 Backend Development
Backend Development
 Python Tutorial
Python Tutorial
 How to use Python Celery to dynamically add scheduled tasks
How to use Python Celery to dynamically add scheduled tasks
How to use Python Celery to dynamically add scheduled tasks
1. Background
In actual work, there will be some time-consuming asynchronous tasks that need to be scheduled, such as sending emails, pulling data, and executing scheduled tasks. Script
The main idea of implementing scheduling through celery is to introduce the middleman redis, start workers for task execution, and celery-beat for scheduled task data storage
2. Official document of Celery dynamically adding scheduled tasks
celery documentation: https://docs.celeryproject.org/en/latest/userguide/periodic-tasks.html#beat-custom-schedulers
celery custom scheduling class description:
Custom scheduler classes can be specified on the command line (--scheduler parameter)
django-celery-beat documentation: https://pypi.org/project/django-celery-beat/
Instructions about the django-celery-beat plugin:
This extension enables you to store periodic task schedules in the database. Periodic tasks can be managed from the Django admin interface, where you can Create, edit and delete periodic tasks and how often they should run
3. Celery is simple and practical
3.1 Basic environment configuration
1. Install the latest version Django
pip3 install django #当前我安装的版本是 3.0.6
2. Create project
django-admin startproject typeidea django-admin startapp blog
3. Install celery
pip3 install django-celery pip3 install -U Celery pip3 install "celery[librabbitmq,redis,auth,msgpack]" pip3 install django-celery-beat # 用于动态添加定时任务 pip3 install django-celery-results pip3 install redis
3.2 Test using Celery application
1. Create Blog directory, create new tasks.py
First create a blog folder in the Django project, and create the tasks.py module under the blog folder, as follows:
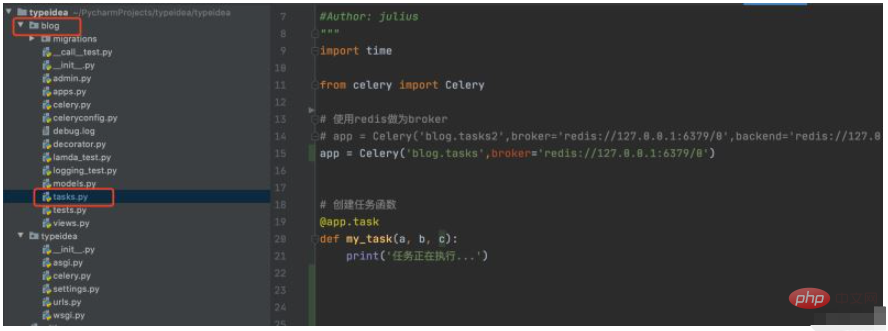
The tasks.py code is as follows:
#!/usr/bin/env python
# -*- coding: UTF-8 -*-
"""
#File: tasks.py
#Time: 2022/3/30 2:26 下午
#Author: julius
"""
from celery import Celery
# 使用redis做为broker
app = Celery('blog.tasks2',broker='redis://127.0.0.1:6379/0')
# 创建任务函数
@app.task
def my_task():
print('任务正在执行...')The first parameter of Celery is to set a name for it. The second parameter is to set a middleman broker. Here we use Redis as the middleman. The my_task function is a task function we wrote. By adding the decorator app.task, it is registered in the broker's queue.
2. Start redis and create a worker
Now we are creating a worker and waiting to process the tasks in the queue.
Enter the root directory of the project and execute the command: celery -A celery_tasks.tasks worker -l info
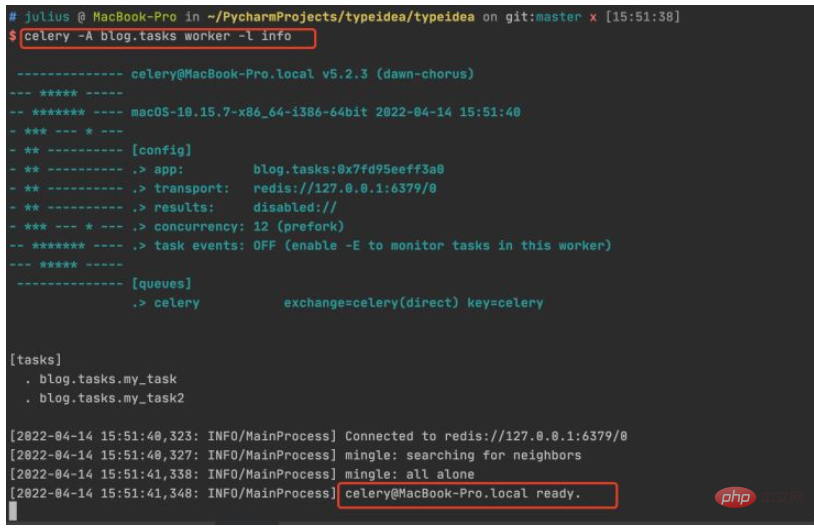
##3. Call the task
Let’s test the function, create a task, add it to the task queue, and provide worker execution. Enter the python terminal and execute the following code:$ python manage.py shell >>> from blog.tasks import my_task >>> my_task.delay() <AsyncResult: 83484dfe-f729-417b-8e51-6c7ae32a1377>
4. Check the results
Check the task execution status in the worker terminal. You can see that the 83484dfe-f729-417b-8e51-6c7ae32a1377 task has been received and printed. Get the task execution information
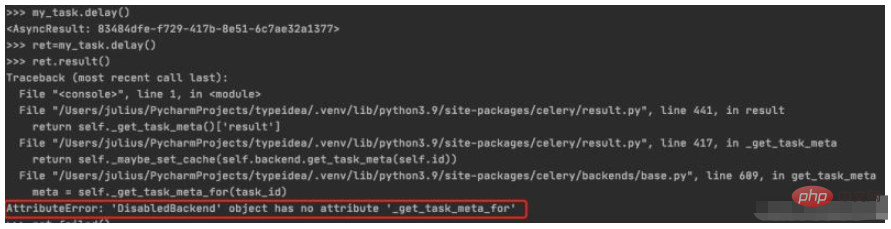
5. Store and view the task execution status
Assign the task execution result to ret, and then call result () will generate a DisabledBackend error. It can be seen that the status information of task execution cannot be saved when backend storage is not configured. In the next section, we will talk about how to configure backend to save task execution results$ python manage.py shell >>> from blog.tasks import my_task >>> ret=my_task.delay() >>> ret.result()
1. Add the backend parameter
In this example we use Redis as the solution for storing results, and set the task result storage address through Celery's backend parameter. We modified the tasks module as follows:from celery import Celery
# 使用redis作为broker以及backend
app = Celery('celery_tasks.tasks',
broker='redis://127.0.0.1:6379/8',
backend='redis://127.0.0.1:6379/9')
# 创建任务函数
@app.task
def my_task(a, b):
print("任务函数正在执行....")
return a + b2. Call the task/View the task execution result
Let’s call the task again and see.$ python manage.py shell >>> from blog.tasks import my_task >>> res=my_task.delay(10,40) >>> res.result 50 >>> res.failed() False

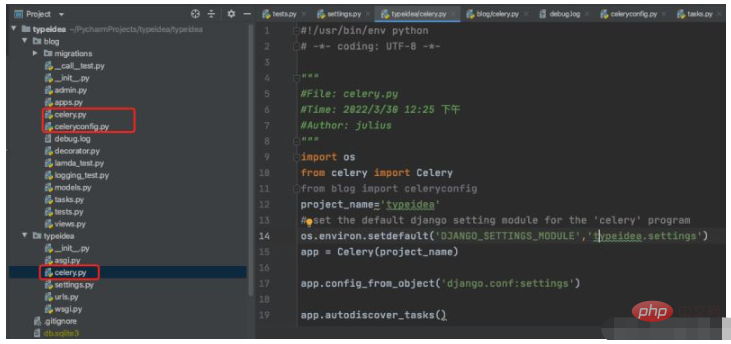 ##$ vim typeidea/celery.py (Celery application file)
##$ vim typeidea/celery.py (Celery application file)
#!/usr/bin/env python # -*- coding: UTF-8 -*- """ #File: celery.py #Time: 2022/3/30 12:25 下午 #Author: julius """ import os from celery import Celery from blog import celeryconfig project_name='typeidea' # set the default django setting module for the 'celery' program os.environ.setdefault('DJANGO_SETTINGS_MODULE','typeidea.settings') app = Celery(project_name) app.config_from_object('django.conf:settings') app.autodiscover_tasks()
vim blog/celeryconfig.py (配置Celery的参数文件)
#!/usr/bin/env python
# -*- coding: UTF-8 -*-
"""
#File: celeryconfig.py
#Time: 2022/3/30 2:54 下午
#Author: julius
"""
# 设置结果存储
from typeidea import settings
import os
os.environ.setdefault("DJANGO_SETTINGS_MODULE", "typeidea.settings")
CELERY_RESULT_BACKEND = 'redis://127.0.0.1:6379/0'
# 设置代理人broker
BROKER_URL = 'redis://127.0.0.1:6379/1'
# celery 的启动工作数量设置
CELERY_WORKER_CONCURRENCY = 20
# 任务预取功能,就是每个工作的进程/线程在获取任务的时候,会尽量多拿 n 个,以保证获取的通讯成本可以压缩。
CELERYD_PREFETCH_MULTIPLIER = 20
# 非常重要,有些情况下可以防止死锁
CELERYD_FORCE_EXECV = True
# celery 的 worker 执行多少个任务后进行重启操作
CELERY_WORKER_MAX_TASKS_PER_CHILD = 100
# 禁用所有速度限制,如果网络资源有限,不建议开足马力。
CELERY_DISABLE_RATE_LIMITS = True
CELERY_ENABLE_UTC = False
CELERY_TIMEZONE = settings.TIME_ZONE
DJANGO_CELERY_BEAT_TZ_AWARE = False
CELERY_BEAT_SCHEDULER = 'django_celery_beat.schedulers:DatabaseScheduler'vim blog/tasks.py (tasks 任务文件)
import time
from blog.celery import app
# 创建任务函数
@app.task
def my_task(a, b, c):
print('任务正在执行...')
print('任务1函数休眠10s')
time.sleep(10)
return a + b + c五、开始使用django-celery-beat调度器
使用 django-celery-beat 动态添加定时任务 celery 4.x 版本在 django 框架中是使用 django-celery-beat 进行动态添加定时任务的。前面虽然已经安装了这个库,但是还要再说明一下。
1. 安装 django-celery-beat
pip3 install django-celery-beat
2.在项目的 settings 文件配置 django-celery-beat
INSTALLED_APPS = [
'blog',
'django_celery_beat',
...
]
# Django设置时区
LANGUAGE_CODE = 'zh-hans' # 使用中国语言
TIME_ZONE = 'Asia/Shanghai' # 设置Django使用中国上海时间
# 如果USE_TZ设置为True时,Django会使用系统默认设置的时区,此时的TIME_ZONE不管有没有设置都不起作用
# 如果USE_TZ 设置为False,TIME_ZONE = 'Asia/Shanghai', 则使用上海的UTC时间。
USE_TZ = False3. 创建 django-celery-beat 相关表
执行Django数据库迁移: python manage.py migrate
4. 配置Celery使用 django-celery-beat
配置 celery.py
import os
from celery import Celery
from blog import celeryconfig
# 为celery 设置环境变量
os.environ.setdefault("DJANGO_SETTINGS_MODULE","typeidea.settings")
# 创建celery app
app = Celery('blog')
# 从单独的配置模块中加载配置
app.config_from_object(celeryconfig)
# 设置app自动加载任务
app.autodiscover_tasks([
'blog',
])配置 celeryconfig.py
# 设置结果存储
from typeidea import settings
import os
os.environ.setdefault("DJANGO_SETTINGS_MODULE", "typeidea.settings")
CELERY_RESULT_BACKEND = 'redis://127.0.0.1:6379/0'
# 设置代理人broker
BROKER_URL = 'redis://127.0.0.1:6379/1'
# celery 的启动工作数量设置
CELERY_WORKER_CONCURRENCY = 20
# 任务预取功能,就是每个工作的进程/线程在获取任务的时候,会尽量多拿 n 个,以保证获取的通讯成本可以压缩。
CELERYD_PREFETCH_MULTIPLIER = 20
# 非常重要,有些情况下可以防止死锁
CELERYD_FORCE_EXECV = True
# celery 的 worker 执行多少个任务后进行重启操作
CELERY_WORKER_MAX_TASKS_PER_CHILD = 100
# 禁用所有速度限制,如果网络资源有限,不建议开足马力。
CELERY_DISABLE_RATE_LIMITS = True
CELERY_ENABLE_UTC = False
CELERY_TIMEZONE = settings.TIME_ZONE
DJANGO_CELERY_BEAT_TZ_AWARE = False
CELERY_BEAT_SCHEDULER = 'django_celery_beat.schedulers:DatabaseScheduler'编写任务 tasks.py
import time
from celery import Celery
from blog.celery import app
# 使用redis做为broker
# app = Celery('blog.tasks2',broker='redis://127.0.0.1:6379/0',backend='redis://127.0.0.1:6379/1')
# 创建任务函数
@app.task
def my_task(a, b, c):
print('任务正在执行...')
print('任务1函数休眠10s')
time.sleep(10)
return a + b + c
@app.task
def my_task2():
print("任务2函数正在执行....")
print('任务2函数休眠10s')
time.sleep(10)5. 启动定时任务work
启动定时任务首先需要有一个work执行异步任务,然后再启动一个定时器触发任务。
启动任务 work
$ celery -A blog worker -l info
启动定时器触发 beat
celery -A blog beat -l info --scheduler django_celery_beat.schedulers:DatabaseScheduler
六、具体操作演练
6.1 创建基于间隔时间的周期性任务
1. 初始化周期间隔对象interval 对象
>>> from django_celery_beat.models import PeriodicTask, IntervalSchedule >>> schedule, created = IntervalSchedule.objects.get_or_create( ... every=10, ... period=IntervalSchedule.SECONDS, ... ) >>> IntervalSchedule.objects.all() <QuerySet [<IntervalSchedule: every 10 seconds>]>
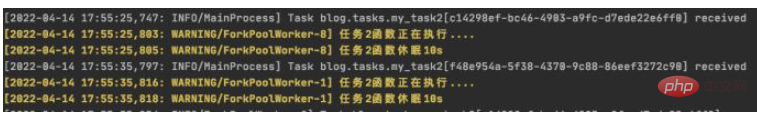
2.创建一个无参数的周期性间隔任务
>>>PeriodicTask.objects.create(interval=schedule,name='my_task2',task='blog.tasks.my_task2',) <PeriodicTask: my_task2: every 10 seconds>
beat 调度服务日志显示如下:

worker 服务日志显示如下:
3.创建一个带参数的周期性间隔任务
>>> PeriodicTask.objects.create(interval=schedule,name='my_task',task='blog.tasks.my_task',args=json.dumps([10,20,30])) <PeriodicTask: my_task: every 10 seconds>
beat 调度服务日志结果:
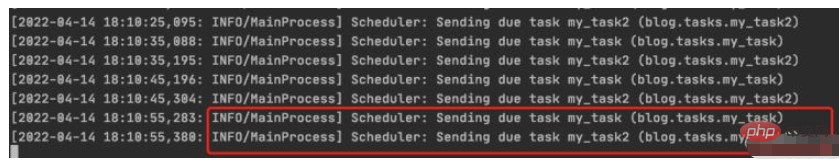
worker 服务日志结果:
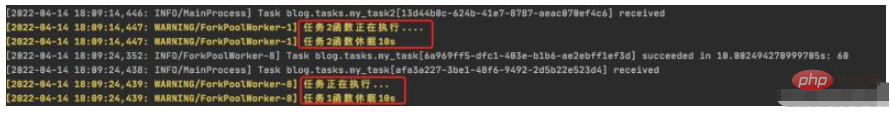
4.如何高并发执行任务
需要并行执行任务的时候,就需要设置多个worker来执行任务。
6.2 创建一个不带参数的周期性间隔任务
1.初始化 crontab 的调度对象
>>> import pytz >>> schedule, _ = CrontabSchedule.objects.get_or_create( ... minute='*', ... hour='*', ... day_of_week='*', ... day_of_month='*', ... timezone=pytz.timezone('Asia/Shanghai') ... )
2. 创建不带参数的定时任务
PeriodicTask.objects.create(crontab=schedule,name='my_task2_crontab',task='blog.tasks.my_task2',)
beat 调度服务执行结果
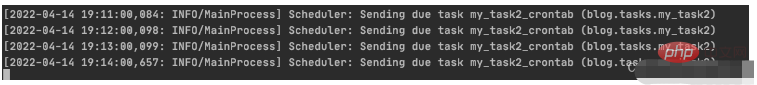
worker 执行服务结果
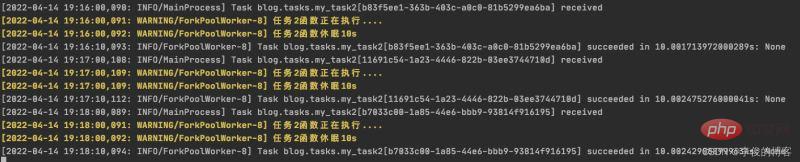
6.3 周期性任务的查询、删除操作
1. 周期性任务的查询
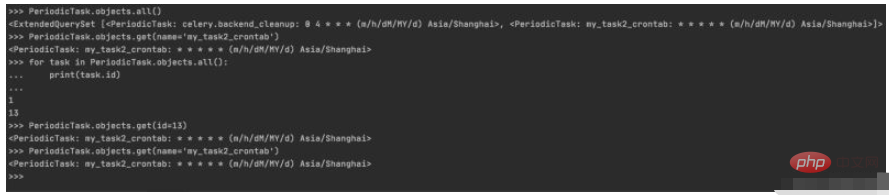
>>> PeriodicTask.objects.all() <ExtendedQuerySet [<PeriodicTask: celery.backend_cleanup: 0 4 * * * (m/h/dM/MY/d) Asia/Shanghai>, <PeriodicTask: my_task2_crontab: * * * * * (m/h/dM/MY/d) Asia/Shanghai>]> >>> PeriodicTask.objects.get(name='my_task2_crontab') <PeriodicTask: my_task2_crontab: * * * * * (m/h/dM/MY/d) Asia/Shanghai> >>> for task in PeriodicTask.objects.all(): ... print(task.id) ... 1 13 >>> PeriodicTask.objects.get(id=13) <PeriodicTask: my_task2_crontab: * * * * * (m/h/dM/MY/d) Asia/Shanghai> >>> PeriodicTask.objects.get(name='my_task2_crontab') <PeriodicTask: my_task2_crontab: * * * * * (m/h/dM/MY/d) Asia/Shanghai>
控制台实际操作记录
2.周期性任务的暂停/启动
2.1 设置my_taks2_crontab 暂停任务
>>> my_task2_crontab = PeriodicTask.objects.get(id=13) >>> my_task2_crontab.enabled True >>> my_task2_crontab.enabled=False >>> my_task2_crontab.save()
查看worker输出:
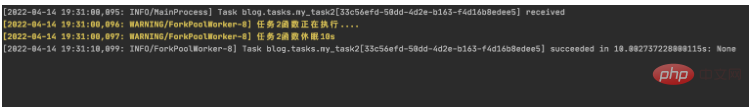
可以看到worker从19:31以后已经没有输出了,说明已经成功吧my_task2_crontab 任务暂停
2.2 设置my_task2_crontab 开启任务
把任务的 enabled 为 True 即可:
>>> my_task2_crontab.enabled False >>> my_task2_crontab.enabled=True >>> my_task2_crontab.save()
查看worker输出:
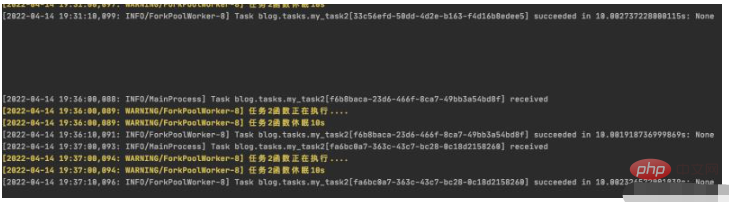
可以看到worker从19:36开始有输出,说明已把my_task2_crontab 任务重新启动
3. 周期性任务的删除
获取到指定的任务后调用delete(),再次查询指定任务会发现已经不存在了
PeriodicTask.objects.get(name='my_task2_crontab').delete()
>>> PeriodicTask.objects.get(name='my_task2_crontab')
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "<console>", line 1, in <module>
File "/Users/julius/PycharmProjects/typeidea/.venv/lib/python3.9/site-packages/django/db/models/manager.py", line 85, in manager_method
return getattr(self.get_queryset(), name)(*args, **kwargs)
File "/Users/julius/PycharmProjects/typeidea/.venv/lib/python3.9/site-packages/django/db/models/query.py", line 435, in get
raise self.model.DoesNotExist(
django_celery_beat.models.PeriodicTask.DoesNotExist: PeriodicTask matching query does not exist.The above is the detailed content of How to use Python Celery to dynamically add scheduled tasks. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 How to control the size of XML converted to images?
Apr 02, 2025 pm 07:24 PM
How to control the size of XML converted to images?
Apr 02, 2025 pm 07:24 PM
To generate images through XML, you need to use graph libraries (such as Pillow and JFreeChart) as bridges to generate images based on metadata (size, color) in XML. The key to controlling the size of the image is to adjust the values of the <width> and <height> tags in XML. However, in practical applications, the complexity of XML structure, the fineness of graph drawing, the speed of image generation and memory consumption, and the selection of image formats all have an impact on the generated image size. Therefore, it is necessary to have a deep understanding of XML structure, proficient in the graphics library, and consider factors such as optimization algorithms and image format selection.
 Is the conversion speed fast when converting XML to PDF on mobile phone?
Apr 02, 2025 pm 10:09 PM
Is the conversion speed fast when converting XML to PDF on mobile phone?
Apr 02, 2025 pm 10:09 PM
The speed of mobile XML to PDF depends on the following factors: the complexity of XML structure. Mobile hardware configuration conversion method (library, algorithm) code quality optimization methods (select efficient libraries, optimize algorithms, cache data, and utilize multi-threading). Overall, there is no absolute answer and it needs to be optimized according to the specific situation.
 Is there any mobile app that can convert XML into PDF?
Apr 02, 2025 pm 08:54 PM
Is there any mobile app that can convert XML into PDF?
Apr 02, 2025 pm 08:54 PM
An application that converts XML directly to PDF cannot be found because they are two fundamentally different formats. XML is used to store data, while PDF is used to display documents. To complete the transformation, you can use programming languages and libraries such as Python and ReportLab to parse XML data and generate PDF documents.
 Is there a mobile app that can convert XML into PDF?
Apr 02, 2025 pm 09:45 PM
Is there a mobile app that can convert XML into PDF?
Apr 02, 2025 pm 09:45 PM
There is no APP that can convert all XML files into PDFs because the XML structure is flexible and diverse. The core of XML to PDF is to convert the data structure into a page layout, which requires parsing XML and generating PDF. Common methods include parsing XML using Python libraries such as ElementTree and generating PDFs using ReportLab library. For complex XML, it may be necessary to use XSLT transformation structures. When optimizing performance, consider using multithreaded or multiprocesses and select the appropriate library.
 How to convert XML files to PDF on your phone?
Apr 02, 2025 pm 10:12 PM
How to convert XML files to PDF on your phone?
Apr 02, 2025 pm 10:12 PM
It is impossible to complete XML to PDF conversion directly on your phone with a single application. It is necessary to use cloud services, which can be achieved through two steps: 1. Convert XML to PDF in the cloud, 2. Access or download the converted PDF file on the mobile phone.
 What is the function of C language sum?
Apr 03, 2025 pm 02:21 PM
What is the function of C language sum?
Apr 03, 2025 pm 02:21 PM
There is no built-in sum function in C language, so it needs to be written by yourself. Sum can be achieved by traversing the array and accumulating elements: Loop version: Sum is calculated using for loop and array length. Pointer version: Use pointers to point to array elements, and efficient summing is achieved through self-increment pointers. Dynamically allocate array version: Dynamically allocate arrays and manage memory yourself, ensuring that allocated memory is freed to prevent memory leaks.
 How to open xml format
Apr 02, 2025 pm 09:00 PM
How to open xml format
Apr 02, 2025 pm 09:00 PM
Use most text editors to open XML files; if you need a more intuitive tree display, you can use an XML editor, such as Oxygen XML Editor or XMLSpy; if you process XML data in a program, you need to use a programming language (such as Python) and XML libraries (such as xml.etree.ElementTree) to parse.
 Recommended XML formatting tool
Apr 02, 2025 pm 09:03 PM
Recommended XML formatting tool
Apr 02, 2025 pm 09:03 PM
XML formatting tools can type code according to rules to improve readability and understanding. When selecting a tool, pay attention to customization capabilities, handling of special circumstances, performance and ease of use. Commonly used tool types include online tools, IDE plug-ins, and command-line tools.





