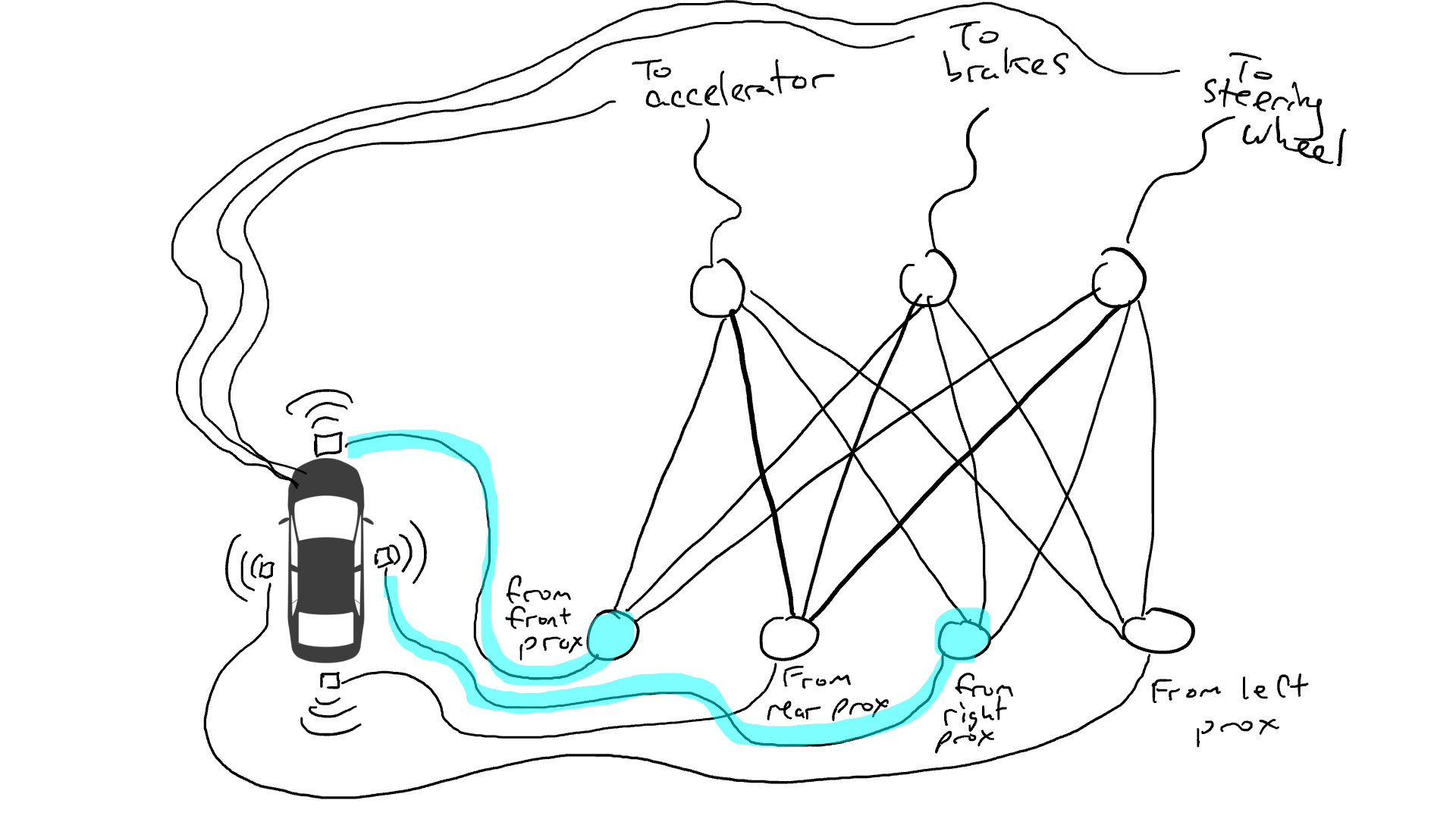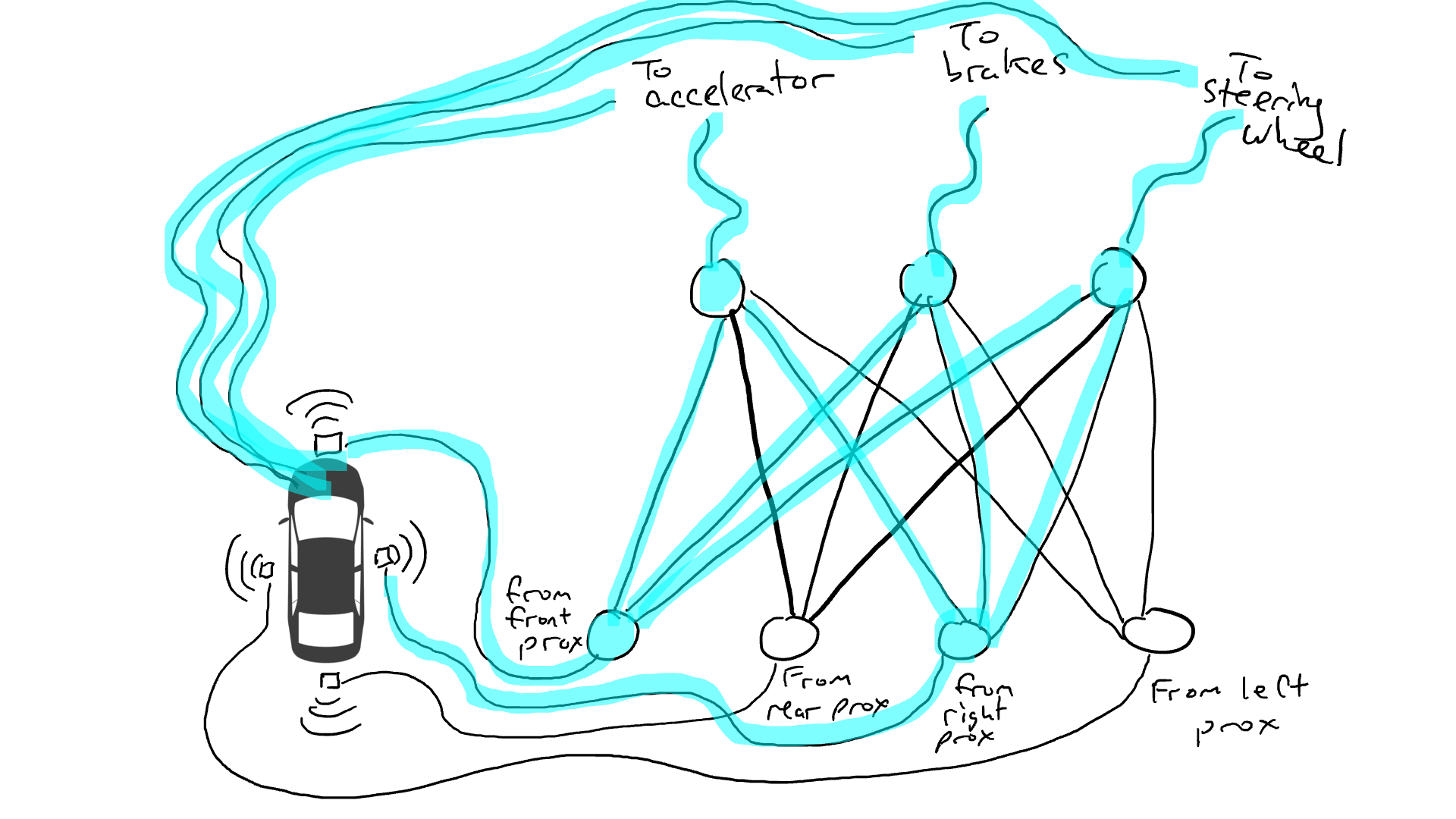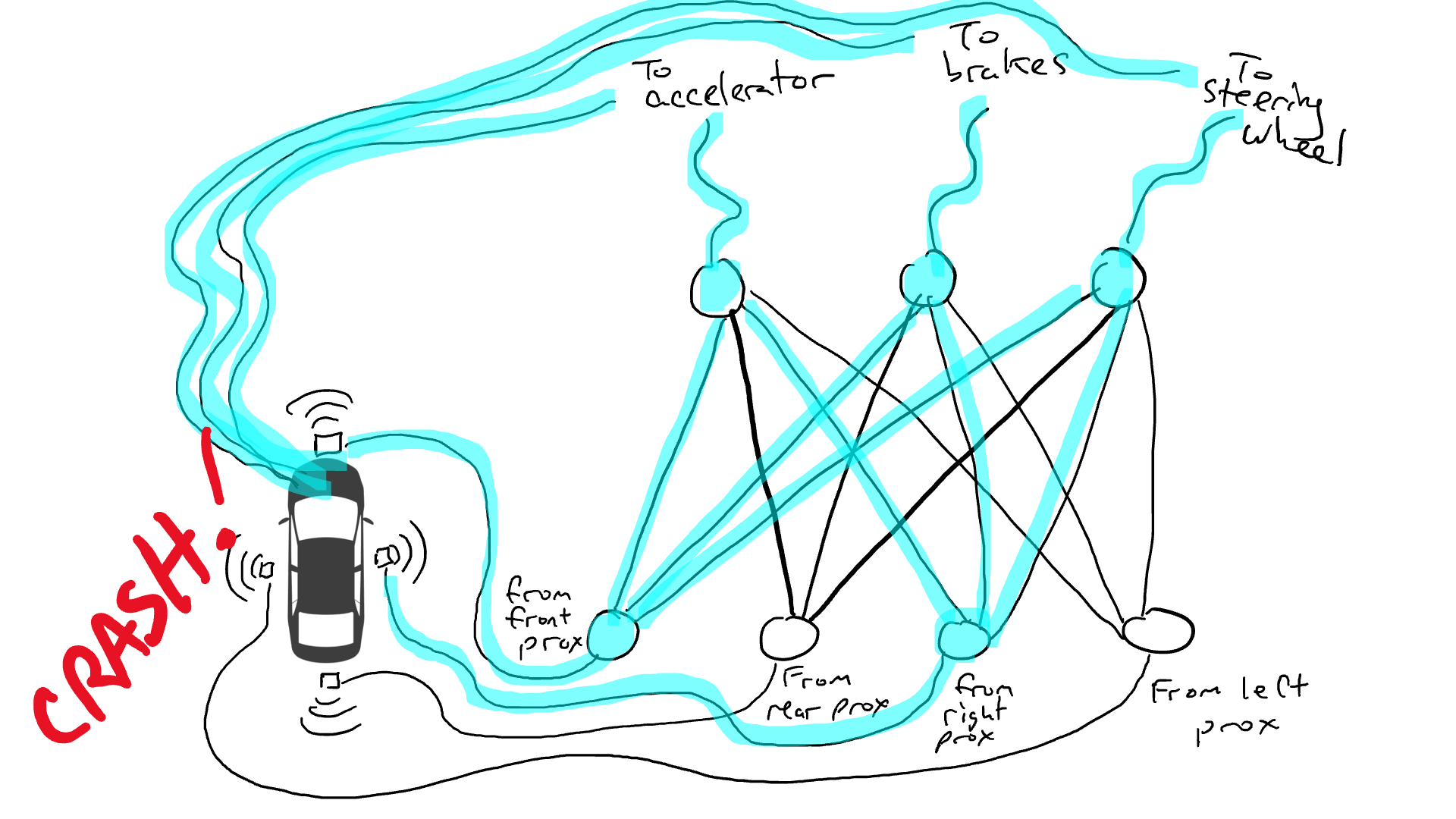
Get out the resistors and start placing them in different parts of the circuit so that current can flow more freely between certain sensors and certain robotic arms. For example, we would like the current to flow more freely from the front proximity sensor to the brakes rather than the steering mechanism. We also installed elements called gates that would either stop current from flowing until enough charge had accumulated to trigger the switch (only allowing current to flow when both the front and rear proximity sensors reported a high number), or only allow the current to flow when the input power Send power forward when the intensity is low (send more power to the accelerator when the forward proximity sensor reports a low value).
But where should we place these resistors and gates? I don't know either. Place them randomly in various locations. Then try again. Maybe the car drives better this time, which means it sometimes brakes and steers when the data says it's best to brake and steer, etc., but it doesn't get it right every time. And there are some things it does worse (it accelerates when the data suggests it sometimes needs to brake). So we kept randomly trying different combinations of resistors and gates. Eventually, we'll stumble upon a combination that's good enough, and we'll declare success. For example, this combination:
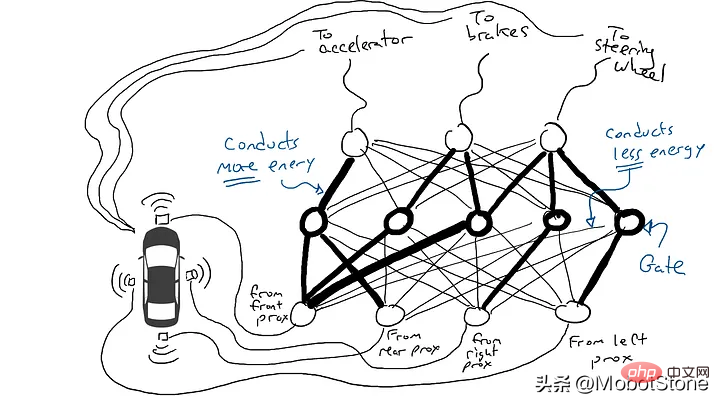
(Actually, we won’t add or remove doors, but we will modify them so that they can be activated from below with lower energy, Either more energy needs to come out from below, or a lot of energy is released only when there is very little energy below. Machine learning purists may feel uncomfortable with this description. Technically, this is done by tuning This is done with a bias on the gate, this is not usually shown in such diagrams, but from a circuit metaphor perspective it can be thought of as a cable that plugs in directly to the power supply and can act like all the other wires Modify it like a cable.)
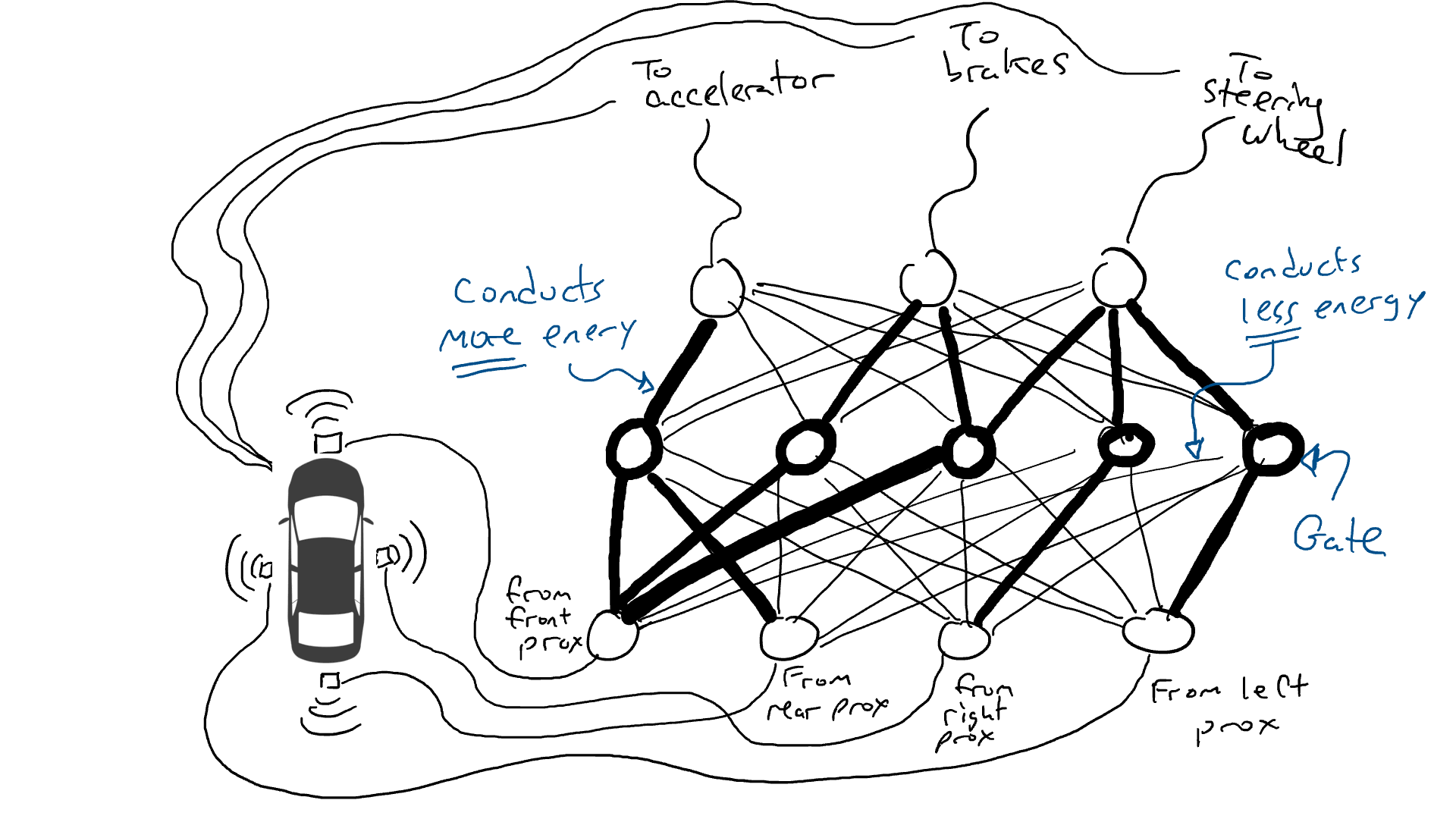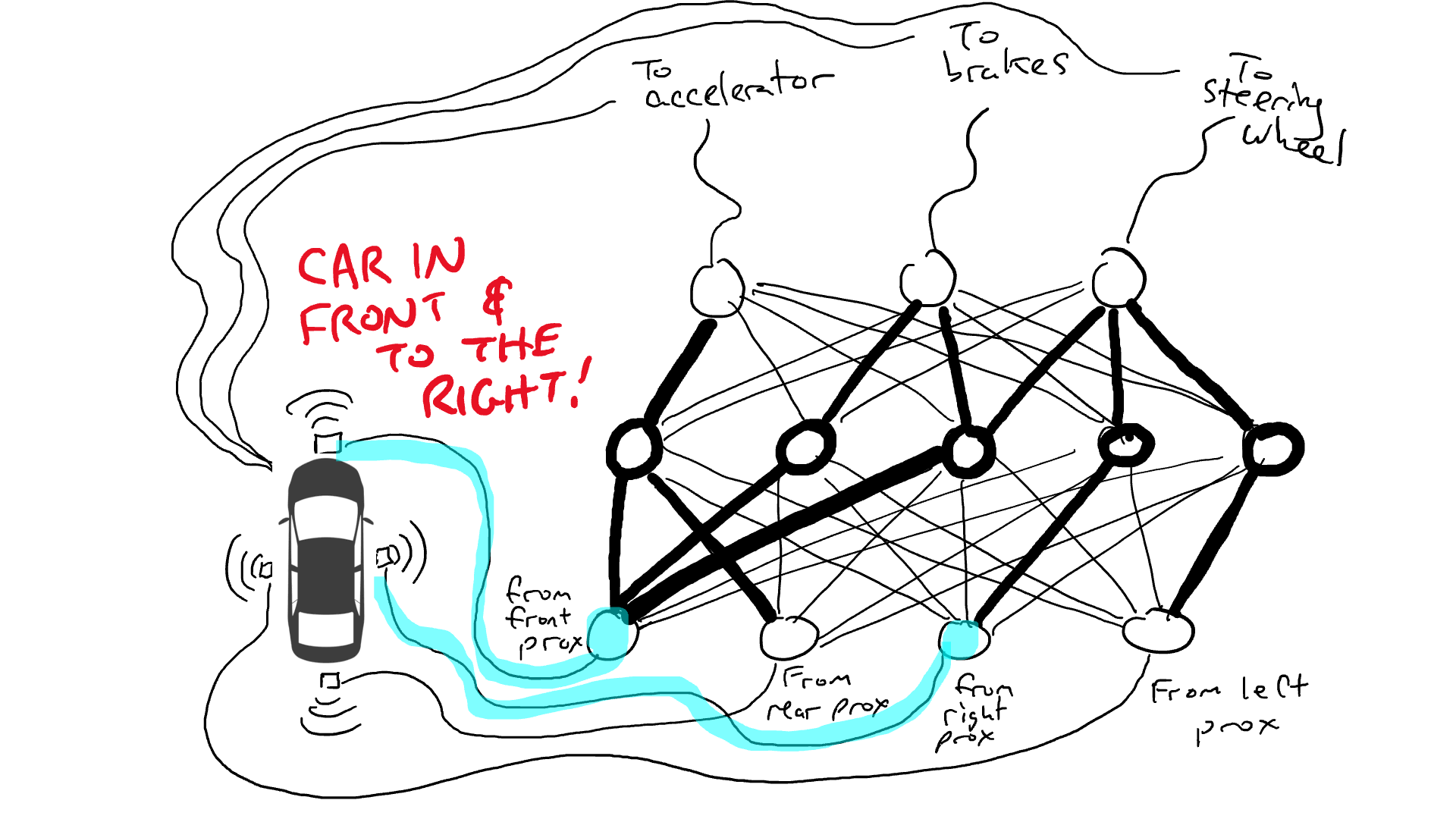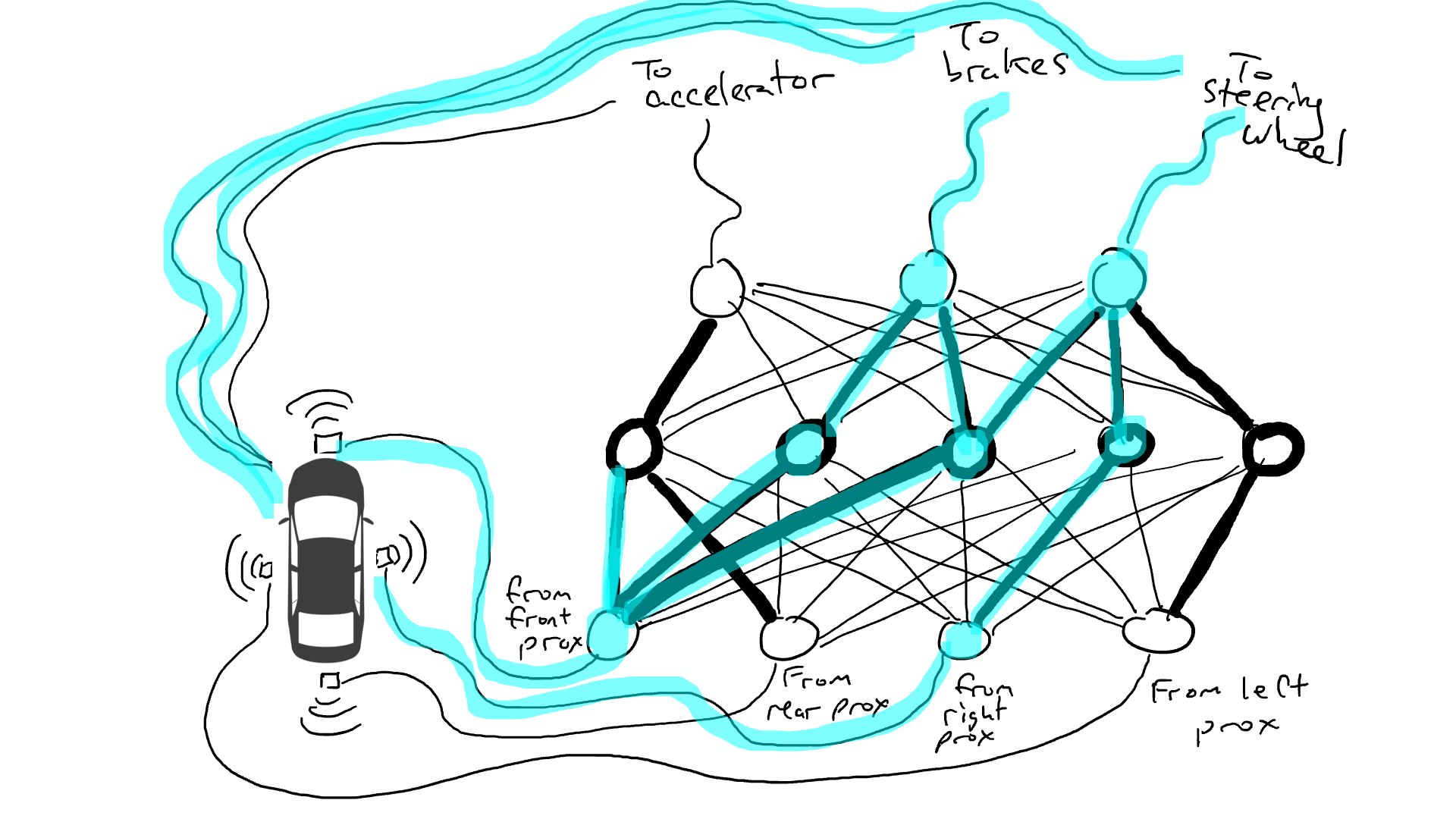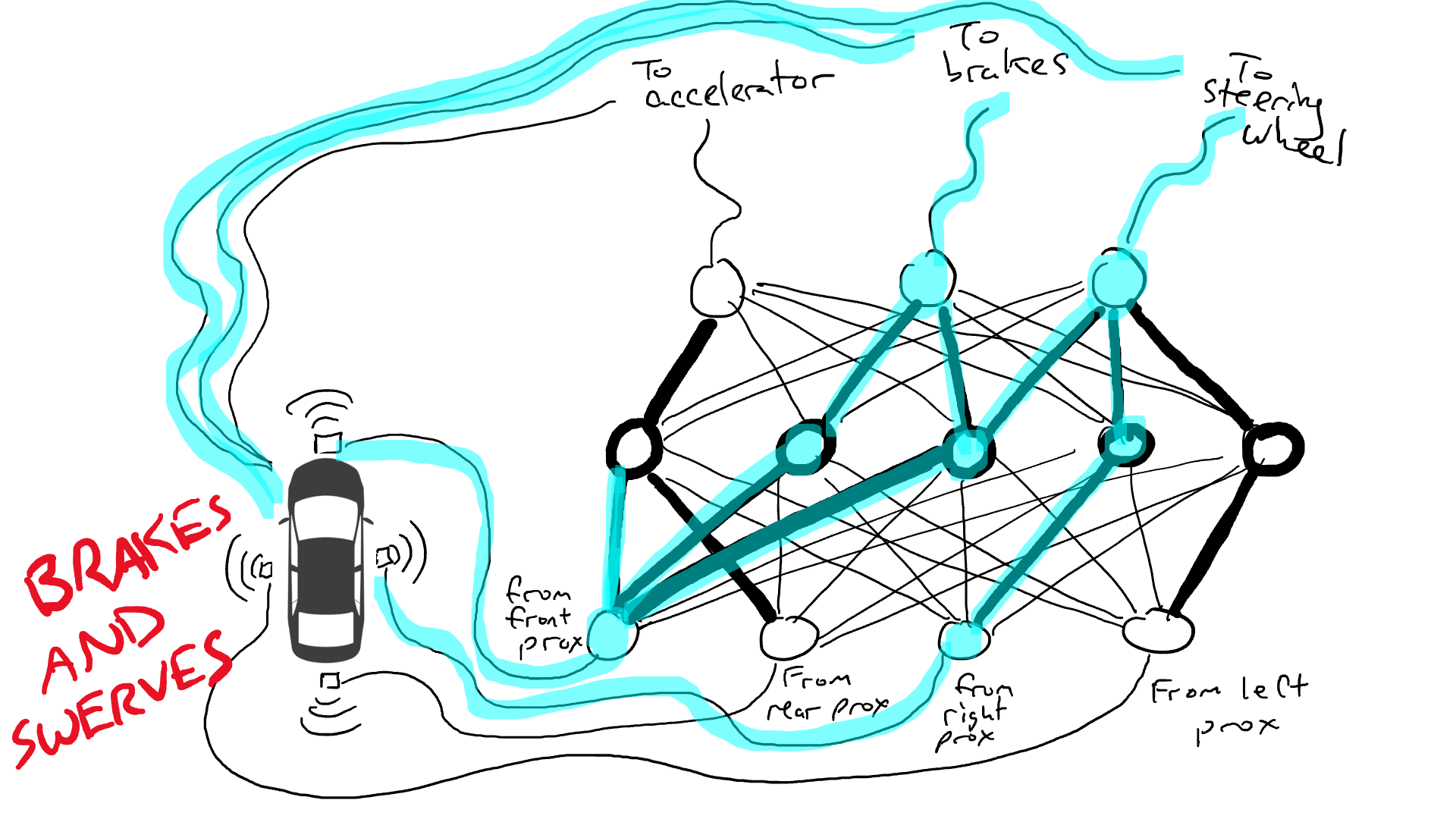
#It is not good to try randomly. An algorithm called backpropagation makes a pretty good guess at changing circuit configurations. The details of the algorithm don't matter, just know that it fine-tunes the circuit to make it behave closer to what the data suggests, and after thousands of fine-tunings, you can eventually get results that match the data.
We call resistors and gates parameters because they are actually everywhere, and what the backpropagation algorithm does is declares each resistor to be stronger or weaker. Therefore, if we know the layout and parameter values of the circuit, the entire circuit can be replicated on other cars.
The above is the detailed content of An easy and objective way to introduce large models to avoid over-interpretation. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1386
1386
 52
52
 ChatGPT now allows free users to generate images by using DALL-E 3 with a daily limit
Aug 09, 2024 pm 09:37 PM
ChatGPT now allows free users to generate images by using DALL-E 3 with a daily limit
Aug 09, 2024 pm 09:37 PM
DALL-E 3 was officially introduced in September of 2023 as a vastly improved model than its predecessor. It is considered one of the best AI image generators to date, capable of creating images with intricate detail. However, at launch, it was exclus
 The second generation Ameca is here! He can communicate with the audience fluently, his facial expressions are more realistic, and he can speak dozens of languages.
Mar 04, 2024 am 09:10 AM
The second generation Ameca is here! He can communicate with the audience fluently, his facial expressions are more realistic, and he can speak dozens of languages.
Mar 04, 2024 am 09:10 AM
The humanoid robot Ameca has been upgraded to the second generation! Recently, at the World Mobile Communications Conference MWC2024, the world's most advanced robot Ameca appeared again. Around the venue, Ameca attracted a large number of spectators. With the blessing of GPT-4, Ameca can respond to various problems in real time. "Let's have a dance." When asked if she had emotions, Ameca responded with a series of facial expressions that looked very lifelike. Just a few days ago, EngineeredArts, the British robotics company behind Ameca, just demonstrated the team’s latest development results. In the video, the robot Ameca has visual capabilities and can see and describe the entire room and specific objects. The most amazing thing is that she can also
 How can AI make robots more autonomous and adaptable?
Jun 03, 2024 pm 07:18 PM
How can AI make robots more autonomous and adaptable?
Jun 03, 2024 pm 07:18 PM
In the field of industrial automation technology, there are two recent hot spots that are difficult to ignore: artificial intelligence (AI) and Nvidia. Don’t change the meaning of the original content, fine-tune the content, rewrite the content, don’t continue: “Not only that, the two are closely related, because Nvidia is expanding beyond just its original graphics processing units (GPUs). The technology extends to the field of digital twins and is closely connected to emerging AI technologies. "Recently, NVIDIA has reached cooperation with many industrial companies, including leading industrial automation companies such as Aveva, Rockwell Automation, Siemens and Schneider Electric, as well as Teradyne Robotics and its MiR and Universal Robots companies. Recently,Nvidiahascoll
 How to install chatgpt on mobile phone
Mar 05, 2024 pm 02:31 PM
How to install chatgpt on mobile phone
Mar 05, 2024 pm 02:31 PM
Installation steps: 1. Download the ChatGTP software from the ChatGTP official website or mobile store; 2. After opening it, in the settings interface, select the language as Chinese; 3. In the game interface, select human-machine game and set the Chinese spectrum; 4 . After starting, enter commands in the chat window to interact with the software.
 After 2 months, the humanoid robot Walker S can fold clothes
Apr 03, 2024 am 08:01 AM
After 2 months, the humanoid robot Walker S can fold clothes
Apr 03, 2024 am 08:01 AM
Editor of Machine Power Report: Wu Xin The domestic version of the humanoid robot + large model team completed the operation task of complex flexible materials such as folding clothes for the first time. With the unveiling of Figure01, which integrates OpenAI's multi-modal large model, the related progress of domestic peers has been attracting attention. Just yesterday, UBTECH, China's "number one humanoid robot stock", released the first demo of the humanoid robot WalkerS that is deeply integrated with Baidu Wenxin's large model, showing some interesting new features. Now, WalkerS, blessed by Baidu Wenxin’s large model capabilities, looks like this. Like Figure01, WalkerS does not move around, but stands behind a desk to complete a series of tasks. It can follow human commands and fold clothes
 The first robot to autonomously complete human tasks appears, with five fingers that are flexible and fast, and large models support virtual space training
Mar 11, 2024 pm 12:10 PM
The first robot to autonomously complete human tasks appears, with five fingers that are flexible and fast, and large models support virtual space training
Mar 11, 2024 pm 12:10 PM
This week, FigureAI, a robotics company invested by OpenAI, Microsoft, Bezos, and Nvidia, announced that it has received nearly $700 million in financing and plans to develop a humanoid robot that can walk independently within the next year. And Tesla’s Optimus Prime has repeatedly received good news. No one doubts that this year will be the year when humanoid robots explode. SanctuaryAI, a Canadian-based robotics company, recently released a new humanoid robot, Phoenix. Officials claim that it can complete many tasks autonomously at the same speed as humans. Pheonix, the world's first robot that can autonomously complete tasks at human speeds, can gently grab, move and elegantly place each object to its left and right sides. It can autonomously identify objects
 The humanoid robot can do magic, let the Spring Festival Gala program team find out more
Feb 04, 2024 am 09:03 AM
The humanoid robot can do magic, let the Spring Festival Gala program team find out more
Feb 04, 2024 am 09:03 AM
In the blink of an eye, robots have learned to do magic? It was seen that it first picked up the water spoon on the table and proved to the audience that there was nothing in it... Then it put the egg-like object in its hand, then put the water spoon back on the table and started to "cast a spell"... …Just when it picked up the water spoon again, a miracle happened. The egg that was originally put in disappeared, and the thing that jumped out turned into a basketball... Let’s look at the continuous actions again: △ This animation shows a set of actions at 2x speed, and it flows smoothly. Only by watching the video repeatedly at 0.5x speed can it be understood. Finally, I discovered the clues: if my hand speed were faster, I might be able to hide it from the enemy. Some netizens lamented that the robot’s magic skills were even higher than their own: Mag was the one who performed this magic for us.
 Ten humanoid robots shaping the future
Mar 22, 2024 pm 08:51 PM
Ten humanoid robots shaping the future
Mar 22, 2024 pm 08:51 PM
The following 10 humanoid robots are shaping our future: 1. ASIMO: Developed by Honda, ASIMO is one of the most well-known humanoid robots. Standing 4 feet tall and weighing 119 pounds, ASIMO is equipped with advanced sensors and artificial intelligence capabilities that allow it to navigate complex environments and interact with humans. ASIMO's versatility makes it suitable for a variety of tasks, from assisting people with disabilities to delivering presentations at events. 2. Pepper: Created by Softbank Robotics, Pepper aims to be a social companion for humans. With its expressive face and ability to recognize emotions, Pepper can participate in conversations, help in retail settings, and even provide educational support. Pepper's



