How to import nginx logs into elasticsearch
Collect nginx logs through filebeat and transfer them to logstash. After processing by logstash, they are written to elasticsearch. Filebeat is only responsible for collection work, while logstash completes log formatting, data replacement, splitting, and index creation after writing logs to elasticsearch.
1. Configure nginx log format
log_format main '$remote_addr $http_x_forwarded_for [$time_local] $server_name $request '
'$status $body_bytes_sent $http_referer '
'"$http_user_agent" '
'"$connection" '
'"$http_cookie" '
'$request_time '
'$upstream_response_time';2. Install and configure filebeat, enable nginx module
tar -zxvf filebeat-6.2.4-linux-x86_64.tar.gz -c /usr/local cd /usr/local;ln -s filebeat-6.2.4-linux-x86_64 filebeat cd /usr/local/filebeat
Enable nginx module
./filebeat modules enable nginx
View module
./filebeat modules list
Create configuration file
vim /usr/local/filebeat/blog_module_logstash.yml filebeat.modules: - module: nginx access: enabled: true var.paths: ["/home/weblog/blog.cnfol.com_access.log"] #error: # enabled: true # var.paths: ["/home/weblogerr/blog.cnfol.com_error.log"] output.logstash: hosts: ["192.168.15.91:5044"]
Start filebeat
./filebeat -c blog_module_logstash.yml -e
3. Configure logstash
tar -zxvf logstash-6.2.4.tar.gz /usr/local cd /usr/local;ln -s logstash-6.2.4 logstash 创建一个nginx日志的pipline文件 cd /usr/local/logstash
logstash built-in template directory
vendor/bundle/jruby/2.3.0/gems/logstash-patterns-core-4.1.2/patterns
Edit grok-patterns to add a regular pattern that supports multiple IPs
forword (?:%{ipv4}[,]?[ ]?)+|%{word}Official grok
#Create logstash pipline Configuration file
#input {
# stdin {}
#}
# 从filebeat接受数据
input {
beats {
port => 5044
host => "0.0.0.0"
}
}
filter {
# 添加一个调试的开关
mutate{add_field => {"[@metadata][debug]"=>true}}
grok {
# 过滤nginx日志
#match => { "message" => "%{nginxaccess_test2}" }
#match => { "message" => '%{iporhost:clientip} # (?<http_x_forwarded_for>[^\#]*) # \[%{httpdate:[@metadata][webtime]}\] # %{notspace:hostname} # %{word:verb} %{uripathparam:request} http/%{number:httpversion} # %{number:response} # (?:%{number:bytes}|-) # (?:"(?:%{notspace:referrer}|-)"|%{notspace:referrer}|-) # (?:"(?<http_user_agent>[^#]*)") # (?:"(?:%{number:connection}|-)"|%{number:connection}|-) # (?:"(?<cookies>[^#]*)") # %{number:request_time:float} # (?:%{number:upstream_response_time:float}|-)' }
#match => { "message" => '(?:%{iporhost:clientip}|-) (?:%{two_ip:http_x_forwarded_for}|%{ipv4:http_x_forwarded_for}|-) \[%{httpdate:[@metadata][webtime]}\] (?:%{hostname:hostname}|-) %{word:method} %{uripathparam:request} http/%{number:httpversion} %{number:response} (?:%{number:bytes}|-) (?:"(?:%{notspace:referrer}|-)"|%{notspace:referrer}|-) %{qs:agent} (?:"(?:%{number:connection}|-)"|%{number:connection}|-) (?:"(?<cookies>[^#]*)") %{number:request_time:float} (?:%{number:upstream_response_time:float}|-)' }
match => { "message" => '(?:%{iporhost:clientip}|-) %{forword:http_x_forwarded_for} \[%{httpdate:[@metadata][webtime]}\] (?:%{hostname:hostname}|-) %{word:method} %{uripathparam:request} http/%{number:httpversion} %{number:response} (?:%{number:bytes}|-) (?:"(?:%{notspace:referrer}|-)"|%{notspace:referrer}|-) %{qs:agent} (?:"(?:%{number:connection}|-)"|%{number:connection}|-) %{qs:cookie} %{number:request_time:float} (?:%{number:upstream_response_time:float}|-)' }
}
# 将默认的@timestamp(beats收集日志的时间)的值赋值给新字段@read_tiimestamp
ruby {
#code => "event.set('@read_timestamp',event.get('@timestamp'))"
#将时区改为东8区
code => "event.set('@read_timestamp',event.get('@timestamp').time.localtime + 8*60*60)"
}
# 将nginx的日志记录时间格式化
# 格式化时间 20/may/2015:21:05:56 +0000
date {
locale => "en"
match => ["[@metadata][webtime]","dd/mmm/yyyy:hh:mm:ss z"]
}
# 将bytes字段由字符串转换为数字
mutate {
convert => {"bytes" => "integer"}
}
# 将cookie字段解析成一个json
#mutate {
# gsub => ["cookies",'\;',',']
#}
# 如果有使用到cdn加速http_x_forwarded_for会有多个ip,第一个ip是用户真实ip
if[http_x_forwarded_for] =~ ", "{
ruby {
code => 'event.set("http_x_forwarded_for", event.get("http_x_forwarded_for").split(",")[0])'
}
}
# 解析ip,获得ip的地理位置
geoip {
source => "http_x_forwarded_for"
# # 只获取ip的经纬度、国家、城市、时区
fields => ["location","country_name","city_name","region_name"]
}
# 将agent字段解析,获得浏览器、系统版本等具体信息
useragent {
source => "agent"
target => "useragent"
}
#指定要删除的数据
#mutate{remove_field=>["message"]}
# 根据日志名设置索引名的前缀
ruby {
code => 'event.set("@[metadata][index_pre]",event.get("source").split("/")[-1])'
}
# 将@timestamp 格式化为2019.04.23
ruby {
code => 'event.set("@[metadata][index_day]",event.get("@timestamp").time.localtime.strftime("%y.%m.%d"))'
}
# 设置输出的默认索引名
mutate {
add_field => {
#"[@metadata][index]" => "%{@[metadata][index_pre]}_%{+yyyy.mm.dd}"
"[@metadata][index]" => "%{@[metadata][index_pre]}_%{@[metadata][index_day]}"
}
}
# 将cookies字段解析成json
# mutate {
# gsub => [
# "cookies", ";", ",",
# "cookies", "=", ":"
# ]
# #split => {"cookies" => ","}
# }
# json_encode {
# source => "cookies"
# target => "cookies_json"
# }
# mutate {
# gsub => [
# "cookies_json", ',', '","',
# "cookies_json", ':', '":"'
# ]
# }
# json {
# source => "cookies_json"
# target => "cookies2"
# }
# 如果grok解析存在错误,将错误独立写入一个索引
if "_grokparsefailure" in [tags] {
#if "_dateparsefailure" in [tags] {
mutate {
replace => {
#"[@metadata][index]" => "%{@[metadata][index_pre]}_failure_%{+yyyy.mm.dd}"
"[@metadata][index]" => "%{@[metadata][index_pre]}_failure_%{@[metadata][index_day]}"
}
}
# 如果不存在错误就删除message
}else{
mutate{remove_field=>["message"]}
}
}
output {
if [@metadata][debug]{
# 输出到rubydebuyg并输出metadata
stdout{codec => rubydebug{metadata => true}}
}else{
# 将输出内容转换成 "."
stdout{codec => dots}
# 将输出到指定的es
elasticsearch {
hosts => ["192.168.15.160:9200"]
index => "%{[@metadata][index]}"
document_type => "doc"
}
}
}Start logstash
nohup bin/logstash -f test_pipline2.conf &
The above is the detailed content of How to import nginx logs into elasticsearch. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1377
1377
 52
52
 How to allow external network access to tomcat server
Apr 21, 2024 am 07:22 AM
How to allow external network access to tomcat server
Apr 21, 2024 am 07:22 AM
To allow the Tomcat server to access the external network, you need to: modify the Tomcat configuration file to allow external connections. Add a firewall rule to allow access to the Tomcat server port. Create a DNS record pointing the domain name to the Tomcat server public IP. Optional: Use a reverse proxy to improve security and performance. Optional: Set up HTTPS for increased security.
 How to generate URL from html file
Apr 21, 2024 pm 12:57 PM
How to generate URL from html file
Apr 21, 2024 pm 12:57 PM
Converting an HTML file to a URL requires a web server, which involves the following steps: Obtain a web server. Set up a web server. Upload HTML file. Create a domain name. Route the request.
 How to deploy nodejs project to server
Apr 21, 2024 am 04:40 AM
How to deploy nodejs project to server
Apr 21, 2024 am 04:40 AM
Server deployment steps for a Node.js project: Prepare the deployment environment: obtain server access, install Node.js, set up a Git repository. Build the application: Use npm run build to generate deployable code and dependencies. Upload code to the server: via Git or File Transfer Protocol. Install dependencies: SSH into the server and use npm install to install application dependencies. Start the application: Use a command such as node index.js to start the application, or use a process manager such as pm2. Configure a reverse proxy (optional): Use a reverse proxy such as Nginx or Apache to route traffic to your application
 Can nodejs be accessed from the outside?
Apr 21, 2024 am 04:43 AM
Can nodejs be accessed from the outside?
Apr 21, 2024 am 04:43 AM
Yes, Node.js can be accessed from the outside. You can use the following methods: Use Cloud Functions to deploy the function and make it publicly accessible. Use the Express framework to create routes and define endpoints. Use Nginx to reverse proxy requests to Node.js applications. Use Docker containers to run Node.js applications and expose them through port mapping.
 How to deploy and maintain a website using PHP
May 03, 2024 am 08:54 AM
How to deploy and maintain a website using PHP
May 03, 2024 am 08:54 AM
To successfully deploy and maintain a PHP website, you need to perform the following steps: Select a web server (such as Apache or Nginx) Install PHP Create a database and connect PHP Upload code to the server Set up domain name and DNS Monitoring website maintenance steps include updating PHP and web servers, and backing up the website , monitor error logs and update content.
 How to use Fail2Ban to protect your server from brute force attacks
Apr 27, 2024 am 08:34 AM
How to use Fail2Ban to protect your server from brute force attacks
Apr 27, 2024 am 08:34 AM
An important task for Linux administrators is to protect the server from illegal attacks or access. By default, Linux systems come with well-configured firewalls, such as iptables, Uncomplicated Firewall (UFW), ConfigServerSecurityFirewall (CSF), etc., which can prevent a variety of attacks. Any machine connected to the Internet is a potential target for malicious attacks. There is a tool called Fail2Ban that can be used to mitigate illegal access on the server. What is Fail2Ban? Fail2Ban[1] is an intrusion prevention software that protects servers from brute force attacks. It is written in Python programming language
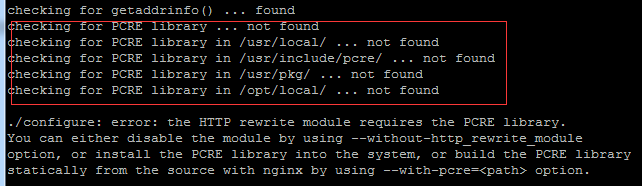 Come with me to learn Linux and install Nginx
Apr 28, 2024 pm 03:10 PM
Come with me to learn Linux and install Nginx
Apr 28, 2024 pm 03:10 PM
Today, I will lead you to install Nginx in a Linux environment. The Linux system used here is CentOS7.2. Prepare the installation tools 1. Download Nginx from the Nginx official website. The version used here is: 1.13.6.2. Upload the downloaded Nginx to Linux. Here, the /opt/nginx directory is used as an example. Run "tar-zxvfnginx-1.13.6.tar.gz" to decompress. 3. Switch to the /opt/nginx/nginx-1.13.6 directory and run ./configure for initial configuration. If the following prompt appears, it means that PCRE is not installed on the machine, and Nginx needs to
 Several points to note when building high availability with keepalived+nginx
Apr 23, 2024 pm 05:50 PM
Several points to note when building high availability with keepalived+nginx
Apr 23, 2024 pm 05:50 PM
After yum installs keepalived, configure the keepalived configuration file. Note that in the keepalived configuration files of master and backup, the network card name is the network card name of the current machine. VIP is selected as an available IP. It is usually used in high availability and LAN environments. There are many, so this VIP is an intranet IP in the same network segment as the two machines. If used in an external network environment, it does not matter whether it is on the same network segment, as long as the client can access it. Stop the nginx service and start the keepalived service. You will see that keepalived pulls the nginx service to start. If it cannot start and fails, it is basically a problem with the configuration files and scripts, or a prevention problem.




