How to increase virtual memory (page file) in Windows 11
If you notice some lag when running high-end applications or games, it may be that the RAM/memory is running full. This is where you increase the virtual memory or page file size in Windows 11.
Virtual memory or page file is one of the most misunderstood concepts and there are many myths surrounding it. No matter what anyone else says or does, it's important to thoroughly understand how to get the best performance from your computer.
In the following sections, we'll walk you through the steps to increase virtual memory in Windows 11, helping you understand its importance and the optimal virtual memory size.
Why do we need virtual memory?
Page file or virtual memory is basically the part of the hard drive that is used as RAM. This becomes useful when the memory is full and cannot store more data.
To understand it better, let us take an example. Let's say you have 4 GB of memory available on your computer, and you're running a program that requires more than that. In this case, many of these programs will crash without virtual memory.
Even if you have enough RAM, it doesn't hurt to allocate specific space on your storage drive to the page file. Because it's better to have virtual memory and not use it than not have it at all.
Also, it is important to mention here that Windows can handle virtual memory or page file itself. However, if you are experiencing freezing or lag issues in Windows 11, increasing it manually may help.
What is the ideal virtual memory size for Windows 11?
Everyone uses their computer differently, and likewise, the optimal size of virtual memory will be different. While some people run video editing applications or play resource-intensive games, others may use their computers for relatively light tasks.
A good virtual memory size will not be the same for these two types of users. While the former requires higher virtual memory, the latter may be minimally better.
Microsoft recommends that you keep the size of your virtual memory between 1.5 and 3 times the RAM available on your computer. So, to set or increase the page file, you first need to check the RAM on your Windows 11 system.
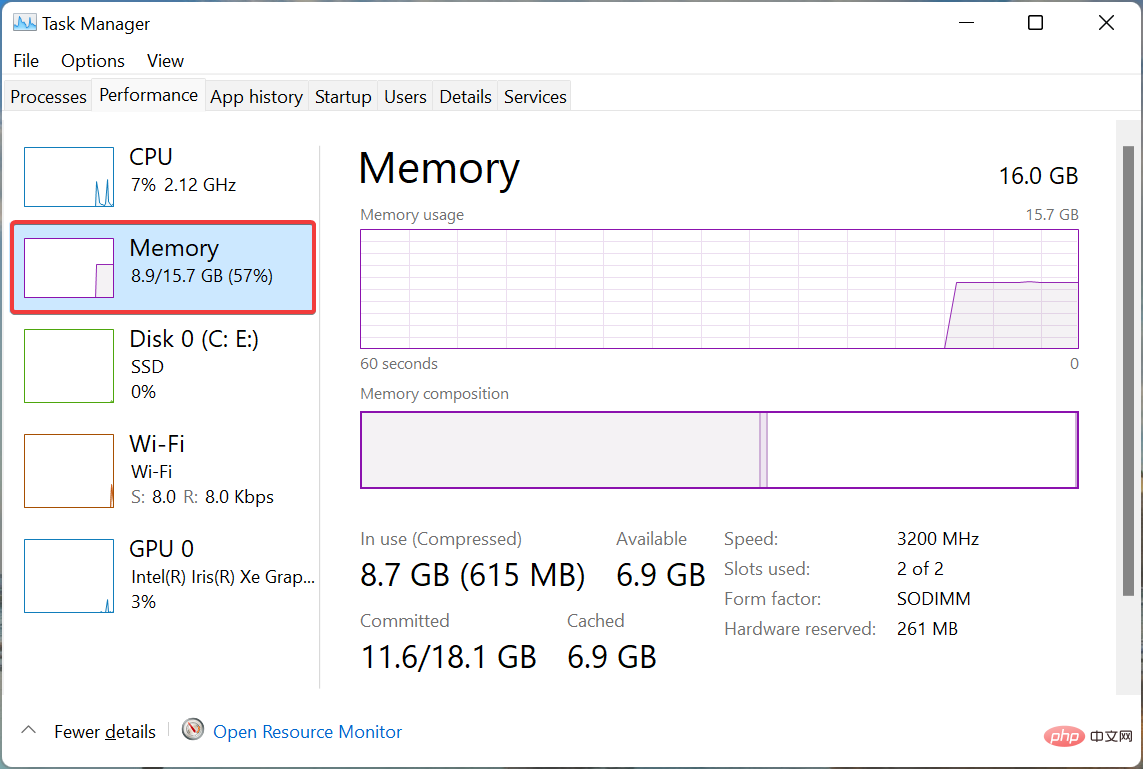
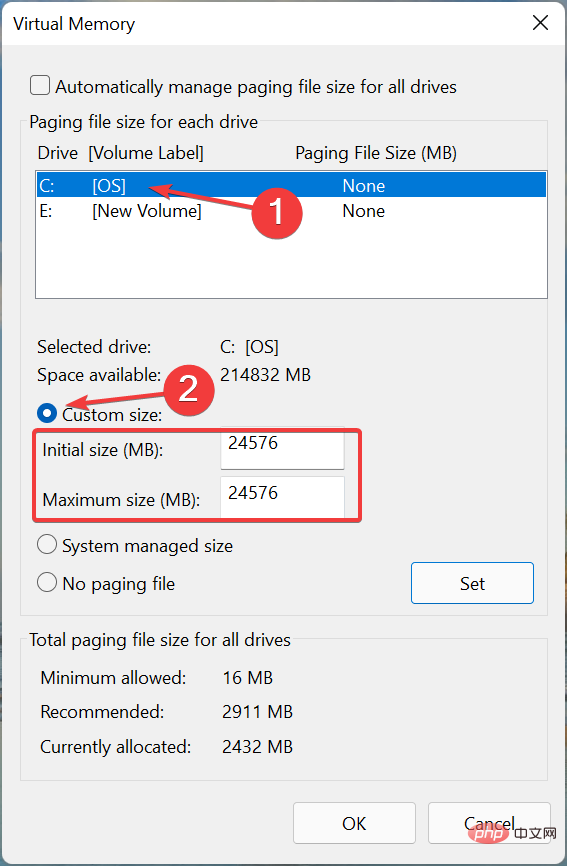
After checking the available RAM, you can easily set up virtual memory or page file in Windows 11. For example, assuming the available memory is 4 GB, the minimum virtual memory to set is 4 x 1.5 = 6GB and the maximum is 4 x 3 = 12 GB.
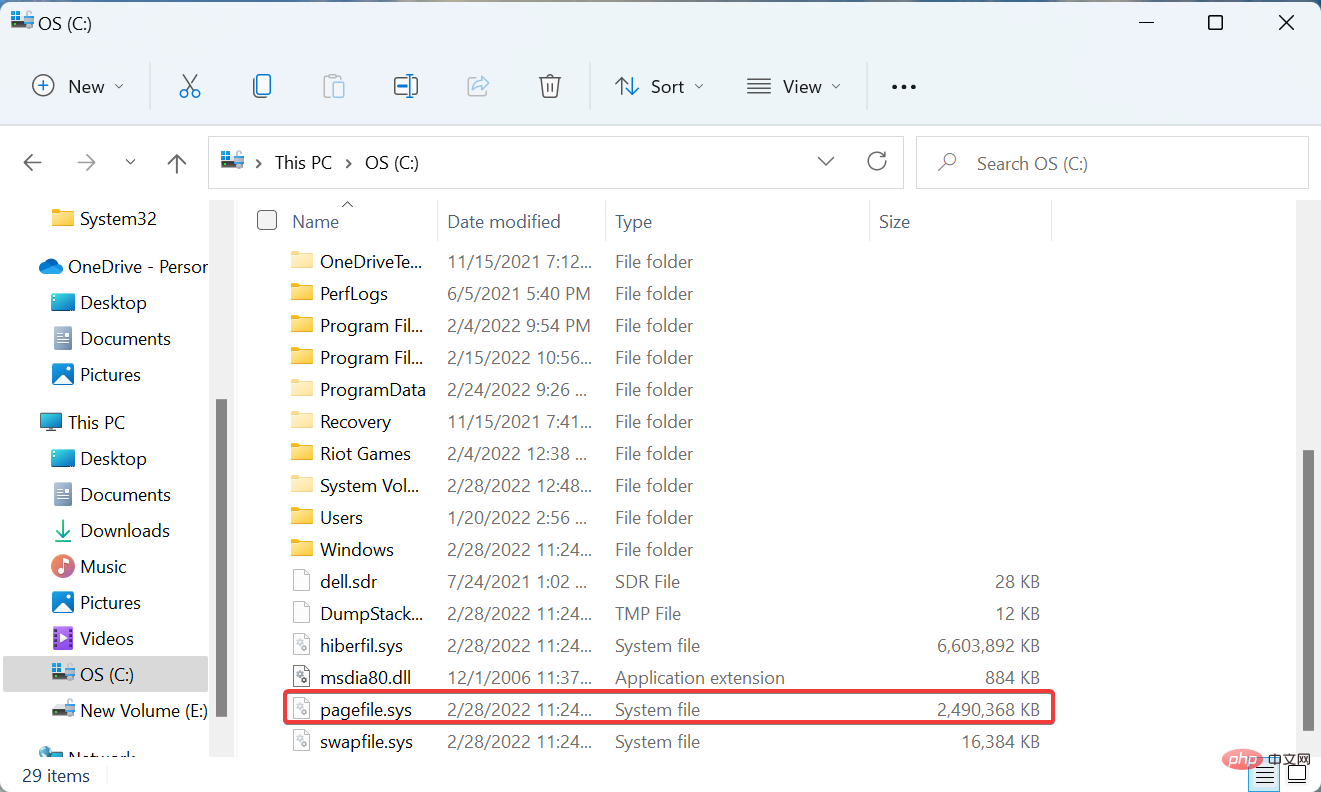
Also, by default, the page file is stored on the system drive, which is where Windows is stored, but you can change that.
So if you have configured your settings to make both protected operating system files and hidden items visible, there will be a pagefile.sys entry in your C: drive.
Now that you know the optimal virtual memory size, let us help you learn how to increase it in Windows 11 Virtual Memory.
How to increase virtual memory in Windows 11?
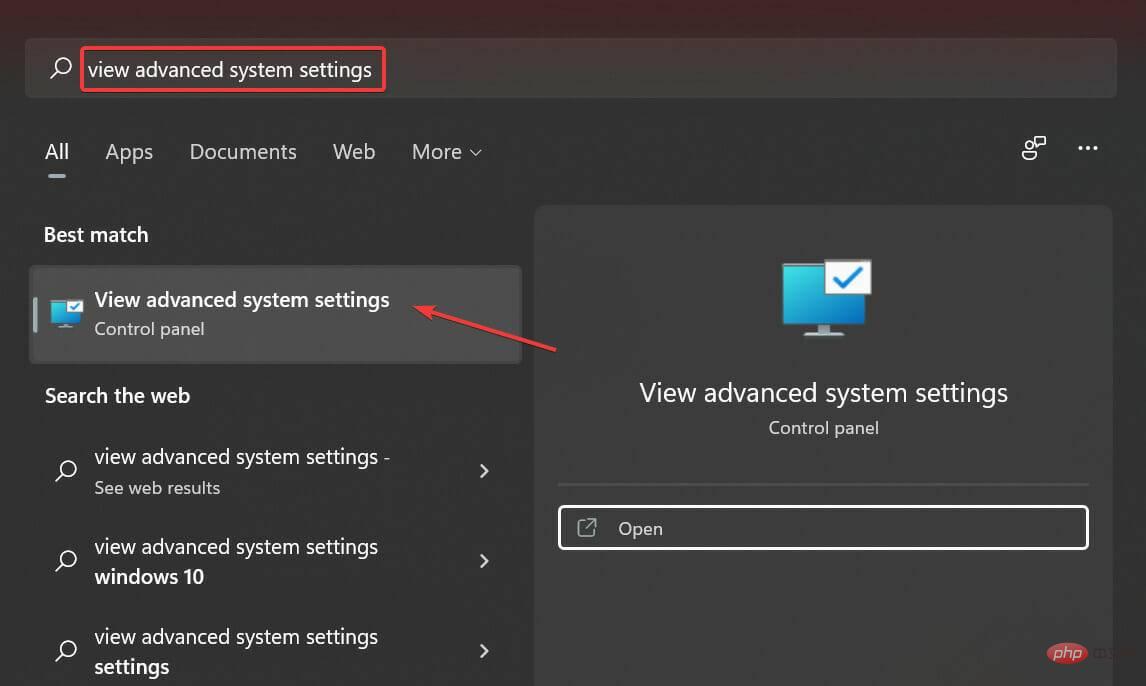
- Press Windows S to launch the search menu, enter in the text field at the top to view advanced system settings, then click the related search that appears result.

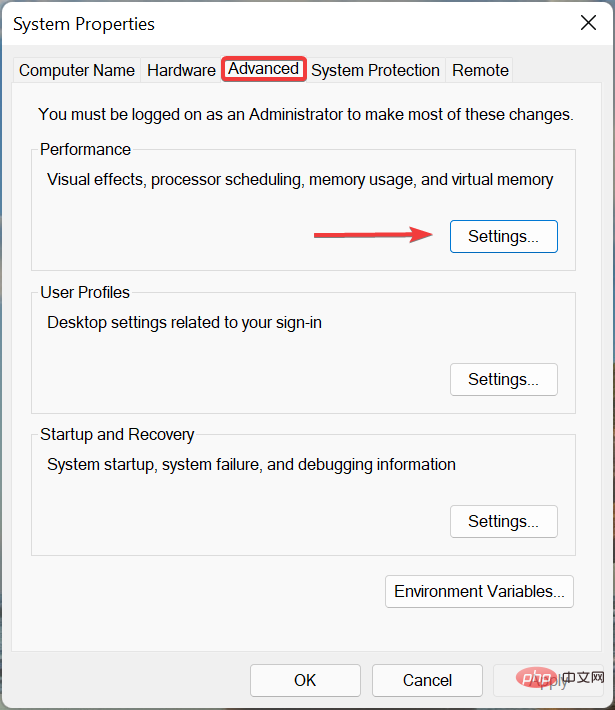
- In the Advanced tab, click the Settings button under Performance.

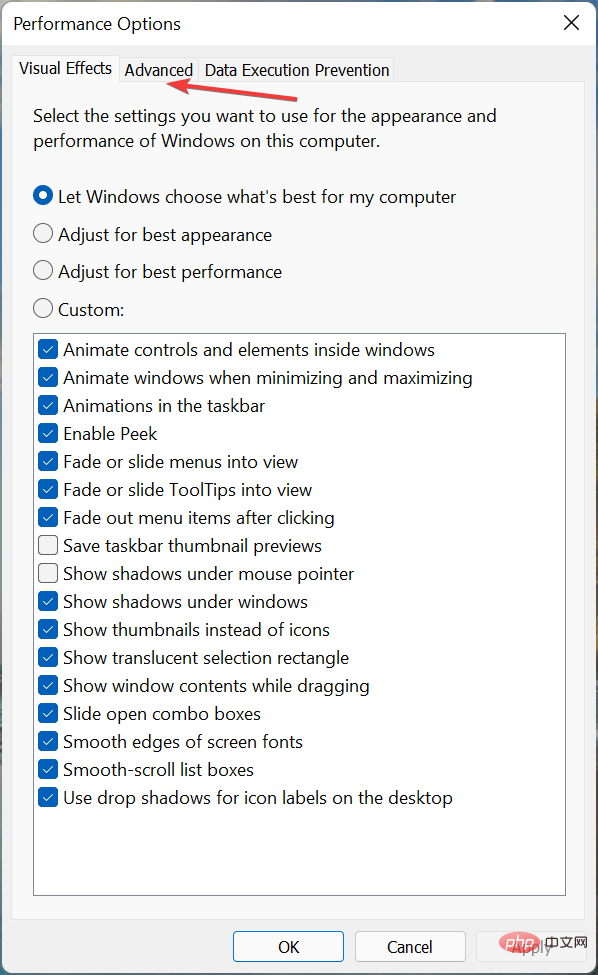
- Navigate to the Advanced tab in the Performance Options window.

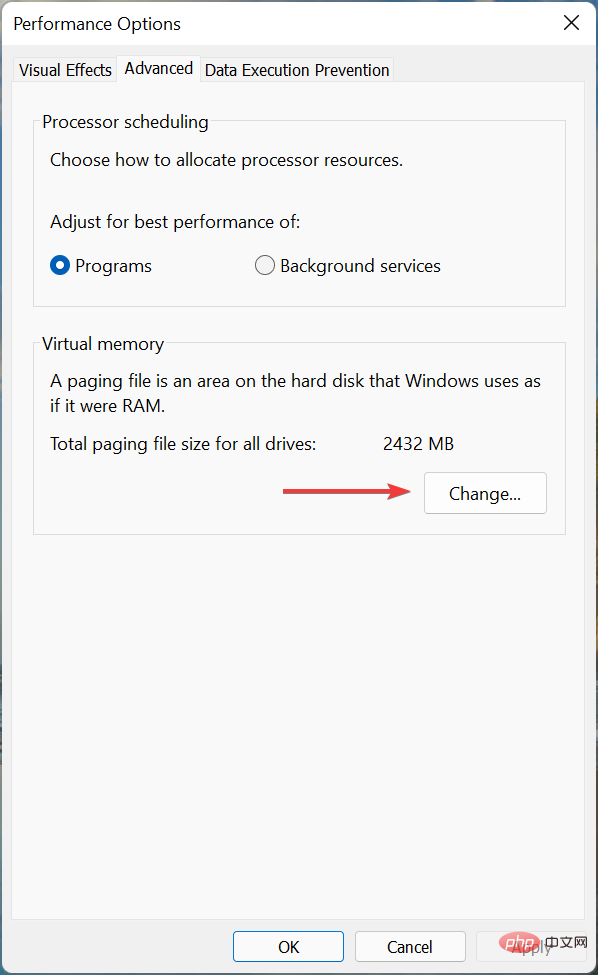
- Next, click Change under Virtual memory.

-
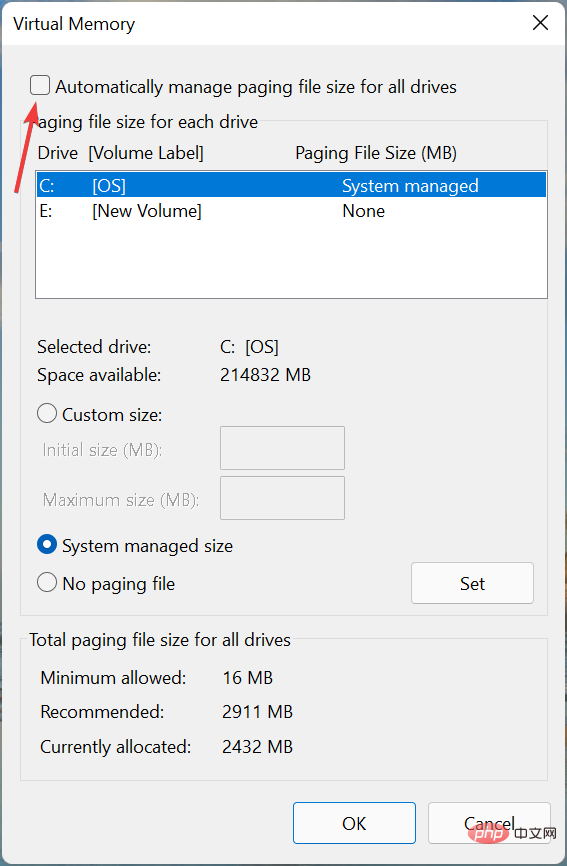
Uncheck the Automatically manage paging file size for all drives checkbox.

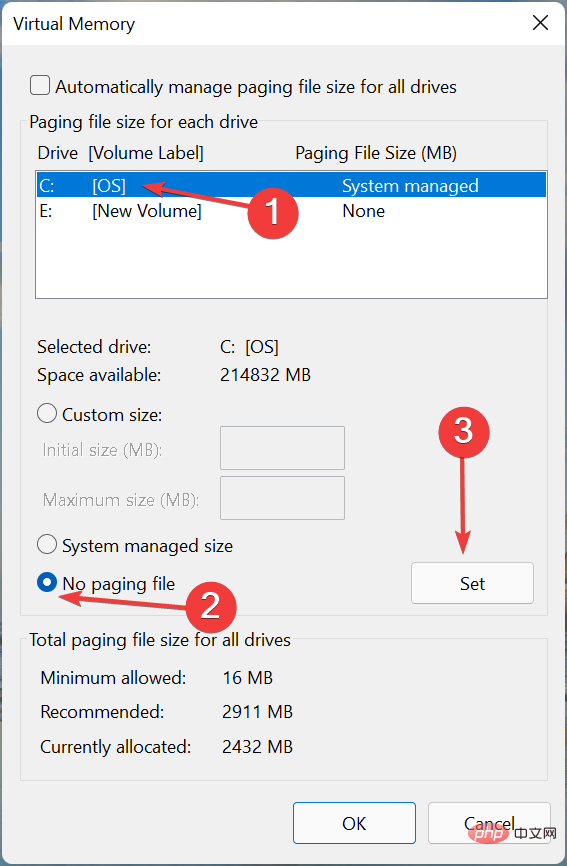
- If Windows was previously managing virtual memory, it is best to clear the previously set value and then increase it. To do this, click List System managed drives, select No paging file, and click Set.

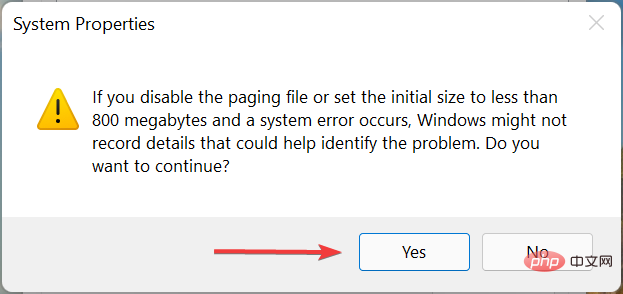
- Click Yes in the pop-up confirmation prompt.

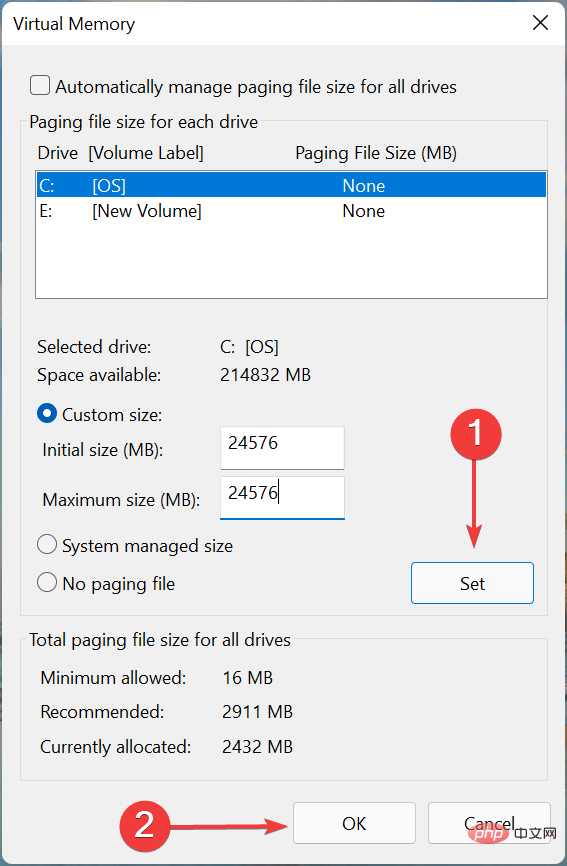
- Now, select a drive or partition from the list, select the Custom size option and enter under the Initial size and Maximum size fields The same value, in MB (1GB=1024MB), takes the hint from the previous section.

- When finished, click Settings and click OK at the bottom to save changes.

- Next, restart your computer for the changes to take effect.
You now know how to increase virtual memory or page file size in Windows 11 and can use it to improve system performance.
However, keep in mind that while virtual memory works the same as available RAM, it's definitely not as fast. Read the next section to learn all about it.
Which is faster, RAM or virtual memory?
RAM is much faster than virtual memory, so the latter only occurs when the former is full.
To understand it better, let us take an example. Suppose you have multiple programs running on your system, some of which are minimized, and you haven't checked them for a while.
When you open the program, it takes longer to load, thus indicating that the operating system moved it to virtual memory to free up space on RAM.
Additionally, RAM is relatively expensive and must be increased by adding more chips. On the other hand, virtual memory can be increased easily since it is located on the storage drive. So if you have free storage space, increasing virtual memory shouldn't be a problem.
Due to speed limitations of virtual memory or page file, it is always recommended to store it on the fastest drive possible. For example, if you have both an HDD and an SSD, it is better to store the page file on the SSD because the data is processed faster.
The above is the detailed content of How to increase virtual memory (page file) in Windows 11. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1376
1376
 52
52
 How to convert XML to PDF on your phone?
Apr 02, 2025 pm 10:18 PM
How to convert XML to PDF on your phone?
Apr 02, 2025 pm 10:18 PM
It is not easy to convert XML to PDF directly on your phone, but it can be achieved with the help of cloud services. It is recommended to use a lightweight mobile app to upload XML files and receive generated PDFs, and convert them with cloud APIs. Cloud APIs use serverless computing services, and choosing the right platform is crucial. Complexity, error handling, security, and optimization strategies need to be considered when handling XML parsing and PDF generation. The entire process requires the front-end app and the back-end API to work together, and it requires some understanding of a variety of technologies.
 How to jump from Word plug-in to browser for login authorization?
Apr 01, 2025 pm 08:27 PM
How to jump from Word plug-in to browser for login authorization?
Apr 01, 2025 pm 08:27 PM
How to achieve login authorization from within the application to outside the application? In some applications, we often encounter the need to jump from one application to another...
 xml online formatting
Apr 02, 2025 pm 10:06 PM
xml online formatting
Apr 02, 2025 pm 10:06 PM
XML Online Format Tools automatically organizes messy XML code into easy-to-read and maintain formats. By parsing the syntax tree of XML and applying formatting rules, these tools optimize the structure of the code, enhancing its maintainability and teamwork efficiency.
 What is the reason why PS keeps showing loading?
Apr 06, 2025 pm 06:39 PM
What is the reason why PS keeps showing loading?
Apr 06, 2025 pm 06:39 PM
PS "Loading" problems are caused by resource access or processing problems: hard disk reading speed is slow or bad: Use CrystalDiskInfo to check the hard disk health and replace the problematic hard disk. Insufficient memory: Upgrade memory to meet PS's needs for high-resolution images and complex layer processing. Graphics card drivers are outdated or corrupted: Update the drivers to optimize communication between the PS and the graphics card. File paths are too long or file names have special characters: use short paths and avoid special characters. PS's own problem: Reinstall or repair the PS installer.
 Does H5 page production require continuous maintenance?
Apr 05, 2025 pm 11:27 PM
Does H5 page production require continuous maintenance?
Apr 05, 2025 pm 11:27 PM
The H5 page needs to be maintained continuously, because of factors such as code vulnerabilities, browser compatibility, performance optimization, security updates and user experience improvements. Effective maintenance methods include establishing a complete testing system, using version control tools, regularly monitoring page performance, collecting user feedback and formulating maintenance plans.
 How to implement cross-application jump for Word plug-in login authorization?
Apr 01, 2025 pm 11:27 PM
How to implement cross-application jump for Word plug-in login authorization?
Apr 01, 2025 pm 11:27 PM
How to implement cross-application jump for Word plug-in login authorization? When using certain Word plugins, we often encounter this scenario: click on the login in the plugin...
 Is there a free XML to PDF tool for mobile phones?
Apr 02, 2025 pm 09:12 PM
Is there a free XML to PDF tool for mobile phones?
Apr 02, 2025 pm 09:12 PM
There is no simple and direct free XML to PDF tool on mobile. The required data visualization process involves complex data understanding and rendering, and most of the so-called "free" tools on the market have poor experience. It is recommended to use computer-side tools or use cloud services, or develop apps yourself to obtain more reliable conversion effects.
 How to speed up the loading speed of PS?
Apr 06, 2025 pm 06:27 PM
How to speed up the loading speed of PS?
Apr 06, 2025 pm 06:27 PM
Solving the problem of slow Photoshop startup requires a multi-pronged approach, including: upgrading hardware (memory, solid-state drive, CPU); uninstalling outdated or incompatible plug-ins; cleaning up system garbage and excessive background programs regularly; closing irrelevant programs with caution; avoiding opening a large number of files during startup.