How to configure pathinfo mode in nginx
Reason
I haven’t used apache for a long time, and I gradually feel unfamiliar with apache, because a friend has a zendframework framework that was moved from apache to nginx and requires pathinfo mode support.
Online Search
So I started searching for articles related to nginx pathinfo. I thought it would be easy to configure it at first. After searching, I found that there are a lot of articles introducing nginx to enable pathinfo mode, and it seems that it is not difficult. But after several hours, it is still not configured properly. And the contents of a large number of articles are very similar, and they are basically reprinted.
I’m starting to get a little anxious! Because one day has passed and the preparation has not been completed.
Continue to search
No choice, continue searching. For the convenience of verification, I used a.com to download the thinkphp framework and set up an environment. And added the useraction.class.php controller class, added an app method in the class and output a line of text.
So, I started to constantly rewrite the nginx.conf file, restart nginx, and constantly refresh the a.com/index.php/user/app address. The result is either an address corruption prompt, 502, or access defind.
Another day passed, and I started to feel a little hesitant.
Finally persisted
Logically speaking, I feel that there should be a precedent for nginx thinkphp, but I didn’t search for the answer. Suddenly I feel so confused on the Internet, and I can't find an answer to a small question. Tonight, I tried to use nginx thinkphp keyword search again. After I clicked to more than ten pages, I found a code
Copy code The code is as follows:
location / {
if (!-e $request_filename) {
rewrite ^/(.*)$ /index.php/$1 last;
break;
}
}
location ~ \.php {
fastcgi_pass 127.0.0.1:9000;
fastcgi_index index.php;
include fcgi.conf;
set $real_script_name $fastcgi_script_name;
if ($fastcgi_script_name ~ "^ (. ?\.php)(/. )$") {
set $real_script_name $1;
set $path_info $2;
}
fastcgi_param script_filename $document_root$real_script_name;
fastcgi_param script_name $real_script_name;
fastcgi_param path_info $path_info;
}
Save the changes, restart nginx, refresh the browser
An unexpected page appears
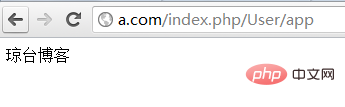
I was finally able to access it, and I finally breathed a sigh of relief. It was really not easy.
Post the nginx.conf code:
Copy the code The code is as follows:
user www www;
worker_processes 2;
worker_cpu_affinity 01 10;
error_log /data1/logs/nginx_error.log crit;
pid /usr/local/webserver/nginx/nginx.pid;
worker_rlimit_nofile 65535;
events
{
use epoll;
worker_connections 65535;
}
http
{
include mime.types;
default_type application/octet-stream;
server_names_hash_bucket_size 128;
client_header_buffer_size 32k;
large_client_header_buffers 4 32k;
client_max_body_size 8m;
sendfile on;
tcp_nopush on;
keepalive_timeout 60;
tcp_nodelay on;
fastcgi_connect_timeout 300;
fastcgi_send_timeout 300;
fastcgi_read_timeout 300;
fastcgi_buffer_size 64k;
fastcgi_buffers 4 64k;
fastcgi_busy_buffers_size 128k;
fastcgi_temp_file_write_size 128k;
server
{
listen 80;
server_name a.com;
index index.php;
root /data0/htdocs/a.com/www;
location / {
if (!-e $request_filename) {
rewrite ^/(.*)$ /index.php/$1 last;
break;
}
}
location ~ \.php {
fastcgi_pass 127.0.0.1:9000;
fastcgi_index index.php;
include fcgi.conf;
set $real_script_name $fastcgi_script_name;
if ($fastcgi_script_name ~ "^(. ?\.php)(/. )$") {
set $real_script_name $1;
set $path_info $2;
}
fastcgi_param script_filename $document_root$real_script_name;
fastcgi_param script_name $real_script_name;
fastcgi_param path_info $path_info;
}
}
}
The above is the detailed content of How to configure pathinfo mode in nginx. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1386
1386
 52
52
 How to configure cloud server domain name in nginx
Apr 14, 2025 pm 12:18 PM
How to configure cloud server domain name in nginx
Apr 14, 2025 pm 12:18 PM
How to configure an Nginx domain name on a cloud server: Create an A record pointing to the public IP address of the cloud server. Add virtual host blocks in the Nginx configuration file, specifying the listening port, domain name, and website root directory. Restart Nginx to apply the changes. Access the domain name test configuration. Other notes: Install the SSL certificate to enable HTTPS, ensure that the firewall allows port 80 traffic, and wait for DNS resolution to take effect.
 How to check nginx version
Apr 14, 2025 am 11:57 AM
How to check nginx version
Apr 14, 2025 am 11:57 AM
The methods that can query the Nginx version are: use the nginx -v command; view the version directive in the nginx.conf file; open the Nginx error page and view the page title.
 How to start nginx server
Apr 14, 2025 pm 12:27 PM
How to start nginx server
Apr 14, 2025 pm 12:27 PM
Starting an Nginx server requires different steps according to different operating systems: Linux/Unix system: Install the Nginx package (for example, using apt-get or yum). Use systemctl to start an Nginx service (for example, sudo systemctl start nginx). Windows system: Download and install Windows binary files. Start Nginx using the nginx.exe executable (for example, nginx.exe -c conf\nginx.conf). No matter which operating system you use, you can access the server IP
 How to check the name of the docker container
Apr 15, 2025 pm 12:21 PM
How to check the name of the docker container
Apr 15, 2025 pm 12:21 PM
You can query the Docker container name by following the steps: List all containers (docker ps). Filter the container list (using the grep command). Gets the container name (located in the "NAMES" column).
 How to check whether nginx is started
Apr 14, 2025 pm 01:03 PM
How to check whether nginx is started
Apr 14, 2025 pm 01:03 PM
How to confirm whether Nginx is started: 1. Use the command line: systemctl status nginx (Linux/Unix), netstat -ano | findstr 80 (Windows); 2. Check whether port 80 is open; 3. Check the Nginx startup message in the system log; 4. Use third-party tools, such as Nagios, Zabbix, and Icinga.
 How to run nginx apache
Apr 14, 2025 pm 12:33 PM
How to run nginx apache
Apr 14, 2025 pm 12:33 PM
To get Nginx to run Apache, you need to: 1. Install Nginx and Apache; 2. Configure the Nginx agent; 3. Start Nginx and Apache; 4. Test the configuration to ensure that you can see Apache content after accessing the domain name. In addition, you need to pay attention to other matters such as port number matching, virtual host configuration, and SSL/TLS settings.
 How to create a mirror in docker
Apr 15, 2025 am 11:27 AM
How to create a mirror in docker
Apr 15, 2025 am 11:27 AM
Steps to create a Docker image: Write a Dockerfile that contains the build instructions. Build the image in the terminal, using the docker build command. Tag the image and assign names and tags using the docker tag command.
 How to start containers by docker
Apr 15, 2025 pm 12:27 PM
How to start containers by docker
Apr 15, 2025 pm 12:27 PM
Docker container startup steps: Pull the container image: Run "docker pull [mirror name]". Create a container: Use "docker create [options] [mirror name] [commands and parameters]". Start the container: Execute "docker start [Container name or ID]". Check container status: Verify that the container is running with "docker ps".




