 Technology peripherals
Technology peripherals
 AI
AI
 When will AI technology help the pharmaceutical industry break 'Inverted Moore's Law'?
When will AI technology help the pharmaceutical industry break 'Inverted Moore's Law'?
When will AI technology help the pharmaceutical industry break 'Inverted Moore's Law'?

In 2020, the first year of the COVID-19 outbreak, the US Food and Drug Administration approved only 53 new drugs. In the same year, the global pharmaceutical industry’s overall drug R&D investment reached nearly US$200 billion. This means that the average cost of each drug approved in 2020 is close to $3.8 billion. A study published that year gave a relatively conservative estimate of the cost of new drugs, arguing that although the cost of new drugs has increased dramatically over the past decade, the specific range is still between US$314 million and US$2.8 billion. The study also found that the median total research and development expenditure invested in bringing a new drug to the market is close to US$1 billion, while the average is estimated to be around US$1.3 billion. In addition, the average launch cycle of new drugs is 10 to 15 years, of which about half of the time and investment is spent on the clinical trial stage, and the remaining half of the cost is used to support preclinical compound discovery, testing and supervision. As for why each new drug costs so much and has a long cycle, the reasons include lack of clinical efficacy, lack of commercial benefits and improper strategic planning. In short, all these complex factors have turned the effectiveness of the pharmaceutical industry into a metaphysics. Many people have even become skeptics due to the high cost of launching new drugs, questioning why the pharmaceutical industry has made significant progress since its technical level and management capabilities have improved significantly. You will still be stuck in the current predicament and unable to extricate yourself.
These are the proponents of what’s known as “Inverted Moore’s Law,” in which the cost of developing new drugs has grown exponentially over the past few decades despite improvements in technology. Inverse Moore's Law states that the cost of developing a new drug doubles approximately every nine years, discounting the effects of inflation. This observation proposes a law similar to diminishing returns. According to the concept of economics, if a certain input in the production of a certain commodity is increased while all other inputs remain unchanged, the overall situation will eventually Reaching a critical point - if you continue to increase input, the corresponding output will begin to gradually decrease. The term "Inverse Moore's Law" was proposed by Dr. Jack Scannell and colleagues in "Nature·Reviews·Drug Discovery" in 2012.
Inverted Moore’s Law naturally points to the famous Moore’s Law. This conceptual observation from the 1960s found that the number of transistors on large-scale integrated circuits doubled every two years or so. Moore's Law is named after Gordon Moore, co-founder of Intel Corporation, and is his observation and summary of historical trends.
Dr. Scannell emphasized that there are four main reasons for the current predicament. First of all, regulatory agencies have increasingly higher standards for therapies; regulatory agencies are less and less able to bear risks, which increases the cost and difficulty of research and development; a money-throwing mentality, which relies on flooding resources to promote projects , it is easy to cause project overruns; and then there is brute force cracking of basic research, that is, overestimating the possibility of using crude trial and error to break through basic research problems.
Despite all the difficult factors we face, we will one day defeat the challenge of Moore's Law, and a powerful weapon that will determine the outcome of the battle is AI. The good news is that someone has already taken the first steps toward exploring this path.
Dr. Scannell and his co-scientists are calling on pharmaceutical companies to appoint a chief drug officer who will be responsible for summarizing the causes of failures at each stage of the development process and publishing the results in scientific journals. Currently, pharmaceutical companies rarely even publish failed experiments or clinical results, and most have not yet thought of appointing dedicated executives to handle the valuable information in failed cases. However, Dr. Scannell emphasized that in order to break the inverse Moore's Law, companies must first change their R&D processes. Collaboration and information sharing are of course a good starting point, but in the pharmaceutical industry, there is only one way to truly break Moore's Law - AI.
In the past few years, people have made many attempts to use AI to break the inverse Moore's Law. Now, many institutions such as Exscientia and Insilico Medicine are sprinting towards this end.
Headquartered in Oxford, Exscientia is a global pharmaceutical technology company that puts patients at the center and accelerates drug discovery through AI technology. Last year, the company announced that the first immuno-oncology molecule designed by AI had entered human clinical trials. In the project, Exsientia is collaborating with Evotec to develop A2a receptor antagonists for adult patients with advanced TB, using the former's Centaur Chemist drug discovery platform. This is not the first attempt made by Exscientia. In 2020, the company announced an obsessive-compulsive disorder treatment drug designed by AI-driven software and has entered Phase I clinical trials.
In addition, there is Schrodinger, who have developed the most advanced chemical simulation software in the pharmaceutical industry. Schrodinger recently received FDA approval to study its computer-designed treatment for non-Hodgkin's lymphoma in early-stage trials. The company's platform, based on machine learning technology, classified 8.2 billion potential compounds within 10 months and ultimately identified 78 compounds that could successfully pass preclinical experimental synthesis and screening. Now, the company has plans to launch a Phase I clinical study and begin recruiting patients with relapsed or refractory non-Hodgkin lymphoma.
Meanwhile, Utah-based Recursion Pharmaceuticals is also using AI technology to find new uses for existing drugs. Last year, Roche and Genetech established a project collaboration with Recursion to jointly explore new areas of cell biology and try to develop new treatments in the fields of neuroscience and oncology indications. Through the collaboration, the two companies will use Recursion's AI drug discovery platform to conduct comprehensive screening of new drug targets, thereby accelerating the development of small molecule drugs.
In Insilico, a leading anti-fibrosis drug candidate has also successfully completed Phase 0 clinical research and officially entered the Phase I clinical stage. The new target of this drug candidate was discovered by the Pharma.AI platform. The total time from target discovery to the launch of the first phase of the project was even less than 30 months, which has set a new record for the speed of new drug development in the pharmaceutical industry.
Don’t forget that AI technology will also play a role in brain-computer interface, deep learning, human-computer interface, machine learning and other intelligent simulation scenarios. These concepts have existed for decades. Early medical AI systems once relied heavily on clinical knowledge and logical rules provided by medical experts, but now trained supercomputers can complete these tasks on their own.
In order to break the inverse Moore's Law, data scientists and medical scientists must jointly plan achievable use cases, apply AI technology to various clinical trials, and combine AI technology with existing technologies that will replace/complement it. Contrast. In this way, AI is expected to smoothly enter the clinical trial ecosystem, effectively reducing R&D failure rates and costs while rapidly improving the industry's drug discovery and development processes. Today, almost all large pharmaceutical companies are using internal original research algorithms, cooperating with AI vendors, or directly acquiring AI vendors/technology to enrich their product portfolios and drug discovery pipelines. The partnership statements from Massive Financing and multiple pharmaceutical companies also tell us that the industry has high expectations for the application of AI tools in the drug research and development process. There have been many changes in this field. It is hoped that in the next few years, companies will be able to combine better investment strategies with advanced AI technology to break the "curse" of inverted Moore's Law in one fell swoop.
The above is the detailed content of When will AI technology help the pharmaceutical industry break 'Inverted Moore's Law'?. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1386
1386
 52
52
 Bytedance Cutting launches SVIP super membership: 499 yuan for continuous annual subscription, providing a variety of AI functions
Jun 28, 2024 am 03:51 AM
Bytedance Cutting launches SVIP super membership: 499 yuan for continuous annual subscription, providing a variety of AI functions
Jun 28, 2024 am 03:51 AM
This site reported on June 27 that Jianying is a video editing software developed by FaceMeng Technology, a subsidiary of ByteDance. It relies on the Douyin platform and basically produces short video content for users of the platform. It is compatible with iOS, Android, and Windows. , MacOS and other operating systems. Jianying officially announced the upgrade of its membership system and launched a new SVIP, which includes a variety of AI black technologies, such as intelligent translation, intelligent highlighting, intelligent packaging, digital human synthesis, etc. In terms of price, the monthly fee for clipping SVIP is 79 yuan, the annual fee is 599 yuan (note on this site: equivalent to 49.9 yuan per month), the continuous monthly subscription is 59 yuan per month, and the continuous annual subscription is 499 yuan per year (equivalent to 41.6 yuan per month) . In addition, the cut official also stated that in order to improve the user experience, those who have subscribed to the original VIP
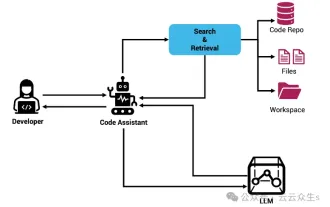 Context-augmented AI coding assistant using Rag and Sem-Rag
Jun 10, 2024 am 11:08 AM
Context-augmented AI coding assistant using Rag and Sem-Rag
Jun 10, 2024 am 11:08 AM
Improve developer productivity, efficiency, and accuracy by incorporating retrieval-enhanced generation and semantic memory into AI coding assistants. Translated from EnhancingAICodingAssistantswithContextUsingRAGandSEM-RAG, author JanakiramMSV. While basic AI programming assistants are naturally helpful, they often fail to provide the most relevant and correct code suggestions because they rely on a general understanding of the software language and the most common patterns of writing software. The code generated by these coding assistants is suitable for solving the problems they are responsible for solving, but often does not conform to the coding standards, conventions and styles of the individual teams. This often results in suggestions that need to be modified or refined in order for the code to be accepted into the application
 Can fine-tuning really allow LLM to learn new things: introducing new knowledge may make the model produce more hallucinations
Jun 11, 2024 pm 03:57 PM
Can fine-tuning really allow LLM to learn new things: introducing new knowledge may make the model produce more hallucinations
Jun 11, 2024 pm 03:57 PM
Large Language Models (LLMs) are trained on huge text databases, where they acquire large amounts of real-world knowledge. This knowledge is embedded into their parameters and can then be used when needed. The knowledge of these models is "reified" at the end of training. At the end of pre-training, the model actually stops learning. Align or fine-tune the model to learn how to leverage this knowledge and respond more naturally to user questions. But sometimes model knowledge is not enough, and although the model can access external content through RAG, it is considered beneficial to adapt the model to new domains through fine-tuning. This fine-tuning is performed using input from human annotators or other LLM creations, where the model encounters additional real-world knowledge and integrates it
 Seven Cool GenAI & LLM Technical Interview Questions
Jun 07, 2024 am 10:06 AM
Seven Cool GenAI & LLM Technical Interview Questions
Jun 07, 2024 am 10:06 AM
To learn more about AIGC, please visit: 51CTOAI.x Community https://www.51cto.com/aigc/Translator|Jingyan Reviewer|Chonglou is different from the traditional question bank that can be seen everywhere on the Internet. These questions It requires thinking outside the box. Large Language Models (LLMs) are increasingly important in the fields of data science, generative artificial intelligence (GenAI), and artificial intelligence. These complex algorithms enhance human skills and drive efficiency and innovation in many industries, becoming the key for companies to remain competitive. LLM has a wide range of applications. It can be used in fields such as natural language processing, text generation, speech recognition and recommendation systems. By learning from large amounts of data, LLM is able to generate text
 Five schools of machine learning you don't know about
Jun 05, 2024 pm 08:51 PM
Five schools of machine learning you don't know about
Jun 05, 2024 pm 08:51 PM
Machine learning is an important branch of artificial intelligence that gives computers the ability to learn from data and improve their capabilities without being explicitly programmed. Machine learning has a wide range of applications in various fields, from image recognition and natural language processing to recommendation systems and fraud detection, and it is changing the way we live. There are many different methods and theories in the field of machine learning, among which the five most influential methods are called the "Five Schools of Machine Learning". The five major schools are the symbolic school, the connectionist school, the evolutionary school, the Bayesian school and the analogy school. 1. Symbolism, also known as symbolism, emphasizes the use of symbols for logical reasoning and expression of knowledge. This school of thought believes that learning is a process of reverse deduction, through existing
 To provide a new scientific and complex question answering benchmark and evaluation system for large models, UNSW, Argonne, University of Chicago and other institutions jointly launched the SciQAG framework
Jul 25, 2024 am 06:42 AM
To provide a new scientific and complex question answering benchmark and evaluation system for large models, UNSW, Argonne, University of Chicago and other institutions jointly launched the SciQAG framework
Jul 25, 2024 am 06:42 AM
Editor |ScienceAI Question Answering (QA) data set plays a vital role in promoting natural language processing (NLP) research. High-quality QA data sets can not only be used to fine-tune models, but also effectively evaluate the capabilities of large language models (LLM), especially the ability to understand and reason about scientific knowledge. Although there are currently many scientific QA data sets covering medicine, chemistry, biology and other fields, these data sets still have some shortcomings. First, the data form is relatively simple, most of which are multiple-choice questions. They are easy to evaluate, but limit the model's answer selection range and cannot fully test the model's ability to answer scientific questions. In contrast, open-ended Q&A
 SOTA performance, Xiamen multi-modal protein-ligand affinity prediction AI method, combines molecular surface information for the first time
Jul 17, 2024 pm 06:37 PM
SOTA performance, Xiamen multi-modal protein-ligand affinity prediction AI method, combines molecular surface information for the first time
Jul 17, 2024 pm 06:37 PM
Editor | KX In the field of drug research and development, accurately and effectively predicting the binding affinity of proteins and ligands is crucial for drug screening and optimization. However, current studies do not take into account the important role of molecular surface information in protein-ligand interactions. Based on this, researchers from Xiamen University proposed a novel multi-modal feature extraction (MFE) framework, which for the first time combines information on protein surface, 3D structure and sequence, and uses a cross-attention mechanism to compare different modalities. feature alignment. Experimental results demonstrate that this method achieves state-of-the-art performance in predicting protein-ligand binding affinities. Furthermore, ablation studies demonstrate the effectiveness and necessity of protein surface information and multimodal feature alignment within this framework. Related research begins with "S
 SK Hynix will display new AI-related products on August 6: 12-layer HBM3E, 321-high NAND, etc.
Aug 01, 2024 pm 09:40 PM
SK Hynix will display new AI-related products on August 6: 12-layer HBM3E, 321-high NAND, etc.
Aug 01, 2024 pm 09:40 PM
According to news from this site on August 1, SK Hynix released a blog post today (August 1), announcing that it will attend the Global Semiconductor Memory Summit FMS2024 to be held in Santa Clara, California, USA from August 6 to 8, showcasing many new technologies. generation product. Introduction to the Future Memory and Storage Summit (FutureMemoryandStorage), formerly the Flash Memory Summit (FlashMemorySummit) mainly for NAND suppliers, in the context of increasing attention to artificial intelligence technology, this year was renamed the Future Memory and Storage Summit (FutureMemoryandStorage) to invite DRAM and storage vendors and many more players. New product SK hynix launched last year



