How to deploy your own django project with nginx+uwsgi
Step 1: Change the source
Enter the command to replace the Ubuntu download source
sudo nano /etc/apt/sources.list
Replace all the following with the original file, What I use here is Alibaba’s source, you can also change it to other sources.
deb http://mirrors.aliyun.com/ubuntu/ bionic main restricted deb http://mirrors.aliyun.com/ubuntu/ bionic-updates main restricted deb http://mirrors.aliyun.com/ubuntu/ bionic universe deb http://mirrors.aliyun.com/ubuntu/ bionic-updates universe deb http://mirrors.aliyun.com/ubuntu/ bionic multiverse deb http://mirrors.aliyun.com/ubuntu/ bionic-updates multiverse deb http://mirrors.aliyun.com/ubuntu/ bionic-backports main restricted universe multiverse deb http://mirrors.aliyun.com/ubuntu/ bionic-security main restricted deb http://mirrors.aliyun.com/ubuntu/ bionic-security universe deb [arch=amd64] https://mirrors.aliyun.com/docker-ce/linux/ubuntu bionic stable
分别输入以下命令,更新源 sudo apt update sudo apt upgrade
Step 2: Install related packages
1. Install python3
# 安装python3 sudo apt install python3 # 查看python安装路径: which python # 查看python版本:建议使用3.6之后的版本,因为其他的笔者没试过,笔者用的是3.6.9版本 python
2. Install openssh-server and net-tools
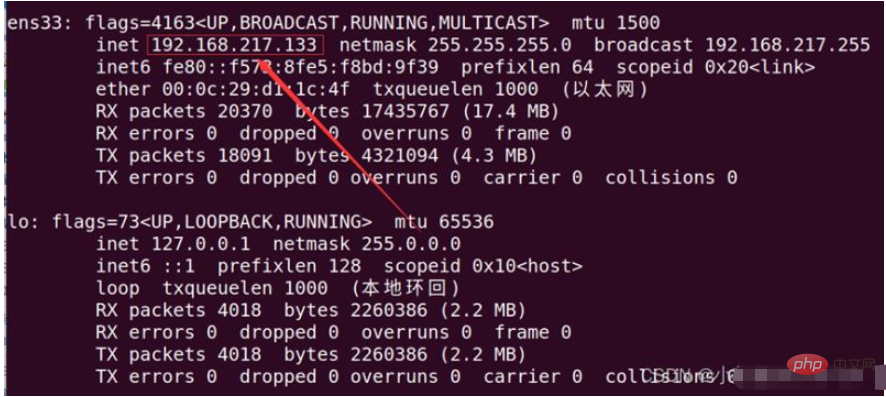
# 安装 openssh-server sudo apt install openssh-server #开启: sudo service ssh start # 安装net-tools sudo apt install net-tools # 查看虚拟机ip: ifconfig
as shown below As shown, it is our virtual machine IP
Install the running environment of django
#安装django运行环境: sudo apt install virtualenv # 创建环境 virtualenv --python=/usr/bin/python3 myblog # 进入环境: cd myblog # 激活环境: source bin/activate
Install django:pip3 install Django
Create project:django-admin.py startproject blog
After activating and creating the project, it will basically look like the picture below
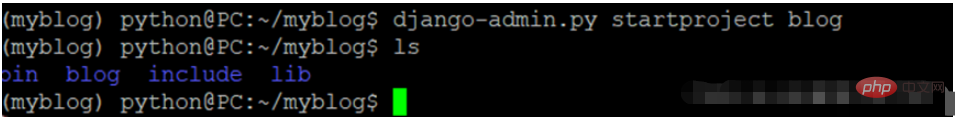
# 进入到blog中安装 uwsgi: pip3 install uwsgi
Step 3: Write a test file and test run
1. Write a test file
After installation, we will write a test file to test us The way the project is run is the same as the actual project. Here I use the nano editing and writing method. You can also use vim. The method is not limited. If you can create and write, you can write the command:
sudo nano test.py
Required The written file content is:
def application(env,start_response):
start_response('200 ok',[('Content-Type','text/html')])
return [b"Hello World"]2. Test run
The test command is: uwsgi --http :8000 --wsgi-file test.py
After pressing Enter, we enter the IP and port number in the browser. Mine is 192.168.217.133:8000. When I opened it in the browser, I found the following error.
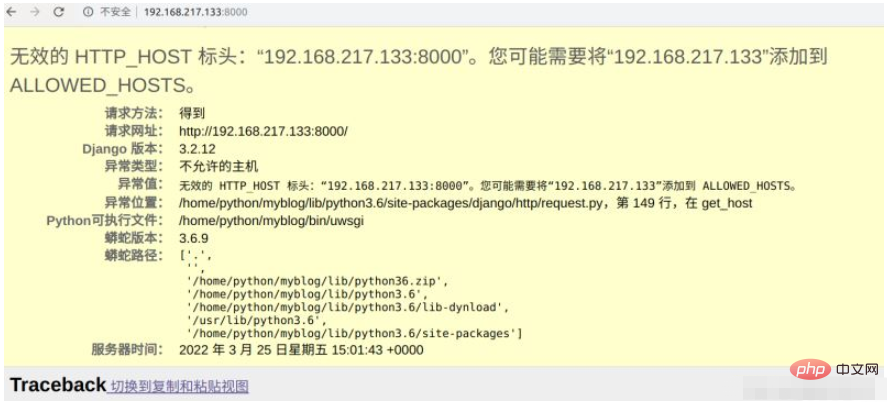
For this error, we only need to open the settings.py file of the project file, add the address of our virtual machine in ALLOWED_HOSTS, and it will be ok, and then we will test and run , found to be normal, the web page outputs hello world. This shows that uwsgi can run the test file normally.
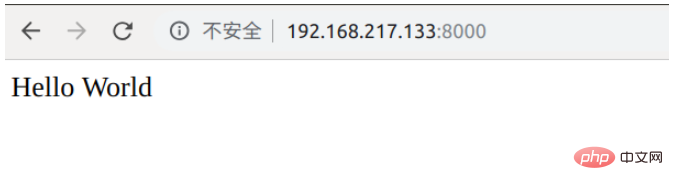
But we are not running the test.py file, we are running our own django project. Here we need to modify the previous command to: uwsgi - -http :8000 --module blog.wsgi
Step 4: Introduce nginx
1. Install and start nginx
In order to avoid not entering the port number when entering the ip It can also be used normally. We introduce lightweight nginx. Here we use the command line to install and start nginx
Installation: sudo apt install nginx
Start: sudo service nginx start
2. Write the conf configuration file
Enter the command: sudo nano /etc/nginx/sites-available/blog_nginx.conf
Create a new conf file and write the following content. Change all the paths involved in it to the path of your own project:
upstream django {
# server unix:///home/python/myblog/blog/blog.sock; # 这里的路径改为你自己项目路径
server 127.0.0.1:8001; # for a web port socket (we'll use this first)
}
server {
listen 8000;
server_name 192.168.217.133; # 将这里的ip地址改为你自己的虚拟机或者服务器地址
charset utf-8;
client_max_body_size 75M; # adjust to taste
location /media {
alias /home/python/myblog/blog/media; # your Django project's media files - amend as required
}
location /static {
alias /home/python/myblog/blog/static; # your Django project's static files - amend as required
}
location / {
uwsgi_pass django;
include /home/python/myblog/blog/uwsgi_params; # the uwsgi_params file you installed
}
}After creating the file, we need to create the file A soft link, you need to enter the following command:
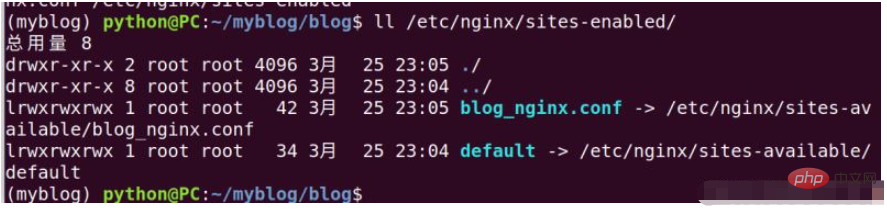
sudo ln -s /etc/nginx/sites-available/blog_nginx.conf /etc/nginx/sites-enabled
After completion, we can use the command ll /etc/nginx/sites-enabled/ to check whether the settings are correct. Refer to the figure below
sudo nano uwsgi_params
uwsgi_param QUERY_STRING $query_string; uwsgi_param REQUEST_METHOD $request_method; uwsgi_param CONTENT_TYPE $content_type; uwsgi_param CONTENT_LENGTH $content_length; uwsgi_param REQUEST_URI $request_uri; uwsgi_param PATH_INFO $document_uri; uwsgi_param DOCUMENT_ROOT $document_root; uwsgi_param SERVER_PROTOCOL $server_protocol; uwsgi_param REQUEST_SCHEME $scheme; uwsgi_param HTTPS $https if_not_empty; uwsgi_param REMOTE_ADDR $remote_addr; uwsgi_param REMOTE_PORT $remote_port; uwsgi_param SERVER_PORT $server_port; uwsgi_param SERVER_NAME $server_name;
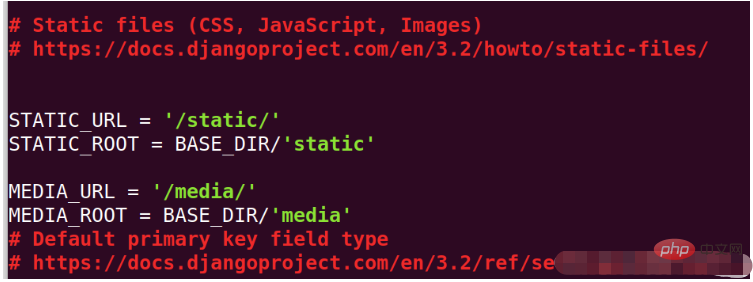
python manage. py collectstatic
mkdir media
server unix:///home/python/myblog/blog.sock; # for a file socket
# server 127.0.0.1:8001; # for a web port socket (we'll use this first)
保存退出,重启nginx:sudo service nginx restart
将uwsgi参数套节字改为blog.sock
uwsgi --socket blog.sock --wsgi-file test.py
回到浏览器输入:192.168.217.133:8000得到502:如图
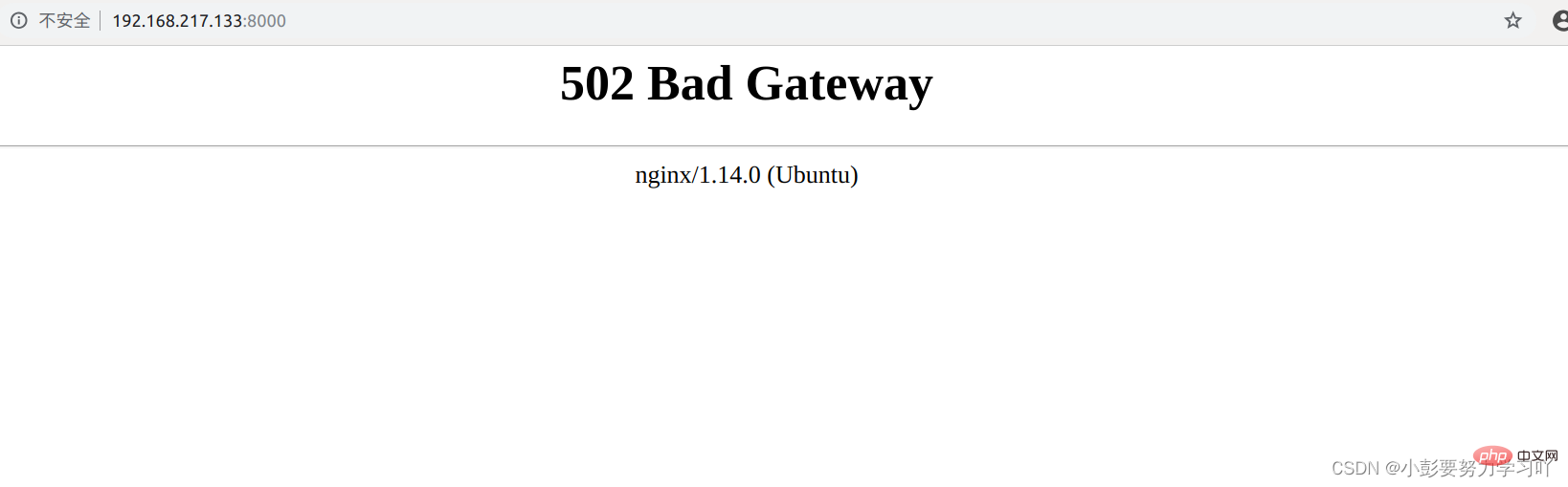
我们查看一下错误日志,发现是因为权限问题,解决办法,在命令行后面加入--chmod=666
uwsgi --socket blog.sock --wsgi-file test.py --chmod=666
运行之后发现没有问题,并且正常显示Hello World界面。
现在我们运行django项目,命令为:uwsgi --socket blog.sock --module blog.wsgi --chmod=666
刷新192.168.217.133:8000得到django的基础页面。
目前可以说明nginx和uwsgi管道通信正常。
第六步:将项目改为后台运行
创建一个uwsgi的配置文件:sudo nano blog_uwsgi.ini
写入一下内容,将其中的路径改为自己的项目路径
# mysite_uwsgi.ini file [uwsgi] # Django-related settings # the base directory (full path) chdir = /home/python/myblog/blog # Django's wsgi file module = blog.wsgi # the virtualenv (full path) home = /home/python/myblog # process-related settings # master master = true # maximum number of worker processes processes = 10 # the socket (use the full path to be safe socket = /home/python/myblog/blog/mysite.sock # ... with appropriate permissions - may be needed chmod-socket = 664 # clear environment on exit vacuum = true # daemonize uwsgi and write messages into given log daemonize = /home/python/myblog/blog/uwsgi.log
保存退出并且启动配置文件,命令为:uwsgi --ini blog_uwsgi.ini
我们可以查看一下后台进程,是否正常启动,输入:ps aux
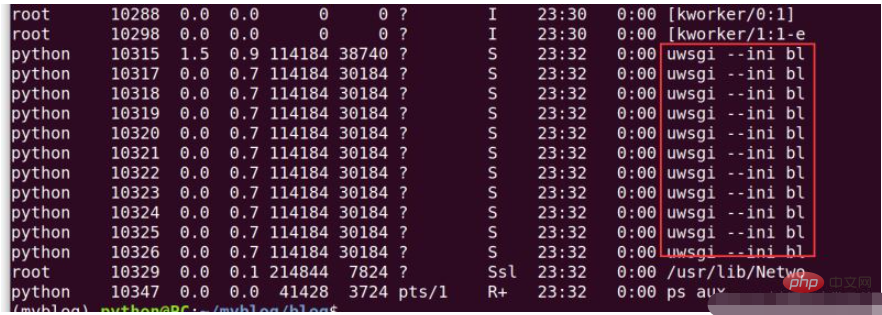
最后回到nginx配置文件中,将监听端口改为80,重启nginx即可。在浏览器中输192.168.217.133得到django页面结果,表示项目运行正常。
The above is the detailed content of How to deploy your own django project with nginx+uwsgi. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1386
1386
 52
52
 How to configure cloud server domain name in nginx
Apr 14, 2025 pm 12:18 PM
How to configure cloud server domain name in nginx
Apr 14, 2025 pm 12:18 PM
How to configure an Nginx domain name on a cloud server: Create an A record pointing to the public IP address of the cloud server. Add virtual host blocks in the Nginx configuration file, specifying the listening port, domain name, and website root directory. Restart Nginx to apply the changes. Access the domain name test configuration. Other notes: Install the SSL certificate to enable HTTPS, ensure that the firewall allows port 80 traffic, and wait for DNS resolution to take effect.
 How to check whether nginx is started
Apr 14, 2025 pm 01:03 PM
How to check whether nginx is started
Apr 14, 2025 pm 01:03 PM
How to confirm whether Nginx is started: 1. Use the command line: systemctl status nginx (Linux/Unix), netstat -ano | findstr 80 (Windows); 2. Check whether port 80 is open; 3. Check the Nginx startup message in the system log; 4. Use third-party tools, such as Nagios, Zabbix, and Icinga.
 How to check nginx version
Apr 14, 2025 am 11:57 AM
How to check nginx version
Apr 14, 2025 am 11:57 AM
The methods that can query the Nginx version are: use the nginx -v command; view the version directive in the nginx.conf file; open the Nginx error page and view the page title.
 How to create a mirror in docker
Apr 15, 2025 am 11:27 AM
How to create a mirror in docker
Apr 15, 2025 am 11:27 AM
Steps to create a Docker image: Write a Dockerfile that contains the build instructions. Build the image in the terminal, using the docker build command. Tag the image and assign names and tags using the docker tag command.
 How to start nginx server
Apr 14, 2025 pm 12:27 PM
How to start nginx server
Apr 14, 2025 pm 12:27 PM
Starting an Nginx server requires different steps according to different operating systems: Linux/Unix system: Install the Nginx package (for example, using apt-get or yum). Use systemctl to start an Nginx service (for example, sudo systemctl start nginx). Windows system: Download and install Windows binary files. Start Nginx using the nginx.exe executable (for example, nginx.exe -c conf\nginx.conf). No matter which operating system you use, you can access the server IP
 How to run nginx apache
Apr 14, 2025 pm 12:33 PM
How to run nginx apache
Apr 14, 2025 pm 12:33 PM
To get Nginx to run Apache, you need to: 1. Install Nginx and Apache; 2. Configure the Nginx agent; 3. Start Nginx and Apache; 4. Test the configuration to ensure that you can see Apache content after accessing the domain name. In addition, you need to pay attention to other matters such as port number matching, virtual host configuration, and SSL/TLS settings.
 How to check the name of the docker container
Apr 15, 2025 pm 12:21 PM
How to check the name of the docker container
Apr 15, 2025 pm 12:21 PM
You can query the Docker container name by following the steps: List all containers (docker ps). Filter the container list (using the grep command). Gets the container name (located in the "NAMES" column).
 How to check whether nginx is started?
Apr 14, 2025 pm 12:48 PM
How to check whether nginx is started?
Apr 14, 2025 pm 12:48 PM
In Linux, use the following command to check whether Nginx is started: systemctl status nginx judges based on the command output: If "Active: active (running)" is displayed, Nginx is started. If "Active: inactive (dead)" is displayed, Nginx is stopped.




