How to use Vue3 to implement an elegant element dragging function
Recommend several useful tools
var-conv is a quick conversion tool for code variable names suitable for VSCode IDE
generator-vite-plugin Quickly generates Vite plug-in template projects
generator-babel-plugin Quickly generates Babel plug-in template projects
Get to the point
Element dragging is a typical front-end learning case, which requires a certain understanding of JavaScript events. I also learned this in my recent work I picked up this content again and explained it clearly by dragging the element once in a declarative programming style framework such as Vue3.
PS: The centered attribute in the Vue3 template global style may cause experimental interference, please be careful! ! !
The position and movement of elements
When implementing element dragging, we use the mouse event, and the callback of the mouse event The position of the element when the current event occurs can be obtained in the function. The corresponding attributes are clientX and clientY in MouseEvent. We will read these two later. Property to update the element's position in real time. It is recommended to use
in transform to move the element first, instead of modifying top and left## of the element. # Attributes will not cause changes to the element layout, avoiding the performance impact caused by reflow and redrawing.
Define three sets of coordinates
define a set of coordinates used to record the initial position of the element (originalPosition) and the pointer when the element is pressed The coordinates on the element (mousedownOffset) and a set of coordinates that update in real time as the element moves (elementPosition).
const originalPosition = reactive({
x: 10,
y: 10,
})const mousedownOffset = reactive({
x: 0,
y: 0,
})originalPosition. When the mousemove event occurs, the real-time coordinates of the pointer - mousedownOffset are obtained:
const elementPosition = reactive({
x: 0,
y: 0,
})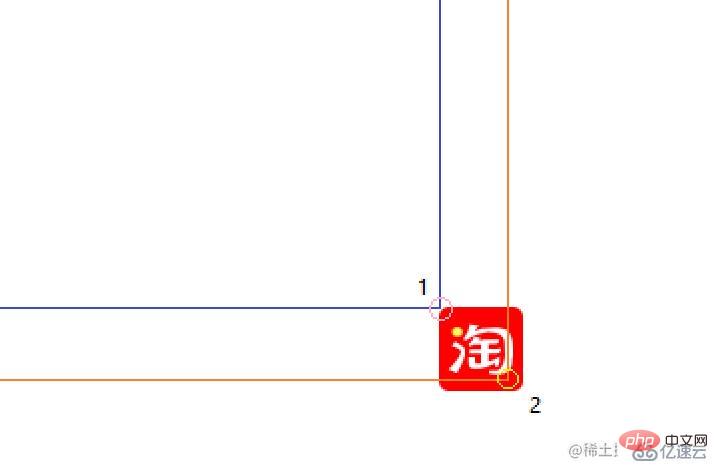
originalPosition or elementPosition, point 2 The point represents the coordinates when the pointer is pressed. When the origin is point 1, point 2 in the figure represents mousedownOffset;
Register mousedown event
When implementing element dragging, you only need to add themousedown event to the dragged element. Remember to clear the listening event after using it. The habit of appearing in pairs must be developed.
mousemove and mouseup to the dragged element, you will find that there is an out-of-control phenomenon.
mousedown event. After the component is unloaded, delete the mousedown event:
const restore = () => {
elementPosition.x = originalPosition.x;
elementPosition.y = originalPosition.y;
}
onMounted(() => {
restore();
floatButton.value.addEventListener('mousedown', onMousedown, true);
})
onUnmounted(() => {
floatButton.value.removeEventListener('mousedown', onMousedown, true);
})The core of drag and drop
The reason why we chooseVuejs is because it is a MVVM type framework, our focus In terms of declaration, the framework is responsible for the internal operating mechanism, so in the following event processing, you only need to update the three sets of coordinates declared at the beginning in the corresponding event.
onMousedown, the coordinates of the pointer on the dragged element are obtained through the coordinates of the pointer - the coordinates of the initial position of the dragged element, onMousedown When document, add mousemove and mouseup events:
const onMousedown = (event: MouseEvent) => {
event.stopPropagation();
mousedownOffset.x = event.clientX - originalPosition.x;
mousedownOffset.y = event.clientY - originalPosition.y;
document.addEventListener('mousemove', onMousemove, true);
document.addEventListener('mouseup', onMouseup, true);
}onMousemove, pass the coordinates of the pointer - The position of the pointer on the dragged element gets the distance between the upper left corner of the dragged element and the upper left corner of the page, and is updated to elementPosition:
const onMousemove = (event: MouseEvent) => {
event.stopPropagation();
elementPosition.x = event.clientX - mousedownOffset.x;
elementPosition.y = event.clientY - mousedownOffset.y;
}onMouseup , the main thing to do is to remove the two events registered at onMousemove for document. It should be noted that the removed events must be the same event, that is, events with consistent references. , it is recommended to assign the corresponding processing event to a variable for use. Finally, the position of the dragged element can be restored after the drag is completed:
const onMouseup = (event: MouseEvent) => {
event.stopPropagation();
document.removeEventListener('mousemove', onMousemove, true);
document.removeEventListener('mouseup', onMouseup, true);
restore();
}Supplement other parts of the code and demonstration <div
ref="floatButton"
class="float-button"
:style="{
'transition-duration': '0.1s',
transform: `translate(${elementPosition.x}px, ${elementPosition.y}px)`
}">
</div>Copy after login
<div
ref="floatButton"
class="float-button"
:style="{
'transition-duration': '0.1s',
transform: `translate(${elementPosition.x}px, ${elementPosition.y}px)`
}">
</div>.float-button {
position: absolute;
width: 42px;
height: 42px;
background: red;
border-radius: 5px;
user-select: none;
background-image: url(../assets/taobao.svg);
background-size: cover;
}<p><img src="/static/imghw/default1.png" data-src="https://img.php.cn/upload/article/000/887/227/168397476873752.jpg" class="lazy" alt="How to use Vue3 to implement an elegant element dragging function"></p>The above is the detailed content of How to use Vue3 to implement an elegant element dragging function. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1387
1387
 52
52
 How to use tinymce in vue3 project
May 19, 2023 pm 08:40 PM
How to use tinymce in vue3 project
May 19, 2023 pm 08:40 PM
tinymce is a fully functional rich text editor plug-in, but introducing tinymce into vue is not as smooth as other Vue rich text plug-ins. tinymce itself is not suitable for Vue, and @tinymce/tinymce-vue needs to be introduced, and It is a foreign rich text plug-in and has not passed the Chinese version. You need to download the translation package from its official website (you may need to bypass the firewall). 1. Install related dependencies npminstalltinymce-Snpminstall@tinymce/tinymce-vue-S2. Download the Chinese package 3. Introduce the skin and Chinese package. Create a new tinymce folder in the project public folder and download the
 vue3+vite: How to solve the error when using require to dynamically import images in src
May 21, 2023 pm 03:16 PM
vue3+vite: How to solve the error when using require to dynamically import images in src
May 21, 2023 pm 03:16 PM
vue3+vite:src uses require to dynamically import images and error reports and solutions. vue3+vite dynamically imports multiple images. If vue3 is using typescript development, require will introduce image errors. requireisnotdefined cannot be used like vue2 such as imgUrl:require(' .../assets/test.png') is imported because typescript does not support require, so import is used. Here is how to solve it: use awaitimport
 How to refresh partial content of the page in Vue3
May 26, 2023 pm 05:31 PM
How to refresh partial content of the page in Vue3
May 26, 2023 pm 05:31 PM
To achieve partial refresh of the page, we only need to implement the re-rendering of the local component (dom). In Vue, the easiest way to achieve this effect is to use the v-if directive. In Vue2, in addition to using the v-if instruction to re-render the local dom, we can also create a new blank component. When we need to refresh the local page, jump to this blank component page, and then jump back in the beforeRouteEnter guard in the blank component. original page. As shown in the figure below, how to click the refresh button in Vue3.X to reload the DOM within the red box and display the corresponding loading status. Since the guard in the component in the scriptsetup syntax in Vue3.X only has o
 How Vue3 parses markdown and implements code highlighting
May 20, 2023 pm 04:16 PM
How Vue3 parses markdown and implements code highlighting
May 20, 2023 pm 04:16 PM
Vue implements the blog front-end and needs to implement markdown parsing. If there is code, it needs to implement code highlighting. There are many markdown parsing libraries for Vue, such as markdown-it, vue-markdown-loader, marked, vue-markdown, etc. These libraries are all very similar. Marked is used here, and highlight.js is used as the code highlighting library. The specific implementation steps are as follows: 1. Install dependent libraries. Open the command window under the vue project and enter the following command npminstallmarked-save//marked to convert markdown into htmlnpmins
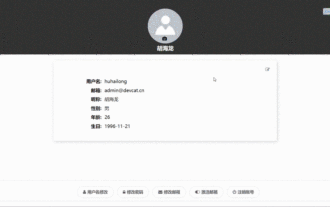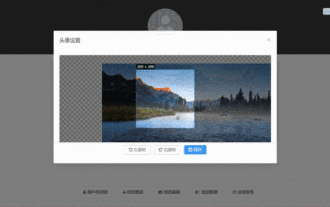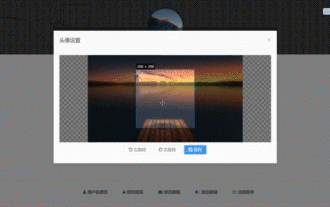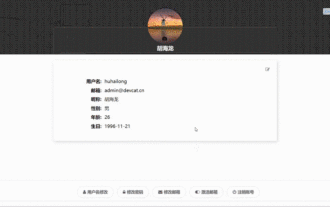 How to select an avatar and crop it in Vue3
May 29, 2023 am 10:22 AM
How to select an avatar and crop it in Vue3
May 29, 2023 am 10:22 AM
The final effect is to install the VueCropper component yarnaddvue-cropper@next. The above installation value is for Vue3. If it is Vue2 or you want to use other methods to reference, please visit its official npm address: official tutorial. It is also very simple to reference and use it in a component. You only need to introduce the corresponding component and its style file. I do not reference it globally here, but only introduce import{userInfoByRequest}from'../js/api' in my component file. import{VueCropper}from'vue-cropper&
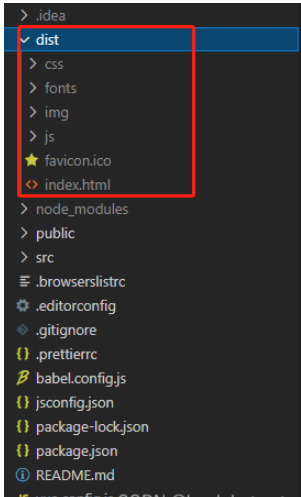 How to solve the problem that after the vue3 project is packaged and published to the server, the access page displays blank
May 17, 2023 am 08:19 AM
How to solve the problem that after the vue3 project is packaged and published to the server, the access page displays blank
May 17, 2023 am 08:19 AM
After the vue3 project is packaged and published to the server, the access page displays blank 1. The publicPath in the vue.config.js file is processed as follows: const{defineConfig}=require('@vue/cli-service') module.exports=defineConfig({publicPath :process.env.NODE_ENV==='production'?'./':'/&
 How to use Vue3 reusable components
May 20, 2023 pm 07:25 PM
How to use Vue3 reusable components
May 20, 2023 pm 07:25 PM
Preface Whether it is vue or react, when we encounter multiple repeated codes, we will think about how to reuse these codes instead of filling a file with a bunch of redundant codes. In fact, both vue and react can achieve reuse by extracting components, but if you encounter some small code fragments and you don’t want to extract another file, in comparison, react can be used in the same Declare the corresponding widget in the file, or implement it through renderfunction, such as: constDemo:FC=({msg})=>{returndemomsgis{msg}}constApp:FC=()=>{return(
 How to use vue3+ts+axios+pinia to achieve senseless refresh
May 25, 2023 pm 03:37 PM
How to use vue3+ts+axios+pinia to achieve senseless refresh
May 25, 2023 pm 03:37 PM
vue3+ts+axios+pinia realizes senseless refresh 1. First download aiXos and pinianpmipinia in the project--savenpminstallaxios--save2. Encapsulate axios request-----Download js-cookienpmiJS-cookie-s//Introduce aixosimporttype{AxiosRequestConfig ,AxiosResponse}from"axios";importaxiosfrom'axios';import{ElMess




