 Backend Development
Backend Development
 Python Tutorial
Python Tutorial
 How to solve TypeError:unhashable type:'dict' error in Python
How to solve TypeError:unhashable type:'dict' error in Python
How to solve TypeError:unhashable type:'dict' error in Python
Python "TypeError: unhashable type: ‘dict’ " occurs when we use a dictionary as a key in another dictionary or as an element in a collection.
To resolve this error, you need to use frozenset instead, or convert the dictionary to a JSON string before using it as a key.
The error occurs when we use a dictionary as a key in another dictionary.
# ????️ using dictionary as a key in a dictionary
# ⛔️ TypeError: unhashable type: 'dict'
my_dict = {'name': 'Jiyik', {'country': 'China'}: 'address'} Or when we use a dictionary as an element in a set object.
# ????️ 使用字典作为集合中的元素
# ⛔️ TypeError: unhashable type: 'dict'
my_set = {{'name': 'Jiyik'}}We cannot use a dictionary as a key in a dictionary or an element in a collection because dictionary objects are mutable and unhashable.
Convert the dictionary to a JSON string to resolve the error
One way to resolve this error is to convert the dictionary to a JSON string before using it as a key.
import json
# ????️ 将字典转换为 JSON 字符串
my_json = json.dumps({'country': 'China'})
my_dict = {'name': 'Jiyik', my_json: 'address'}
print(my_dict) # ????️ {'name': 'Jiyik', '{"country": "China"}': 'address'}
# ????️ 当你必须访问字典中的键时
print(my_dict[json.dumps({'country': 'Austria'})]) # ????️ addressjson.dumps Method converts a Python object into a JSON-formatted string. This works because strings are immutable and hashable.
In contrast, the json.loads method parses a JSON string into a native Python object, such as my_dict = json.loads(my_json_str).
Using frozenset to resolve errors
Another way to resolve errors is to use frozenset.
my_key = {'country': 'China'}
key = frozenset(my_key.items())
print(key) # ????️ frozenset({('country', 'China')})
my_dict = {'name': 'Jiyik', key: 'address'}
# ????️ 当我们必须访问 key 时
print(my_dict[frozenset(my_key.items())]) # ????️ 'address'dict.items Method returns a new view of dictionary items ((key, value) pairs).
# ????️ dict_items([('name', 'jiyik'), ('age', 30)])
print({'name': 'jiyik', 'age': 30}.items()) We use the dictionary's items to create a frozenset that we can use as a key in the dictionary (as well as an element in another set).
frozensetis an immutable version of a Python collection object, so it can be used as a key in a dictionary or as an element in another collection.
Please note that we must use the same method to access the keys in the dictionary.
We can store the result of calling frozenset(my_key.items()) in a variable and reuse the frozenset when setting or accessing keys in the dictionary.
Convert dictionary to tuple to resolve error
Another way to resolve the error is to convert dictionary to tuple.
dict_key = {'id': 1, 'country': 'China'}
# ✅ 转换为元组
my_tuple = tuple(dict_key)
print(my_tuple) # ????️ ('id', 'country')
my_dict = {'name': 'Jiyik', my_tuple: 'address'}
print(my_dict) # ????️ {'name': 'Jiyik', ('id', 'country'): 'address'}
# ????️ 当你必须访问字典中的键时
print(my_dict[my_tuple]) # ????️ addressWhen converting a dictionary to a tuple, the tuple only contains the keys of the dictionary.
Tuples are immutable, so a tuple containing a dictionary key can safely be used as a key in another dictionary.
Using one dictionary as a value in another dictionary
We cannot use a dictionary as a key in another dictionary, but we can use a dictionary as a value.
dict_value = {'id': 1, 'country': 'China'}
my_dict = {'name': 'Jiyik', 'data': dict_value}
# ????️ {'name': 'Jiyik', 'data': {'id': 1, 'country': 'China'}}
print(my_dict)
print(my_dict['data']) # ????️ {'id': 1, 'country': 'China'}We set a dictionary to a value in another dictionary.
This is allowed because the limit does not apply to dictionary values.
Add all key-value pairs of one dictionary to another dictionary
If you need to add all key-value pairs of one dictionary to another dictionary, you can use a for loop.
another_dict = {'id': 1, 'country': 'China'}
my_dict = {'name': 'Jiyik'}
for key, value in another_dict.items():
my_dict[key] = value
# ????️ {'name': 'Jiyik', 'id': 1, 'country': 'China'}
print(my_dict)dict.items Method returns a new view of dictionary items ((key, value) pairs).
my_dict = {'id': 1, 'name': 'Jiyik'}
# ????️ dict_items([('id', 1), ('name', 'Jiyik')])
print(my_dict.items())In each iteration, we set the key-value pairs to another dictionary.
Hashable vs. Unhashable Objects in Python
Most of the immutable built-in objects in Python are hashable, while mutable objects are not hashable.
If an object is hashable, then it can be used as a key in a dictionary and an element in a collection because these data structures use hash values internally.
Hashable objects include - str, int, bool, tuple, frozenset.
Unhashable objects include - list, dict, set.
Checking if an object is hashable
Please note that tuples and frozen sets are hashable only if their elements are hashable.
We can check if an object is hashable by passing it to the built-in
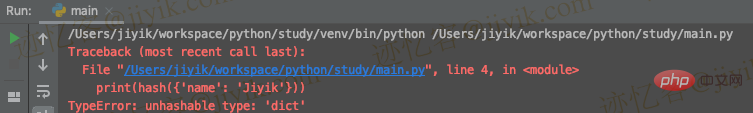
hash() function. <div class="code" style="position:relative; padding:0px; margin:0px;"><pre class='brush:php;toolbar:false;'>print(hash(&#39;jiyik.com&#39;)) # ????️ 4905958875846995527
# ⛔️ TypeError: unhashable type: &#39;dict&#39;
print(hash({&#39;name&#39;: &#39;Jiyik&#39;}))</pre><div class="contentsignin">Copy after login</div></div>
 The hash function returns the hash value of the passed in object (if any).
The hash function returns the hash value of the passed in object (if any).
Hash values are integers used to compare dictionary keys during dictionary lookups.
!> The hash value of a hashable object never changes during its lifetime. This is why most immutable objects are hashable, while mutable objects are not hashable.
Objects like dictionaries are mutable because the contents of the dictionary can change.
my_dict = {'name': 'Fql'}
my_dict['name'] = 'Jiyik'
print(my_dict) # ????️ {'name': 'Jiyik'}On the other hand,
fronzenset and tuple objects containing primitive values are immutable (and hashable). Dictionaries are indexed by keys, which can be any immutable type, such as strings or numbers.
If thefronzenset
or tuple contains a mutable object (such as a list), it cannot be used as a key in a dictionary or an element in a set. If we are not sure what type of object a variable stores, please use the
function. <div class="code" style="position:relative; padding:0px; margin:0px;"><pre class='brush:php;toolbar:false;'>my_dict = {&#39;name&#39;: &#39;Jiyik&#39;}
print(type(my_dict)) # ????️ <class &#39;dict&#39;>
print(isinstance(my_dict, dict)) # ????️ True
my_str = &#39;jiyik.com&#39;
print(type(my_str)) # ????️ <class &#39;str&#39;>
print(isinstance(my_str, str)) # ????️ True</pre><div class="contentsignin">Copy after login</div></div>type<p> The function returns the type of the object. <code><p>If the object passed in is an instance or subclass of the passed class, the <code>isinstance function returns True.
The above is the detailed content of How to solve TypeError:unhashable type:'dict' error in Python. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 How to open xml format
Apr 02, 2025 pm 09:00 PM
How to open xml format
Apr 02, 2025 pm 09:00 PM
Use most text editors to open XML files; if you need a more intuitive tree display, you can use an XML editor, such as Oxygen XML Editor or XMLSpy; if you process XML data in a program, you need to use a programming language (such as Python) and XML libraries (such as xml.etree.ElementTree) to parse.
 How to beautify the XML format
Apr 02, 2025 pm 09:57 PM
How to beautify the XML format
Apr 02, 2025 pm 09:57 PM
XML beautification is essentially improving its readability, including reasonable indentation, line breaks and tag organization. The principle is to traverse the XML tree, add indentation according to the level, and handle empty tags and tags containing text. Python's xml.etree.ElementTree library provides a convenient pretty_xml() function that can implement the above beautification process.
 Does XML modification require programming?
Apr 02, 2025 pm 06:51 PM
Does XML modification require programming?
Apr 02, 2025 pm 06:51 PM
Modifying XML content requires programming, because it requires accurate finding of the target nodes to add, delete, modify and check. The programming language has corresponding libraries to process XML and provides APIs to perform safe, efficient and controllable operations like operating databases.
 Is there a free XML to PDF tool for mobile phones?
Apr 02, 2025 pm 09:12 PM
Is there a free XML to PDF tool for mobile phones?
Apr 02, 2025 pm 09:12 PM
There is no simple and direct free XML to PDF tool on mobile. The required data visualization process involves complex data understanding and rendering, and most of the so-called "free" tools on the market have poor experience. It is recommended to use computer-side tools or use cloud services, or develop apps yourself to obtain more reliable conversion effects.
 Is the conversion speed fast when converting XML to PDF on mobile phone?
Apr 02, 2025 pm 10:09 PM
Is the conversion speed fast when converting XML to PDF on mobile phone?
Apr 02, 2025 pm 10:09 PM
The speed of mobile XML to PDF depends on the following factors: the complexity of XML structure. Mobile hardware configuration conversion method (library, algorithm) code quality optimization methods (select efficient libraries, optimize algorithms, cache data, and utilize multi-threading). Overall, there is no absolute answer and it needs to be optimized according to the specific situation.
 How to convert XML to PDF on your phone?
Apr 02, 2025 pm 10:18 PM
How to convert XML to PDF on your phone?
Apr 02, 2025 pm 10:18 PM
It is not easy to convert XML to PDF directly on your phone, but it can be achieved with the help of cloud services. It is recommended to use a lightweight mobile app to upload XML files and receive generated PDFs, and convert them with cloud APIs. Cloud APIs use serverless computing services, and choosing the right platform is crucial. Complexity, error handling, security, and optimization strategies need to be considered when handling XML parsing and PDF generation. The entire process requires the front-end app and the back-end API to work together, and it requires some understanding of a variety of technologies.
 Is there any mobile app that can convert XML into PDF?
Apr 02, 2025 pm 08:54 PM
Is there any mobile app that can convert XML into PDF?
Apr 02, 2025 pm 08:54 PM
An application that converts XML directly to PDF cannot be found because they are two fundamentally different formats. XML is used to store data, while PDF is used to display documents. To complete the transformation, you can use programming languages and libraries such as Python and ReportLab to parse XML data and generate PDF documents.
 Recommended XML formatting tool
Apr 02, 2025 pm 09:03 PM
Recommended XML formatting tool
Apr 02, 2025 pm 09:03 PM
XML formatting tools can type code according to rules to improve readability and understanding. When selecting a tool, pay attention to customization capabilities, handling of special circumstances, performance and ease of use. Commonly used tool types include online tools, IDE plug-ins, and command-line tools.





