How to use weak references in Python
Background
Before we start discussing weak references (weakref), let’s first take a look at what is a weak reference? What exactly does it do?
Suppose we have a multi-threaded program that processes application data concurrently:
1 2 3 4 |
|
Application data Data is uniquely identified by a key, and the same data may be accessed by multiple threads at the same time. Since Data requires a lot of system resources, the cost of creation and consumption is high. We hope that Data only maintains one copy in the program, and does not want to create it repeatedly even if it is accessed by multiple threads at the same time.
To this end, we try to design a caching middleware Cacher:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 |
|
Cacher internally uses a dict object to cache the created Data copy, and provides a get method for obtaining application data Data. When the get method obtains data, it first checks the cache dictionary. If the data already exists, it will be returned directly; if the data does not exist, it will create one and save it in the dictionary. Therefore, the data is entered into the cache dictionary after it is first created. If other threads access it at the same time later, the same copy in the cache will be used.
Feels very good! But the fly in the ointment is: Cacher has the risk of resource leakage!
Because once Data is created, it is stored in the cache dictionary and will never be released! In other words, the program's resources, such as memory, will continue to grow and may eventually explode. Therefore, we hope that a piece of data can be automatically released after all threads no longer access it.
We can maintain the number of data references in Cacher, and the get method automatically accumulates this count. At the same time, a new remove method is provided for releasing data. It first decrements the number of references and deletes the data from the cache field when the number of references drops to zero.
The thread calls the get method to obtain the data. After the data is used up, the remove method needs to be called to release it. Cacher is equivalent to implementing the reference counting method itself, which is too troublesome! Doesn’t Python have a built-in garbage collection mechanism? Why does the application need to implement it itself?
The main crux of the conflict lies in Cacher's cache dictionary: as a middleware, it does not use data objects itself, so theoretically it should not have a reference to the data. Is there any black technology that can find the target object without generating a reference? We know that assignments generate references!
Typical usage
At this time, weak reference (weakref) makes a grand appearance! A weak reference is a special object that can be associated with the target object without generating a reference.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 |
|
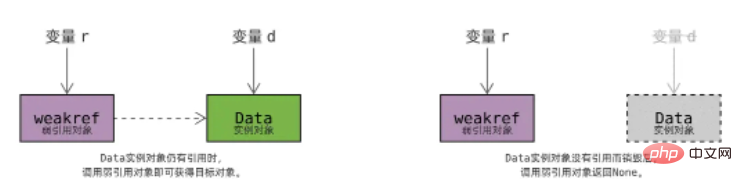
In this way, we only need to change the Cacher cache dictionary to save weak references, and the problem will be solved!
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 |
|
Since the cache dictionary only saves weak references to Data objects, Cacher will not affect the reference count of Data objects. When all threads have finished using the data, the reference count drops to zero and is released.
In fact, it is very common to use dictionaries to cache data objects. For this reason, the weakref module also provides two dictionary objects that only save weak references:
- ##weakref. WeakKeyDictionary , the key only saves the mapping class of weak references (once the key no longer has a strong reference, the key-value pair entry will automatically disappear);
- weakref.WeakValueDictionary , the value only saves weak references Mapping class (once the value no longer has a strong reference, the key-value pair entry will automatically disappear);
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 |
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 |
|
- ##Include/weakrefobject.h The header file contains the object structure and some macro definitions;
- The Objects/weakrefobject.c source file contains weak reference type objects and their method definitions;
- Let’s take a look first The field structure of the weak reference object is defined in lines 10-41 of the Include/weakrefobject.h header file:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 |
|
It can be seen that the PyWeakReference structure is the body of the weak reference object. It is a fixed-length object. In addition to the fixed header, there are 5 fields:

- wr_callback, pointing to a callable object, will be called when the referenced object is destroyed;
hash ,缓存被引用对象的哈希值;
wr_prev 和 wr_next 分别是前后向指针,用于将弱引用对象组织成双向链表;
结合代码中的注释,我们知道:

弱引用对象通过 wr_object 字段关联被引用的对象,如上图虚线箭头所示;
一个对象可以同时被多个弱引用对象关联,图中的 Data 实例对象被两个弱引用对象关联;
所有关联同一个对象的弱引用,被组织成一个双向链表,链表头保存在被引用对象中,如上图实线箭头所示;
当一个对象被销毁后,Python 将遍历它的弱引用链表,逐一处理:
将 wr_object 字段设为 None ,弱引用对象再被调用将返回 None ,调用者便知道对象已经被销毁了;
执行回调函数 wr_callback (如有);
由此可见,弱引用的工作原理其实就是设计模式中的 观察者模式( Observer )。当对象被销毁,它的所有弱引用对象都得到通知,并被妥善处理。
实现细节
掌握弱引用的基本原理,足以让我们将其用好。如果您对源码感兴趣,还可以再深入研究它的一些实现细节。
前面我们提到,对同一对象的所有弱引用,被组织成一个双向链表,链表头保存在对象中。由于能够创建弱引用的对象类型是多种多样的,很难由一个固定的结构体来表示。因此,Python 在类型对象中提供一个字段 tp_weaklistoffset ,记录弱引用链表头指针在实例对象中的偏移量。

由此一来,对于任意对象 o ,我们只需通过 ob_type 字段找到它的类型对象 t ,再根据 t 中的 tp_weaklistoffset 字段即可找到对象 o 的弱引用链表头。
Python 在 Include/objimpl.h 头文件中提供了两个宏定义:
1 2 3 4 5 |
|
PyType_SUPPORTS_WEAKREFS 用于判断类型对象是否支持弱引用,仅当 tp_weaklistoffset 大于零才支持弱引用,内置对象 list 等都不支持弱引用;
PyObject_GET_WEAKREFS_LISTPTR 用于取出一个对象的弱引用链表头,它先通过 Py_TYPE 宏找到类型对象 t ,再找通过 tp_weaklistoffset 字段确定偏移量,最后与对象地址相加即可得到链表头字段的地址;
我们创建弱引用时,需要调用弱引用类型对象 weakref 并将被引用对象 d 作为参数传进去。弱引用类型对象 weakref 是所有弱引用实例对象的类型,是一个全局唯一的类型对象,定义在 Objects/weakrefobject.c 中,即:_PyWeakref_RefType(第 350 行)。

根据对象模型中学到的知识,Python 调用一个对象时,执行的是其类型对象中的 tp_call 函数。因此,调用弱引用类型对象 weakref 时,执行的是 weakref 的类型对象,也就是 type 的 tp_call 函数。tp_call 函数则回过头来调用 weakref 的 tp_new 和 tp_init 函数,其中 tp_new 为实例对象分配内存,而 tp_init 则负责初始化实例对象。
回到 Objects/weakrefobject.c 源文件,可以看到 PyWeakref_RefType 的 tp_new 字段被初始化成 *weakref___new_* (第 276 行)。该函数的主要处理逻辑如下:
解析参数,得到被引用的对象(第 282 行);
调用 PyType_SUPPORTS_WEAKREFS 宏判断被引用的对象是否支持弱引用,不支持就抛异常(第 286 行);
调用 GET_WEAKREFS_LISTPTR 行取出对象的弱引用链表头字段,为方便插入返回的是一个二级指针(第 294 行);
调用 get_basic_refs 取出链表最前那个 callback 为空 基础弱引用对象(如有,第 295 行);
如果 callback 为空,而且对象存在 callback 为空的基础弱引用,则复用该实例直接将其返回(第 296 行);
如果不能复用,调用 tp_alloc 函数分配内存、完成字段初始化,并插到对象的弱引用链表(第 309 行);
If the callback is empty, insert it directly into the front of the linked list to facilitate subsequent reuse (see point 4);
If callback is not empty. Insert it after the basic weak reference object (if any) to ensure that the basic weak reference is at the head of the linked list for easy access;
When an object is recycled , the tp_dealloc function will call the PyObject_ClearWeakRefs function to clean up its weak references. This function takes out the weak reference list of the object, then traverses it one by one, cleans the wr_object field and executes the wr_callback callback function (if any). The specific details will not be expanded. If you are interested, you can check the source code in Objects/weakrefobject.c, located at line 880.
Okay, after studying this section, we have thoroughly mastered the knowledge related to weak references. Weak references can manage the target object without generating a reference count, and are often used in frameworks and middleware. Weak references look magical, but in fact the design principle is a very simple observer pattern. After the weak reference object is created, it is inserted into a linked list maintained by the target object, and the destruction event of the object is observed (subscribed).
The above is the detailed content of How to use weak references in Python. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1378
1378
 52
52
 How to use Debian Apache logs to improve website performance
Apr 12, 2025 pm 11:36 PM
How to use Debian Apache logs to improve website performance
Apr 12, 2025 pm 11:36 PM
This article will explain how to improve website performance by analyzing Apache logs under the Debian system. 1. Log Analysis Basics Apache log records the detailed information of all HTTP requests, including IP address, timestamp, request URL, HTTP method and response code. In Debian systems, these logs are usually located in the /var/log/apache2/access.log and /var/log/apache2/error.log directories. Understanding the log structure is the first step in effective analysis. 2. Log analysis tool You can use a variety of tools to analyze Apache logs: Command line tools: grep, awk, sed and other command line tools.
 Python: Games, GUIs, and More
Apr 13, 2025 am 12:14 AM
Python: Games, GUIs, and More
Apr 13, 2025 am 12:14 AM
Python excels in gaming and GUI development. 1) Game development uses Pygame, providing drawing, audio and other functions, which are suitable for creating 2D games. 2) GUI development can choose Tkinter or PyQt. Tkinter is simple and easy to use, PyQt has rich functions and is suitable for professional development.
 PHP and Python: Comparing Two Popular Programming Languages
Apr 14, 2025 am 12:13 AM
PHP and Python: Comparing Two Popular Programming Languages
Apr 14, 2025 am 12:13 AM
PHP and Python each have their own advantages, and choose according to project requirements. 1.PHP is suitable for web development, especially for rapid development and maintenance of websites. 2. Python is suitable for data science, machine learning and artificial intelligence, with concise syntax and suitable for beginners.
 How debian readdir integrates with other tools
Apr 13, 2025 am 09:42 AM
How debian readdir integrates with other tools
Apr 13, 2025 am 09:42 AM
The readdir function in the Debian system is a system call used to read directory contents and is often used in C programming. This article will explain how to integrate readdir with other tools to enhance its functionality. Method 1: Combining C language program and pipeline First, write a C program to call the readdir function and output the result: #include#include#include#includeintmain(intargc,char*argv[]){DIR*dir;structdirent*entry;if(argc!=2){
 The role of Debian Sniffer in DDoS attack detection
Apr 12, 2025 pm 10:42 PM
The role of Debian Sniffer in DDoS attack detection
Apr 12, 2025 pm 10:42 PM
This article discusses the DDoS attack detection method. Although no direct application case of "DebianSniffer" was found, the following methods can be used for DDoS attack detection: Effective DDoS attack detection technology: Detection based on traffic analysis: identifying DDoS attacks by monitoring abnormal patterns of network traffic, such as sudden traffic growth, surge in connections on specific ports, etc. This can be achieved using a variety of tools, including but not limited to professional network monitoring systems and custom scripts. For example, Python scripts combined with pyshark and colorama libraries can monitor network traffic in real time and issue alerts. Detection based on statistical analysis: By analyzing statistical characteristics of network traffic, such as data
 Python and Time: Making the Most of Your Study Time
Apr 14, 2025 am 12:02 AM
Python and Time: Making the Most of Your Study Time
Apr 14, 2025 am 12:02 AM
To maximize the efficiency of learning Python in a limited time, you can use Python's datetime, time, and schedule modules. 1. The datetime module is used to record and plan learning time. 2. The time module helps to set study and rest time. 3. The schedule module automatically arranges weekly learning tasks.
 Nginx SSL Certificate Update Debian Tutorial
Apr 13, 2025 am 07:21 AM
Nginx SSL Certificate Update Debian Tutorial
Apr 13, 2025 am 07:21 AM
This article will guide you on how to update your NginxSSL certificate on your Debian system. Step 1: Install Certbot First, make sure your system has certbot and python3-certbot-nginx packages installed. If not installed, please execute the following command: sudoapt-getupdatesudoapt-getinstallcertbotpython3-certbot-nginx Step 2: Obtain and configure the certificate Use the certbot command to obtain the Let'sEncrypt certificate and configure Nginx: sudocertbot--nginx Follow the prompts to select
 How to configure HTTPS server in Debian OpenSSL
Apr 13, 2025 am 11:03 AM
How to configure HTTPS server in Debian OpenSSL
Apr 13, 2025 am 11:03 AM
Configuring an HTTPS server on a Debian system involves several steps, including installing the necessary software, generating an SSL certificate, and configuring a web server (such as Apache or Nginx) to use an SSL certificate. Here is a basic guide, assuming you are using an ApacheWeb server. 1. Install the necessary software First, make sure your system is up to date and install Apache and OpenSSL: sudoaptupdatesudoaptupgradesudoaptinsta




